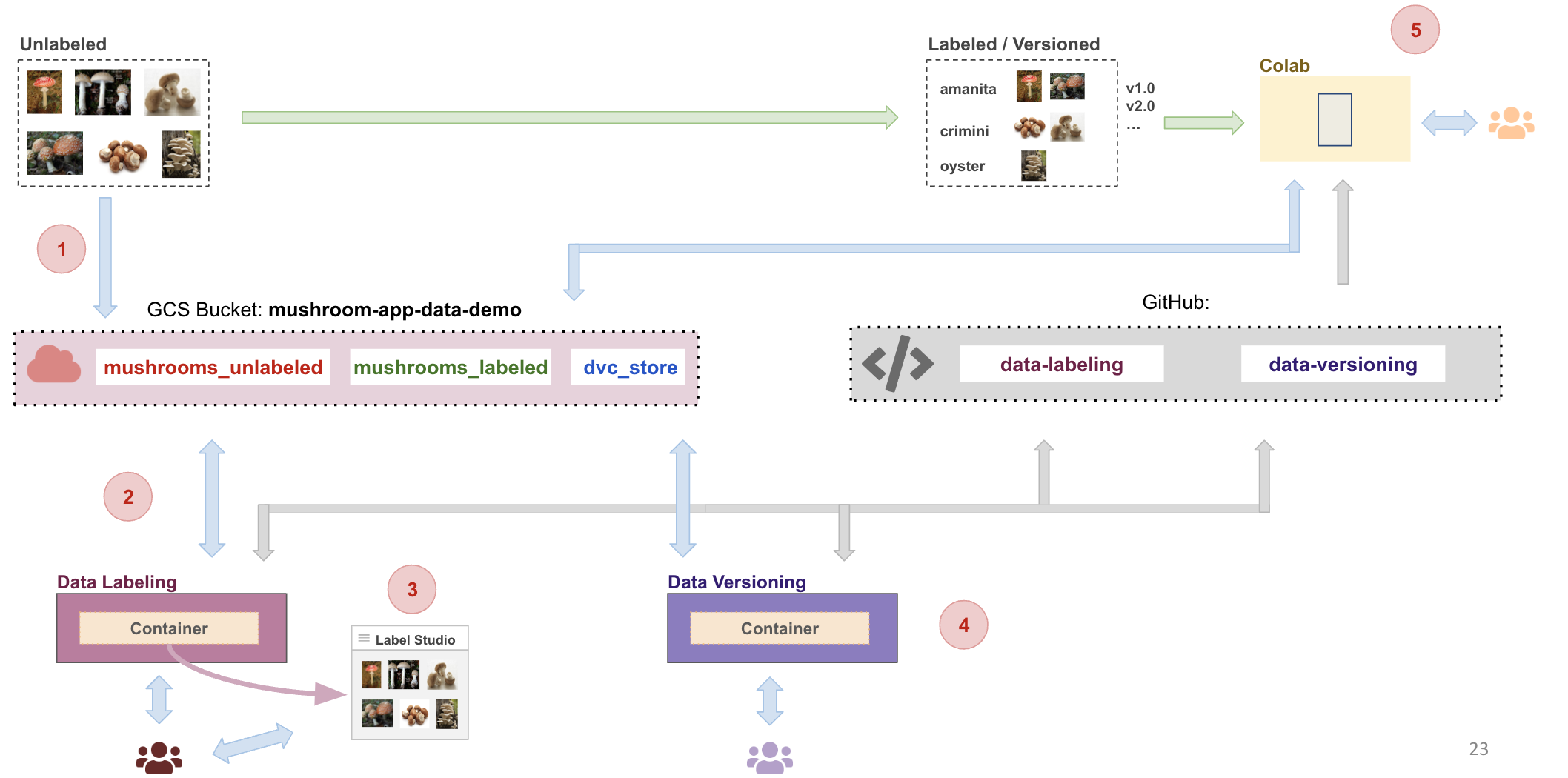
In this tutorial we will build a data pipeline flow as shown:
- Have Docker installed
- Cloned this repository to your local machine with a terminal up and running
- Check that your Docker is running with the following command
docker run hello-world
Install Docker Desktop
- To make sure we can run multiple container go to Docker>Preferences>Resources and in "Memory" make sure you have selected > 4GB
Follow the instructions for your operating system.
If you already have a preferred text editor, skip this step.
In this tutorial we will setup a data labeling web app to label data for the mushroom app. We will use Docker to run everything inside containers.
In order to complete this tutorial you will need your own GCP account setup and your github repo.
- Fork or download from here
Next step is to enable our container to have access to GCP Storage buckets.
It is important to note that we do not want any secure information in Git. So we will manage these files outside of the git folder. At the same level as the data-labeling folder create a folder called secrets
Your folder structure should look like this:
|-data-labeling
|-secrets
- Here are the step to create a service account:
- To setup a service account you will need to go to GCP Console, search for "Service accounts" from the top search box. or go to: "IAM & Admins" > "Service accounts" from the top-left menu and create a new service account called "data-service-account". For "Service account permissions" select "Cloud Storage" > "Storage Admin" (Type "cloud storage" in filter and scroll down till you find). Then click continue and done.
- This will create a service account
- On the right "Actions" column click the vertical ... and select "Manage keys". A prompt for Create private key for "data-service-account" will appear select "JSON" and click create. This will download a Private key json file to your computer. Copy this json file into the secrets folder. Rename the json file to
data-service-account.json
-
To setup GCP Credentials in a container we need to set the environment variable
GOOGLE_APPLICATION_CREDENTIALSinside the container to the path of the secrets file from the previous step -
We do this by setting the
GOOGLE_APPLICATION_CREDENTIALSto/secrets/data-service-account.jsonin the docker compose file -
Make sure the
GCP_PROJECTmatches your GCP Project
docker-compose.yml
version: "3.8"
networks:
default:
name: data-labeling-network
external: true
services:
data-label-cli:
image: data-label-cli
container_name: data-label-cli
volumes:
- ../secrets:/secrets
- ../data-labeling:/app
environment:
GOOGLE_APPLICATION_CREDENTIALS: /secrets/data-service-account.json
GCP_PROJECT: "ac215-project" [REPLACE WITH YOUR GCP PROJECT]
GCP_ZONE: "us-central1-a"
depends_on:
- data-label-studio
data-label-studio:
image: heartexlabs/label-studio:latest
container_name: data-label-studio
ports:
- 8080:8080
volumes:
- ./docker-volumes/label-studio:/label-studio/data
- ../secrets:/secrets
environment:
LABEL_STUDIO_DISABLE_SIGNUP_WITHOUT_LINK: "true"
LABEL_STUDIO_USERNAME: "pavlos@seas.harvard.edu" [REPLACE WITH YOUR EMAIL]
LABEL_STUDIO_PASSWORD: "awesome" [CHANGE IF NECESSARY]
GOOGLE_APPLICATION_CREDENTIALS: /secrets/data-service-account.json
GCP_PROJECT: "ac215-project" [REPLACE WITH YOUR GCP PROJECT]
GCP_ZONE: "us-central1-a"
In this step we will assume we have already collected some data for the mushroom app. The images are of various mushrooms belonging to either amanita, crimini, or oyster type. None of the images are labeled and our task here is to use label studio to manage labeling of images.
- Download the unlabeled data from here
- Extract the zip file
- Go to
https://console.cloud.google.com/storage/browser - Create a bucket
mushroom-app-data-demo(REPLACE WITH YOUR BUCKET NAME) - Create a folder
mushrooms_unlabeledinside the bucket - Create a folder
mushrooms_labeledinside the bucket
- Upload the images from your local folder into the folder
mushrooms_unlabeledinside the bucket
Based on your OS, run the startup script to make building & running the container easy
- Make sure you are inside the
data-labelingfolder and open a terminal at this location - Run
sh docker-shell.shordocker-shell.batfor windows
This will run two container. The label studio container and a CLI container that can call API's to label studio. You can verify them by running docker container ls on another terminal prompt. You should see something like this:
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
00d808ab0386 data-label-cli "pipenv shell" About a minute ago Up About a minute data-labeling-data-label-cli-run
4ab1ec940b4a heartexlabs/label-studio:latest "./deploy/docker-ent…" 2 days ago Up 2 days 0.0.0.0:8080->8080/tcp data-label-studio
Here we will setup the Label Studio App to user our mushroom images so we can annotate them.
- Run the Label Studio App by going to
http://localhost:8080/ - Login with
pavlos@seas.harvard.edu/awesome, use the credentials in the docker compose file that you used - Click
Create Projectto create a new project - Give it a project name
- Skip
Data Importtab and go toLabeling Setup - Select Template: Computer Vision > Image Classification
- Remove the default label choices and add:
amanita,crimini,oyster - Save
Next we will configure Label Studio to read images from a GCS bucket and save annotations to a GCS bucket
- Go the project created in the previous step
- Click on
Settingsand selectCloud Storageon the left options - Click
Add Source Storage - Then in the popup for storage details:
- Storage Type:
Google Cloud Storage - Storage Title:
Mushroom Images - Bucket Name:
mushroom-app-data-demo(REPLACE WITH YOUR BUCKET NAME) - Bucket Prefix:
mushrooms_unlabeled - File Filter Regex:
.* - Enable: Treat every bucket object as a source file
- Enable: Use pre-signed URLs
- Ignore: Google Application Credentials
- Ignore: Google Project ID
- Storage Type:
- You can
Check Connectionto make sure your connection works Saveyour changes- Click
Sync Storageto start syncing from the bucket to label studio - Click
Add Target Storage - Then in the popup for storage details:
- Storage Type:
Google Cloud Storage - Storage Title:
Mushroom Images - Bucket Name:
mushroom-app-data-demo(REPLACE WITH YOUR BUCKET NAME) - Bucket Prefix:
mushrooms_labeled - Ignore: Google Application Credentials
- Ignore: Google Project ID
- Storage Type:
- You can
Check Connectionto make sure your connection works Saveyour changes
In order to view images in Label studio directly from GCS Bucket, we need to enable CORS
- Go to the shell where we ran the docker containers
- Run
python cli.py -c - To view the CORs settings, run
python cli.py -m - To view all the code open
data-labelingfolder in VSCode or any IDE of choice
Go into the newly create project and you should see the images automatically pulled in from the GCS Cloud Storage Bucket
- Click on an item in the grid to annotate using the UI
- Repeat for a few of the images
Here are some examples of mushrooms and their labels:

- Go to
https://console.cloud.google.com/storage/browser - Go into the
mushroom-app-data-demo(REPLACE WITH YOUR BUCKET NAME) and then into the foldermushrooms_labeled - You should see some json files corresponding to the images in the
mushrooms_unlabeledthat have been annotated - Open a json file to see what the annotations look like
- Get the API key from Label studio for programatic access to data
- Go to User Profile > Account & Settings
- You can copy the Access Token from this screen
- Use this token as the -k argument in the following command line calls
- Go to the shell where ran the docker containers
- Run
python cli.py -p -kfollowed by your Access Token. This will list out your projects - Run
python cli.py -t -kfollowed by your Access Token. This will list some tasks from the first project
You will see the some json output of the annotations for each image that is being stored in Label Studio
Annotations: [{'id': 5, 'created_username': ' pavlos@seas.harvard.edu, 1', 'created_ago': '1\xa0hour, 53\xa0minutes', 'completed_by': 1, 'result': [{'value': {'choices': ['amanita']}, 'id': 'qHjUzqXO6W', 'from_name': 'choice', 'to_name': 'image', 'type': 'choices', 'origin': 'manual'}], 'was_cancelled': False, 'ground_truth': False, 'created_at': '2023-09-06T17:33:08.558474Z', 'updated_at': '2023-09-06T17:33:08.558492Z', 'draft_created_at': None, 'lead_time': 5.981, 'import_id': None, 'last_action': None, 'task': 1, 'project': 1, 'updated_by': 1, 'parent_prediction': None, 'parent_annotation': None, 'last_created_by': None}]
Annotations: [{'id': 1, 'created_username': ' pavlos@seas.harvard.edu, 1', 'created_ago': '1\xa0hour, 55\xa0minutes', 'completed_by': 1, 'result': [{'value': {'choices': ['amanita']}, 'id': 'Hp3wZORhBI', 'from_name': 'choice', 'to_name': 'image', 'type': 'choices', 'origin': 'manual'}], 'was_cancelled': False, 'ground_truth': False, 'created_at': '2023-09-06T17:31:04.307102Z', 'updated_at': '2023-09-06T17:31:04.307117Z', 'draft_created_at': None, 'lead_time': 11.197, 'import_id': None, 'last_action': None, 'task': 2, 'project': 1, 'updated_by': 1, 'parent_prediction': None, 'parent_annotation': None, 'last_created_by': None}]
In this tutorial we will setup a data versioning step for the mushroom app pipeline. We will use Docker to run everything inside containers.
- Fork or download from here
Your folder structure should look like this:
|-data-labeling
|---docker-volumes
|-----label-studio
|-data-versioning
|-secrets
- To view all the code open
data-versioningfolder in VSCode or any IDE of choice
- Go to
https://console.cloud.google.com/storage/browser - Go to the bucket
mushroom-app-data-demo(REPLACE WITH YOUR BUCKET NAME) - Create a folder
dvc_storeinside the bucket
We will be using DVC as our data versioning tool. DVC (Data Version Control) is an Open-source, Git-based data science tool. It applies version control to machine learning development, make your repo the backbone of your project.
In order for the DVC container to connect to our GCS Bucket open the file docker-shell.sh and edit some of the values to match your setup
export GCS_BUCKET_NAME="mushroom-app-data-demo" [REPLACE WITH YOUR BUCKET NAME]
export GCP_PROJECT="ac215-project" [REPLACE WITH YOUR GCP PROJECT]
export GCP_ZONE="us-central1-a"
For windows open the file docker-shell.bat
Based on your OS, run the startup script to make building & running the container easy
- Make sure you are inside the
data-versioningfolder and open a terminal at this location - Run
sh docker-shell.shordocker-shell.batfor windows
This will run a container that has DVC already installed. You can verify the containers running by docker container ls on another terminal prompt. You should see something like this:
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
00d808ab0386 data-label-cli "pipenv shell" About a minute ago Up About a minute data-labeling-data-label-cli-run
4ab1ec940b4a heartexlabs/label-studio:latest "./deploy/docker-ent…" 2 days ago Up 2 days 0.0.0.0:8080->8080/tcp data-label-studio
e87e8c6f180f data-version-cli "pipenv shell" 5 seconds ago Up 5 seconds data-version-cli
In this step we will download all the labeled data from the GCS bucket and create dataset_v1 version of our dataset.
- Go to the shell where ran the docker container for
data-versioning - Run
python cli.py -d
If you check inside the data-versioning folder you should see the a mushroom_dataset folder with labeled images in them.
.
|-mushroom_dataset
|---amanita
|---crimini
|---oyster
|-mushroom_dataset_prep
The dataset from the data labeling step will be downloaded to a local folder called mushroom_dataset
Make sure to have your gitignore to ignore the dataset folders. We do not want the dataset files going into our git repo.
/mushroom_dataset_prep
/mushroom_dataset
In this step we will start tracking the dataset using DVC
In this step we create a data registry using DVC
dvc init
dvc remote add -d mushroom_dataset gs://mushroom-app-data-demo/dvc_store
dvc add mushroom_dataset
dvc push
You can go to your GCS Bucket folder dvs_store to view the tracking files
- First run git status
git status - Add changes
git add . - Commit changes
git commit -m 'dataset updates...' - Add a dataset tag
git tag -a 'dataset_v1' -m 'tag dataset' - Push changes
git push --atomic origin main dataset_v1
In this Step we will use Colab to view various version of the dataset
- Open Colab Notebook
- Follow instruction in the Colab Notebook
- Go to Label Studio App at
http://localhost:8080/ - Click on an item in the grid to annotate using the UI
- Repeat for a few of the images
In this step we will download the labeled data from the GCS bucket and create dataset_v2 version of our dataset.
- Go to the shell where ran the docker container for
data-versioning - Run
python cli.py -d
dvc add mushroom_dataset
dvc push
- First run git status
git status - Add changes
git add . - Commit changes
git commit -m 'dataset updates...' - Add a dataset tag
git tag -a 'dataset_v2' -m 'tag dataset' - Push changes
git push --atomic origin main dataset_v2
In this Step we will use Colab to view the new version of the dataset
- Open Colab Notebook
- Follow instruction in the Colab Notebook to view
dataset_v2
By the end of this tutorial your folder structure should look like this:
|-data-labeling
|---docker-volumes
|-----label-studio
|-data-versioning
|-mushroom_dataset
|---amanita
|---crimini
|---oyster
|-mushroom_dataset_prep
|-secrets
To make sure we do not have any running containers and clear up an unused images
- Run
docker container ls - Stop any container that is running
- Run
docker system prune - Run
docker image ls