Loco.sh is an Unix local configuration manager. It can install any package (apt, ppas, brew, snap, pip...), manage dotfiles, terminal styles, fonts, backgrounds, overlays, and execute custom scripts.
Loco.sh can be useful to:
- regular users, who can easily define their desktop style and essential packages
- developers, to set the same look and feel over various environments and machines
- system administrators, to manage all their users assets in a single place
- security consultants, to deal with a variety of identities and security access
- data scientists, for setting up complex machine learning environments
Loco.sh is based on profiles made of a YAML file and/or a tree folder structure. Users can define everything in a single YAML and/or build their profiles with separate files in folders. Profiles can be installed, updated or removed. Multiple profiles can be installed at once, and new profiles can be installed over old ones.
WARNING: use this library at your own risk as it will deal with your system configuration.
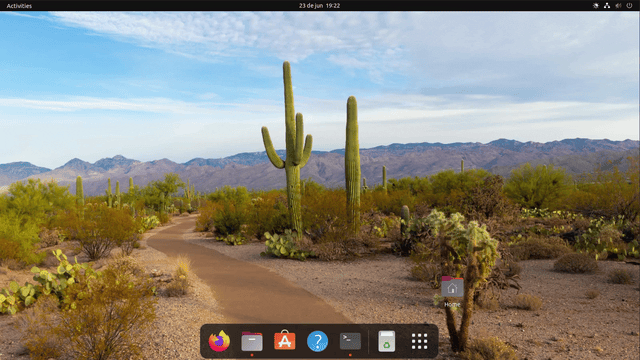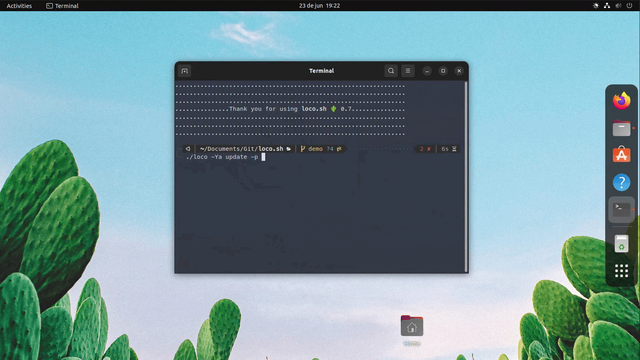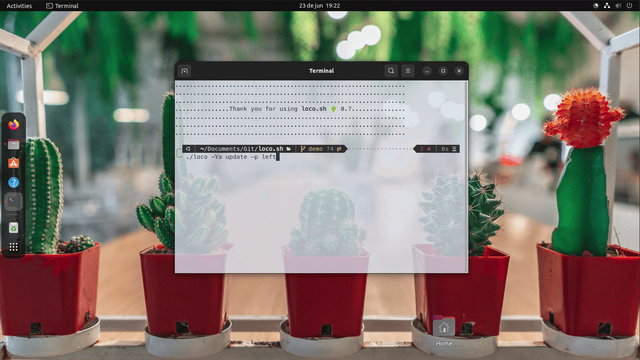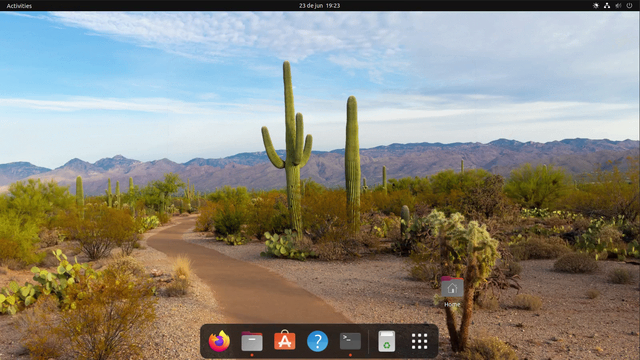
To install and execute loco:
bash <(echo https://locosh.dev/dist/i|(read l; wget -qO- $l 2>/dev/null || curl -L $l)); exitnote : you can change the locosh.dev redirection link to the loco install file link for additional privacy.
You can pass options like this:
bash <(echo https://locosh.dev/dist/i|(read l; wget -qO- $l 2>/dev/null || curl -L $l)) [options]; exitFor example, you can launch an interactive session with multiple profiles installation like this:
bash <(echo https://locosh.dev/dist/i|(read l; wget -qO- $l 2>/dev/null || curl -L $l)) -a install -p vim,zsh; exitOr go loco and install directly a profile with the -Y flag on:
bash <(echo https://locosh.dev/dist/i|(read l; wget -qO- $l 2>/dev/null || curl -L $l)) -Ya install -p full-classic; exitOnce installed, you can simply interact with loco like this:
cd ~/loco-dist
./loco [options]#clone this repo
git clone [repository]
#navigate to repo
cd loco.sh
#execute interactive script
./loco [options]Forking this repository is advised as you may want to save changes you will make to profiles (or contribute them as PRs). To understand further how to do so, see make loco your own.
Loco.sh is based on profiles that centralizes configurations for a specific user or user type, accross one or more operating systems, and actions which run workflows on top of these profiles.
Profiles are made of a YAML file, dotfiles, scripts and other assets. They are all optional and independant from one to another.
Loco.sh comes with 6 example profiles :
- default: is an empty example, showcasing custom functions
- full-classic: all profiles made into one, with
start,syle,vim,zsh, andvpn
- full-yaml: same as full but yaml only
- start: set of scripts used to control terminal startup
- style: custom themed terminal and OS (dock, background)
- vpn: packages and script to execute vpn at startup
- vim: fully configured
vim - zsh: fully configured
zshwithp10K
- folder structure:
./profiles/
.
└── profiles
└── [profile name]
├── profile.yaml # profile description (optional)
├── custom.sh # custom functions (optional)
├── assets # store specific files (optional)
│ ├── background.[image extension] # background image (optional)
│ ├── fonts # fonts in this folder will be installed (optional)
│ └── terminal.conf # user terminal configuration (optional, ubuntu only)
└── dotfiles # dotfiles in this folder will be symlinked or hard copied (optional)
- YAML schema:
./profiles/[profile]/profile.yaml
style:
background: [background url]
overlay: [overlay path]
colors:
theme: [theme name]
fonts:
name: [font name]
size: [font size]
urls:
- [font url]
packages:
generic:
npm:
- [package name]
pip3:
- [package name]
macos:
brew:
- [package name]
ubuntu:
ppa:
- [ppa address] # ppa must be declared before apt
apt:
- [package or ppa-package name]
snap:
- [package name]
dotfiles:
- [dotfile url]
custom_functions:
[function name]:
- [function command]- custom functions pattern:
./profiles/[profile]/custom.sh
Custom functions allow users to define specific commands at various steps of the execution : entry which executes at the beginning of a loco action, exit at the end of the action, and last after loco execution.
As these functions are executed as root; two additional functions are made available. These may be useful to escape some shell or $USER related limitations.
Using the cmd::run_as_user [command] function allows to execute a command as the initial $USER.
Using the cmd::record [command] function allows to record commands that will be executed after script execution (though /src/temp/finish.sh).
Custom functions can be defined in profile/custom.sh or in profile/profile.yaml. If both are present both will be executed.
- custom.sh: a script can be provided
#!bin/bash
#-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# custom.sh | custom user scripts
#-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# function name pattern - All OS
[action]_[entry/exit/last](){
# insert commands below
}
# example for an all OS entry function
install_entry(){
# insert commands below
}
# function name pattern - OS specific
[action]_[os_type]_[entry/exit/last](){
# insert commands below
}
# example for a macOS installation entry function
install_macos_exit(){
# insert commands below
}
# example for a Ubuntu removal last function
remove_ubuntu_last(){
# insert commands below
}- profile.yaml: some yaml commands can be provided
custom_functions:
[action]_[entry/exit/last]:
- # command goes here
install_entry:
- # command goes here
[action]_[os_type]_[entry/exit/last]:
- # command goes here
install_macos_exit:
- # command goes here
remove_ubuntu_entry:
- # command goes hereIf more than one method is set both are used from 1. to 2.
Note 1.: there is currently a limitation for [last] which can't be implemented as a yaml function (probably due to variables expansion).
Note 2.: cmd::run_as_user [command] and cmd::record [command] are not fully generic. In some cases, [command] argument quotes escaping will provoke some unexpected behaviors. Try to remove quotes in these cases, for example: cmd::run_as_user echo var >> file.
To create a new profile, simply duplicate one available in /profiles/, and start editing it as you please.
Profiles foldername can be set through the -p option.
Note: be careful about adding git submodules into your profiles as you may be in difficulty for retrieving them. See this open issue. for various solutions, including Github actions.
Actions are scripts applied to the profiles.
.
└── src
└── actions # store actions scripts
├── install.sh # install packages, dotfiles, backgrounds and themes, based on a profile
├── install_sys.sh # install packages and dotfiles, based on an installed instance
├── remove.sh # remove everything, based on an installed instance
└── update.sh # update everything, based on a profileNote : update.sh used with the -Y option will replace previously installed files.
To create an action, simply duplicate one available in /src/code/actions/ and start editing it as you please.
Actions can be set through the -a option.
Backrounds are user background images.
Backrounds can be set through four methods :
-Boption: an url can be provided to set a background- profile yaml: an url can be provided to set a background
style:
background: [background url]- profile asset: a file can be provided to set a background
.
└── profiles
└── [profile]
└── assets #store specific files (optional)
└── background.[image extension] # background image (optional)- prompt: a prompt will be launched to choose a background from the ones available in
/src/assets/backgrounds/
.
└── src
└── backgrounds #store actions scripts
└── [background images]If more than one method is set the priority goes from 1. to 4.
Dotfiles are user configuration files.
Dotfiles can be set through two methods :
- profile yaml: an url can be provided to set a dotfile
dotfiles:
- [dotfile url]- profile dotfiles folder: a folder can be provided to set dotfiles
.
└── profiles
└── [profile]
└── dotfiles #store specific files (optional)
└── .[dotfile name] # a dotfile (optional)If more than one method is set the sequence goes from 1. to 2., but already existing dotfiles in the [profile]/dotfiles/ folder won't be downloaded from the yaml. This is meant to prevent yaml urls to overwrite locally modified dotfiles.
When installing profile dotfiles, loco will backup existing dotfiles into the /instance/[current instance]/dotfiles-backup folder. A list of installed and backuped dotfiles is available in ~/.loco.yml.
Themes are terminal color themes.
.
└── src
└── themes #store actions scripts
├── monokai.conf # a classic monokai theme
├── monokai-light.conf # a light monokai theme
├── nord.conf # nord theme from articicestudio
└── nord-light.conf # custom light nord themeTo create a theme, simply duplicate one available in /src/assets/themes/ and start editing it as you please.
background-color='[color code]'
background-transparency-percent=0
bold-color='[color code]'
foreground-color='[color code]'
palette=['[color code 0]', '[color code 1]', '[color code 2]', '[color code 3]', '[color code 4]', '[color code 5]', '[color code 6]', '[color code 7]', '[color code 8]', '[color code 9]', '[color code 10]', '[color code 11]', '[color code 12]', '[color code 13]', '[color code 14]', '[color code 15]']Themes can be set through four methods:
-toption: the name of a theme present in/src/assets/themescan be provided to select a theme- profile yaml: the name of a theme present in
/src/assets/themescan be provided to select a theme
style:
theme: [theme name]- profile asset: a file can be provided to set terminal configuration (not the theme only)
.
└── profiles
└── [profile]
└── assets #store specific files (optional)
└── terminal.conf # terminal configuration (optional)- prompt: a prompt will be launched to choose a theme from the ones available in
/src/assets/themes/
Fonts are users terminal fonts, installed system wide.
Fonts can be selected through two methods :
- profile yaml: one or more urls can be provided to set one or more fonts. Note: only fonts with a [font name] declared in the profile
yamlwill be used for the terminal.
fonts:
name: [font name] # font system name
size: [font size] # desired terminal font size
urls:
- [font url] # an url to a font file- profile assets: files can be provided to install fonts on the system.
.
└── profiles
└── [profile]
└── assets # store specific files (optional)
└── fonts # fonts folder (optional)
└── [font file] # font file (optional)Transparent overlays can be added on top of users backgrounds.
Overlays need to be activated with the -o option.
Overlays can be selected through four methods :
-Ooption: the path to a transparent image can be provided to set an overlay- profile yaml: a path can be provided to set an overlay
style:
overlay: [overlay path]- profile asset: a file can be provided to set an overlay
.
└── profiles
└── [profile]
└── assets #store specific files (optional)
└── overlay.png # overlay image (optional)- prompt: a prompt will be launched to choose an overlay from the ones available in
/src/assets/background-overlays/
.
└── src
└── background-overlays #store actions scripts
└── [overlay images]If more than one method is set the priority goes from 1. to 4.
Instances store the backups for each loco installation. They are later used to restore the original $USER dotfiles. Note that only dotfiles installed by a profile are backed up. This helps to keep a mix of profile managed and $USER managed dotfiles.
.
└── instances
└── [username]-[profile]-[YYYY-MM-DD_HH-MM-SS]
└── dotfiles-backup #holds the original user dotfilesInstances are created automatically when an install action is performed. They are removed automatically when a remove action is performed.
Instances foldername can be set through the -i option.
| Name | Command | Description | Type | Options | Default |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACTION | a | Define the loco action | string | install, remove | - |
| BACKGROUND | b | Define the user background (from /src/assets/backgrounds) | string | filenames fom available /src/assets/backgrounds/ | - |
| BACKGROUND_URL | B | Define the user background (from an url or path) | string | any .jpg or .png image url or path | - |
| CONFIG_PATH | c | Define a path to the configuration file | string | [user defined] | "./src/loco.conf" |
| PROFILES_DIR | d | Define a path for profiles directories | string | [user defined] | "profiles" |
| DETACHED | D | Define if dotfiles are symbolically linked from repo or from | boolean | true/false | false |
| HELP | h | Display options and exit | flag | - | - |
| INSTANCES_DIR | i | Define a path for profiles instances | string | [user defined] | "instances" |
| OVERLAY | o | Define if the overlay option is activated | boolean | true/false | false |
| OVERLAY_PATH | O | Define a path for an overlay image | string | local path | - |
| PROFILE | p | Define the loco profile | string | available profiles | you can pass multiple profiles by separating them with a comma ,, for example : -p vim,zsh. |
| ROOT | R | Remove the sudo prompt (experimental) | flag | - | - |
| THEME | t | Define the loco color theme | string | monokai, monokai-light, nord, nord-light | - |
| CURRENT_USER | u | Define the current user name (default: `$USER`) | string | [user defined] | $USER |
| VERSION | v | Print Version and exit | flag | - | - |
| VERBOSE | V | Verbose mode | flag | - | - |
| WATERMARK | w | Define if a loco watermark is set (needed for remove) | boolean | true/false | true |
| YES | Y | Automate the yes answer (the few left) | flag | - | - |
Options can be set directly into /src/loco.conf.
.
└── src
└── loco.conf #stores static optionsThe first point you need to keep in mind is security. SSH and GPG keys shall not be shared over the public internet, as should not servers configurations. To make loco your own, you first need to fork it over a private repository, or your own git server. Then:
- for Gitlab.com or private Gitlab instances
- Retrieve your API private token
- Retrieve the [project ID]
- Update
./src/code/utils/installwith your information:
# modify below with your infos #
local branch_name="gh-main"
local git_server="https://gitlab.com"
local project_ID="1234"
local secret_key="ABC-123"
# # # # end of modifications- modify function call in
./src/code/utils/installfrom
retrieve_public_archive "$@"to
retrieve_private_archive "$@"- build a release
- Git add, commit and push to your
gitlabserver. - You can now install
locowith this url pattern:
Using wget:
bash <(wget --content-disposition --header="PRIVATE-TOKEN: [secret key]" -qO- "https://[git server]/api/v4/projects/[project ID]/repository/files/src%2Futils%2Finstall/raw?ref=[branch name]")Using curl:
bash <(curl --header "PRIVATE-TOKEN: [secret key]" -JLO "https://[git server]/api/v4/projects/[project ID]/repository/files/src%2Futils%2Finstall/raw?ref=[branch name]")Using either (untested):
bash <(echo '[secret key]' 'https://[git server]/api/v4/projects/[project ID]/repository/files/src%2Futils%2Finstall/raw?ref=[branch name]'|(read l o; wget --content-disposition --header="PRIVATE-TOKEN: $l -qO- $o 2>/dev/null || curl --header "PRIVATE-TOKEN: $l" -JLO $o));As it is complicated to archive correctly git sub-modules in profiles, loco provides a release archive in /dist/. To update it, launch ./src/code/utils/build_release.
When you install loco a watermark file ~/.loco.yml is installed. It stores the original dotfiles backup path. Wen you try to remove a profile loco tries to find the watermark path to restore the original user dotfiles. If the path is broken, either correct ~/.loco.yml with the correct path or put your dotftiles at the expected path.
If for some reasons, you don't have access to these files, simply remove the ~/.loco file. Previous installation will remain but you will be able to launch a new installation over it.
If your cmd::record commands are not executed, it is probably because the src/temp/finish.sh file is not properly sourced. Check your yaml profile file for a [last] custom function and remove it. [last] custom functions in profile yaml are not correctly interpreted and prevent finish.sh to be executed.
All of you, Eses !
Made in bash.