Ethereum allows you to build your own cryptocurrency on their blockchain with a standard called ERC-20 token standard. ERC-20 is an API standard that governs how an Ethereum token should be built. This standard allows you to mint your own token, transfer it between wallets, and hold an initial token sale. This standard also allows your token to be accepted across various applications. This means support across different wallets and different cryptocurrency exchanges.
We will be building out the required functionality specified with this standard so our token is compliant with the ERC20 standard. To do this we will use Ganache for rapid blockchain testing on our local machine, along with the Truffle framework to build smart contracts for our token. We will then create a token sale where users can buy our tokens and then deploy Rinkeby test network (not the main Ethereum network) so we do not have to worry about gas cost.
Our token, token sale, client side and backend will be on the blockchain and decentralized.
- node package manager (npm) (install from node js website or with a command line tool like homebrew, type
brew install node). - Truffle framework will allow us to create decentralized applications on the Ethereum network with its suite of tools so we can write, test, and deploy smart contracts. (To install go to command and type
npm install -g truffle). - Ganache, is your local personal blockchain that you can use for testing purposes. (Install directly from their website).
- Metamask, a browser extension that allows you to connect to the Ethereum network. Allowing us to talk to the blockchain from our browser (Found on Chrome browser).
- Solidity syntax highlighting (you can use Ethereum from Package Control for Sublime 2/3)
- lite-server is used as our development server.
- Bootstrap CDN
- Web3 library so our client can communicate with the blockchain
- truffle-contract, a JS library that allows us to interact with our contracts
- Go Ethereum (Geth), a Go implementation of Ethereum. (you can install with homebrew by doing
brew tap ethereum/ethereum, and thenbrew install ethereum). Dowhich gethandget versionto check it downloaded properly
Use truffle init in the command line within your project directory to create a new truffle project. This will create your contract, migration, and test directories including some configuration files.
MyToken.solis the smart contract that will implement the ERC-20 standard and govern behavior for your tokenMyTokenSale.solwill handle the token sale part of this projectapp.jswill handle the sale of tokens, display balance, and etc.- Lite-Server is dependent on BrowserSync (allows use access files and directories), so we must create a
bs-config.json
The contract directory will be used whenever we create other smart contracts(such as token contract and token sale contract). The migration.sol file is the contract that handles the migrations whenever we deploy our contracts to our blockchain. Deploying smart contracts will create transactions and write to the blockchain changing its state. So whenever we push a contract to the blockchain we are in a sense migrating the blockchains state from not having a smart contract to having it. This is why we need a migrations directory.
The migration directory is where all of our migrations files will be placed. 1_initial_migration.js will get runned whenever we deploy our smart contracts. It will take the migrations.sol contract from our contract directory. Whenever we create a new smart contract we will create a new file in this directory to handle migrating those contracts to the blockchain.
Test directory is used to test our smart contracts.
truffle-config.js is used for windows and truffle.js is used for macOS
Make sure to first set Development Configurations in your truffle-config file. Four digit port number can be found at the end of your Ganache RPC Server, as well as the host.
To open the console use the truffle console command. Truffle console is a JS runtime environment used to interact with contracts. Because smart contracts are asynchronous in nature, they will rely upon the usage of JavaScript promises.
truffle migrate and truffle migrate -- reset will allow us to push contracts onto the Ethereum blockchain (either local, tesnet or mainnet) and help us link contracts with other contracts as well as populate them with initial data
How to get attributes of a contract:
First create a tokenInstance by doing,
MyToken.deployed().then(function(instance){tokenInstance=instance}),MyToken.deployed()will give us a deployed instance of our contract. We then save the value of that instance into the variabletokenInstance..deployed()will return a promise, when the promise completes we call thethen()function. We will get a deployed instance of our contract and set it totokenInstance. Note,MyTokenwas created in our migrations.
We can also view the token instance by entering
tokenInstanceinto our console.
After we have the instance of our contract we can use
tokenInstance.addressto get the address of our smart contract.
All the following were declared in our
MyToken.solfile:tokenInstance.name()will return the name of our token.tokenInstance.symbol()will return the symbol of our token.tokenInstance.standard()will return the standard of our token.
How to get totalSupply:
We can then use the
tokenInstanceto find its total supply.tokenInstance.totalSupply().then(function(s){totalSupply=s})thetotalSupplywill return the total supply of your token. JavaScript will give us a BigNumber type, since we are returning units that are too large for JS to handle.totalSupply.toNumber()will also return our total supply.
When our
MyToken.solcontract got deployed our constructor was executed which took_initalSupplyas a parameter and set thetotalSupplywith it._initalSupplywas passed in our_deploy_contracts.js. In the same constructor we also set the initial supply equal to the balance of the administrator, the one that deployed it.
How to get addresses and using web3:
web3 is a library that allows us to interact with the blockchain.
Use
web3.eth.accounts()to see all accounts/addresses that are available.
web3.eth.accounts[0]will show the account found at index 0 of accounts.
Use of
web3.eth.accounts()andweb3.eth.accounts[0]is deprecated in newer versions of Solidity. Instead useaccounts = web3.eth.getAccounts()andweb3.eth.getAccounts().then(function(s) {first = s[0];});then,firstrespectively to get address of first.
Doing
web3.eth.getAccounts().then(function(acc){ accounts = acc }), thenaccounts[0]accounts[1], etc. will give account addresses by index.
How to check balance:
First we need to get an account to its check balance .
web3.eth.getAccounts().then(function(s) {admin = s[0];});, admin will contain our account address. Note: admin is the address that contains the initial supply, this is the 0 index, because Ganache uses the first address (0 index) as default.
We can then do
tokenInstance.balanceOf(admin)to view the supply of admin.
tokenInstance.balanceOf(admin).then(function(bal){balance = bal;}), thenbalance.toNumber()to also view the supply of admin.
Transfers
First we get an account that will receive tokens from the transfer.
web3.eth.getAccounts().then(function(s) {receiver = s[1];});, this will set our receiver to the address at s[1].
We can then call a transfer by doing
tokenInstance.transfer(receiver, 1, {from:admin}). This transfers one token from the admin account to the receiver's account. On completion it will print a receipt.
We can then check the balance of the receiver, which has increased by 1, with
tokenInstance.balanceOf(receiver)and the balance of admin, which has decreased by 1, bytokenInstance.balanceOf(admin)which has decreased by 1.
Approvals
First do,
web3.eth.getAccounts().then(function(acc){ accounts = acc })to access account addresses by index.
tokenInstance.approve(accounts[1], 100, {from: admin})will trigger an approval on accounts[1] for 100 tokens and create a receipt.
tokenInstance.allowance(accounts[0], accounts[1])to check allowance that was approved for expenditure. This is saying accounts[1] is allowed to spend a certain amount of tokens on accounts[0] behalf. Following the syntax ofmapping(address => mapping(address => uint256)) public allowance
Delegated Transfers
First do,
web3.eth.getAccounts().then(function(acc){ accounts = acc })to access account addresses by index.
Set addresses for a fromAccount, toAccount, and spendingAccount
fromAccount = accounts[2]toAccount = accounts[3]spendingAccount = accounts[4]Next, transfer tokens to your fromAccount by doingtokenInstance.transfer(fromAccount, 100, {from: accounts[0]})and check that it has tokens by doingtokenInstance.balanceOf(fromAccount)
Then, we will need to approve spendingAccount to spend tokens on the fromAccounts behalf. We will do this by doing:
tokenInstance.approve(spendingAccount, 10, {from: fromAccount}).
Lastly, we will trigger the delegated transfer by:
tokenInstance.transferFrom(fromAccount, toAccount, 10, {from: spendingAccount})
Allowance of
spendingAccountshould not be 0. You can check by doingtokenInstance.allowance(fromAccount, spendingAccount)and the balance oftoAccountshould have increased by 10. You can check by doingtokenInstance.balanceOf(toAccount).
Use .exit to exit the console.
Testing in Truffle comes bundled with the Mocha testing framework and Chai assertion library.
To test run use truffle test.
Testing smart contracts is very important. Smart contracts and the blockchain are meant to be immutable. So it is important that they are bug free. If they are deployed with a bug, then we will have to disable it and then deploy another.
Use npm run dev to run server.
Connect to your local network with Metamask. You will need to create a Metamask account and create a Custom RPC with your Ganace URL and port to connect to Ganace.
You will also need to import an account using a Ganace private key.
We will need to setup the application by provisioning some tokens to the myTokenSale contract. We do that manually in the Truffle console.
Transferring tokens to tokenSale contract
Do
MyTokenSale.deployed().then(function(i){tokenSale=i});to get tokenSale, entertokenSaleto view tokenSale data.
Do
MyToken.deployed().then(function(i){token=i});to get tokenSale, entertokento view tokenSale data.
set tokens available
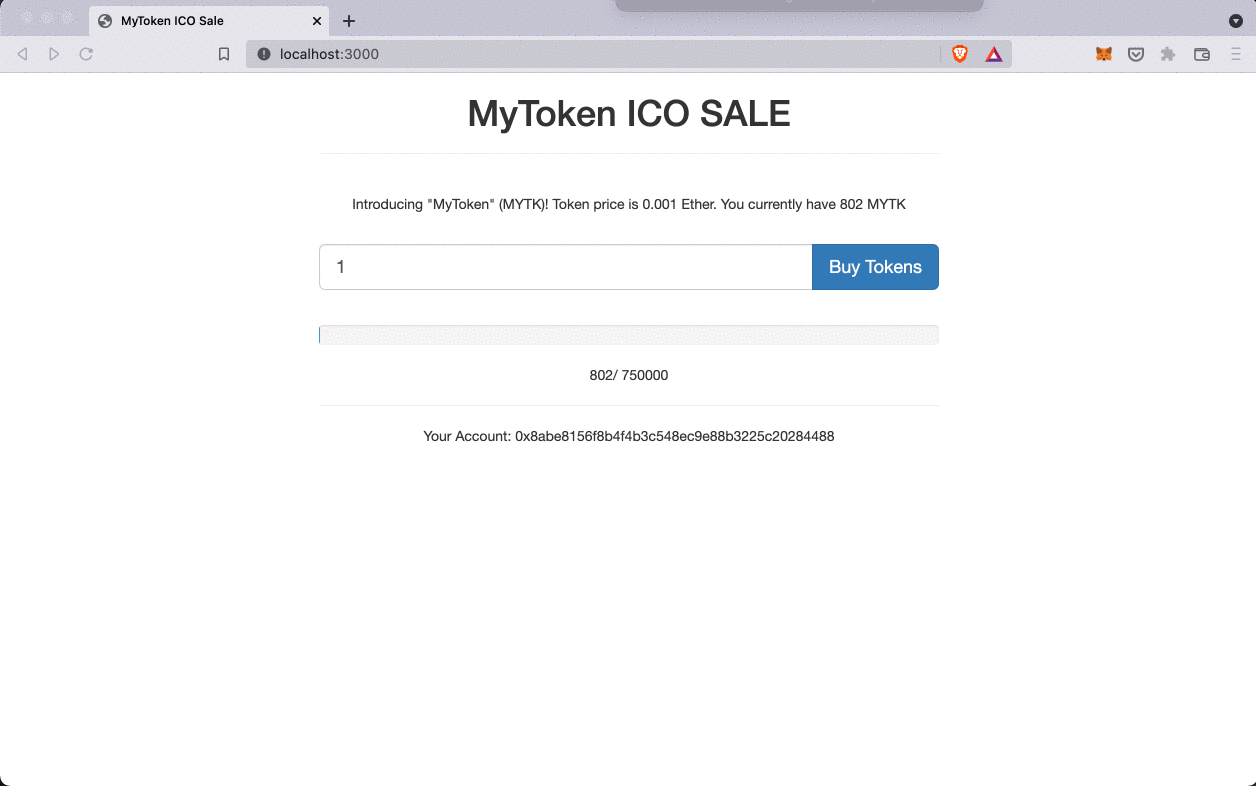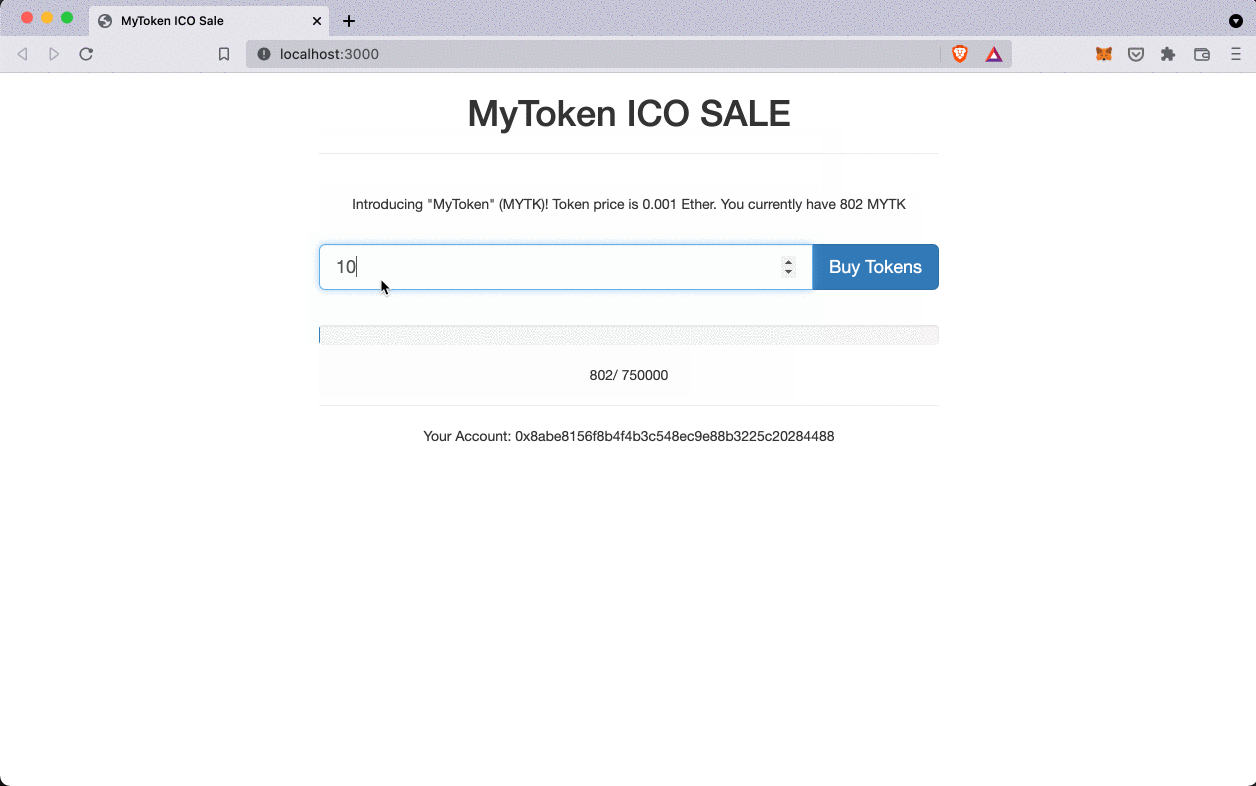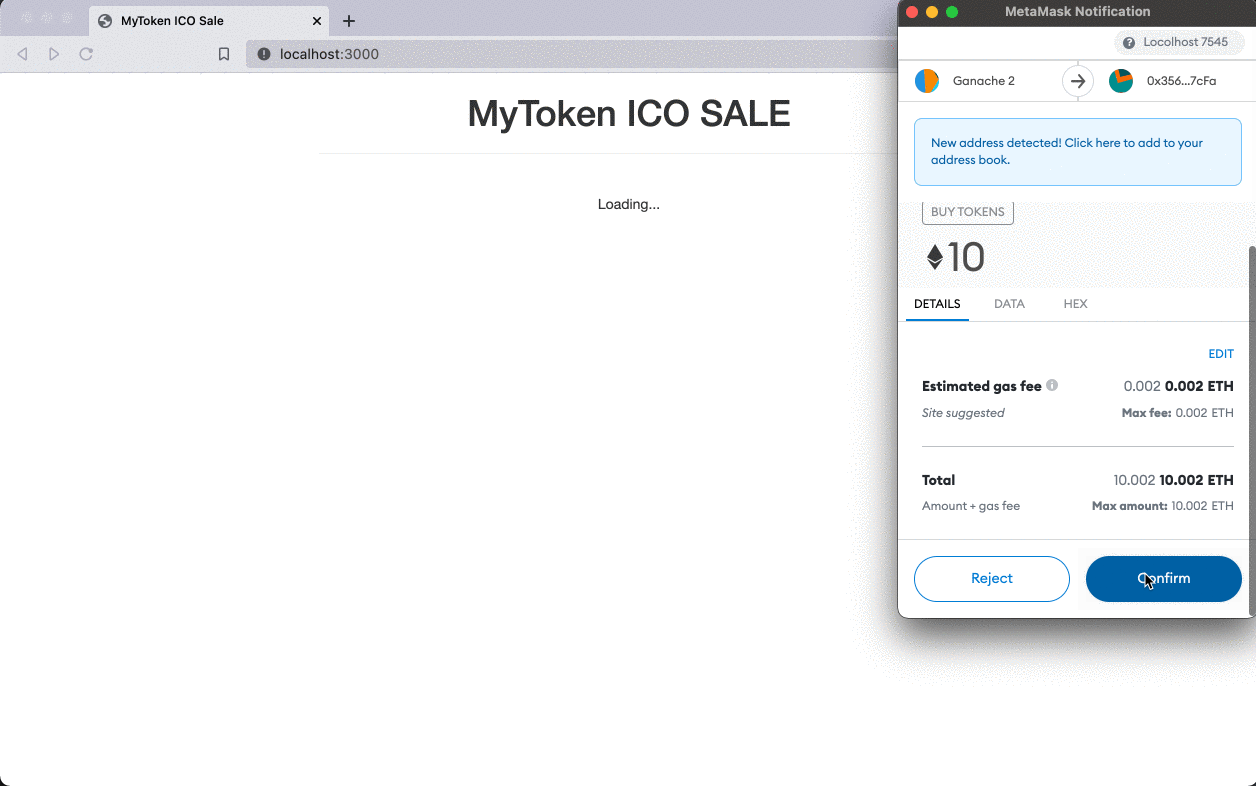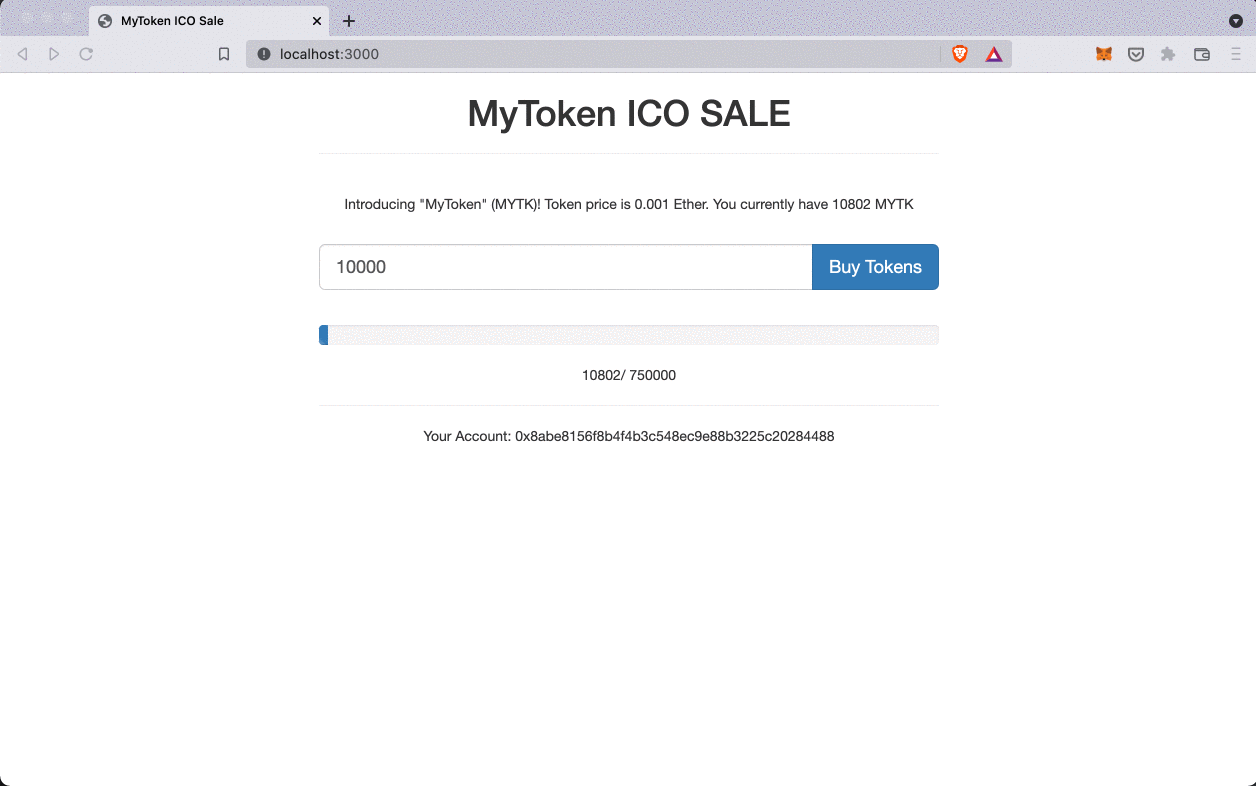
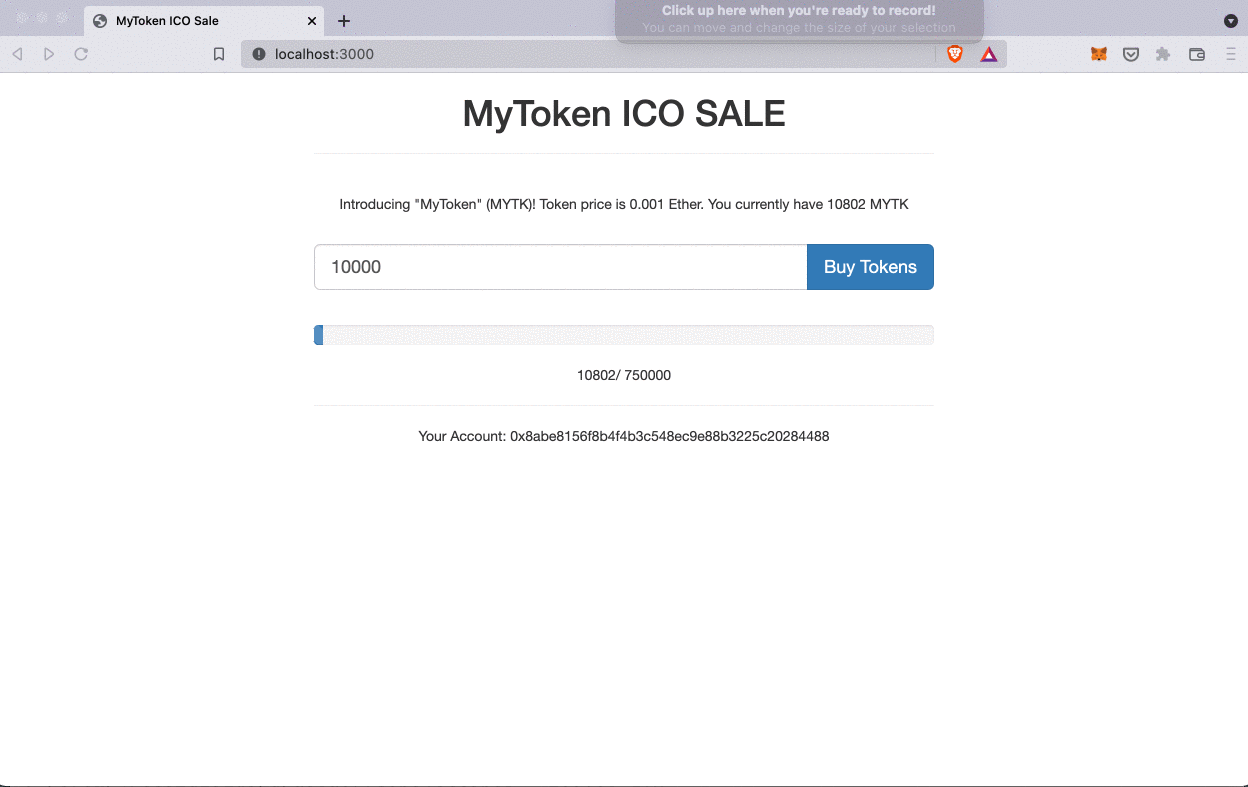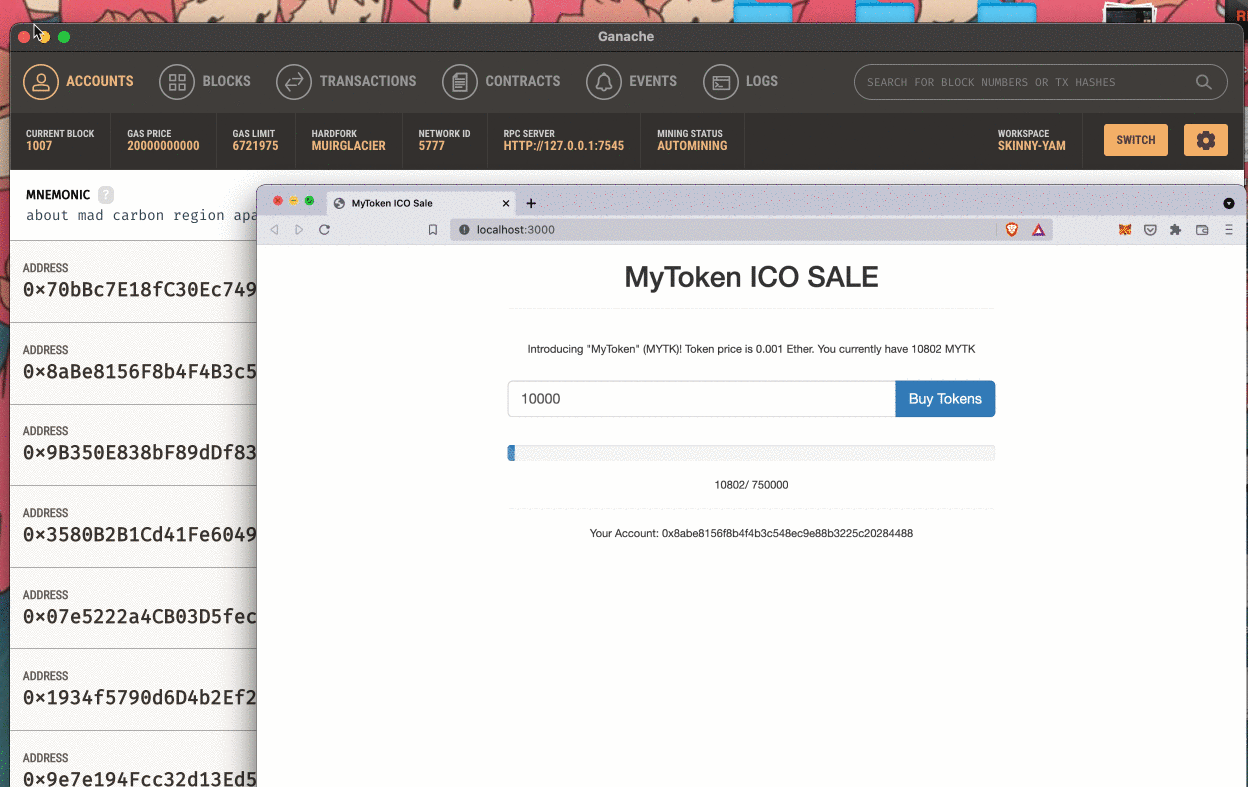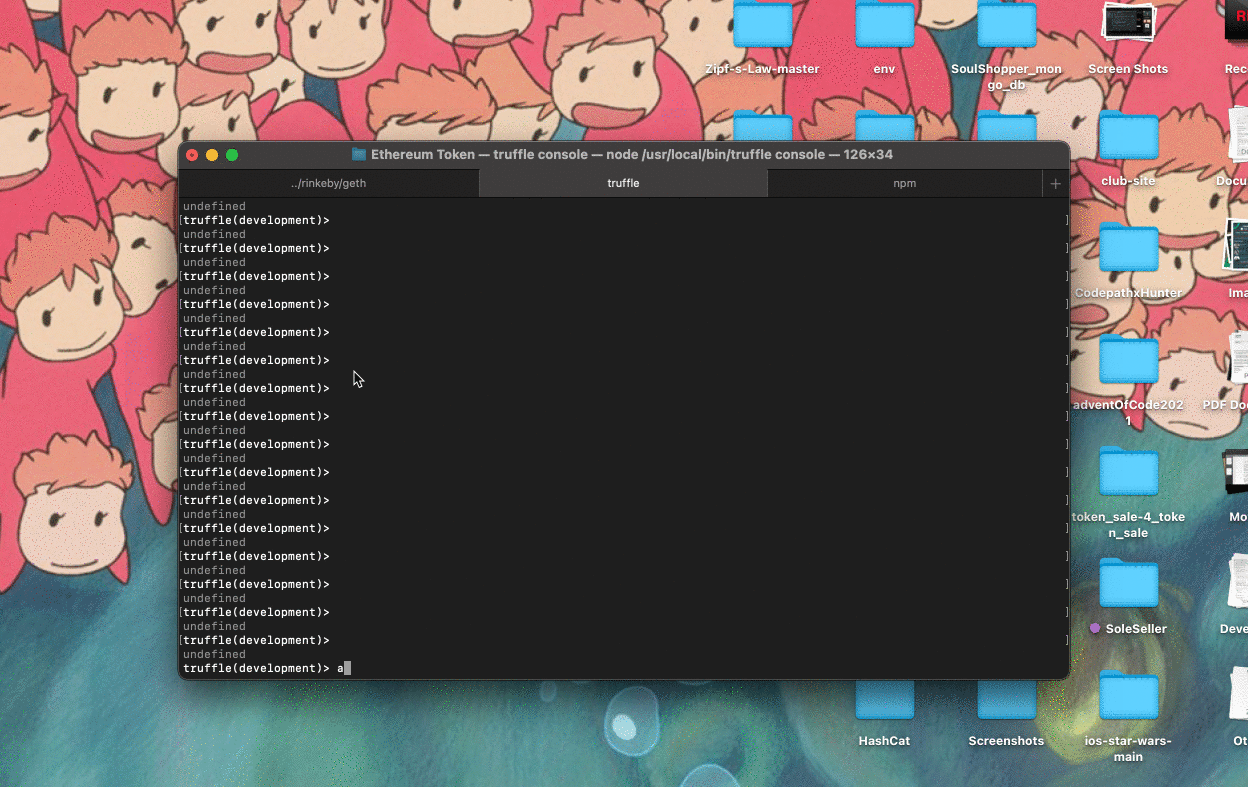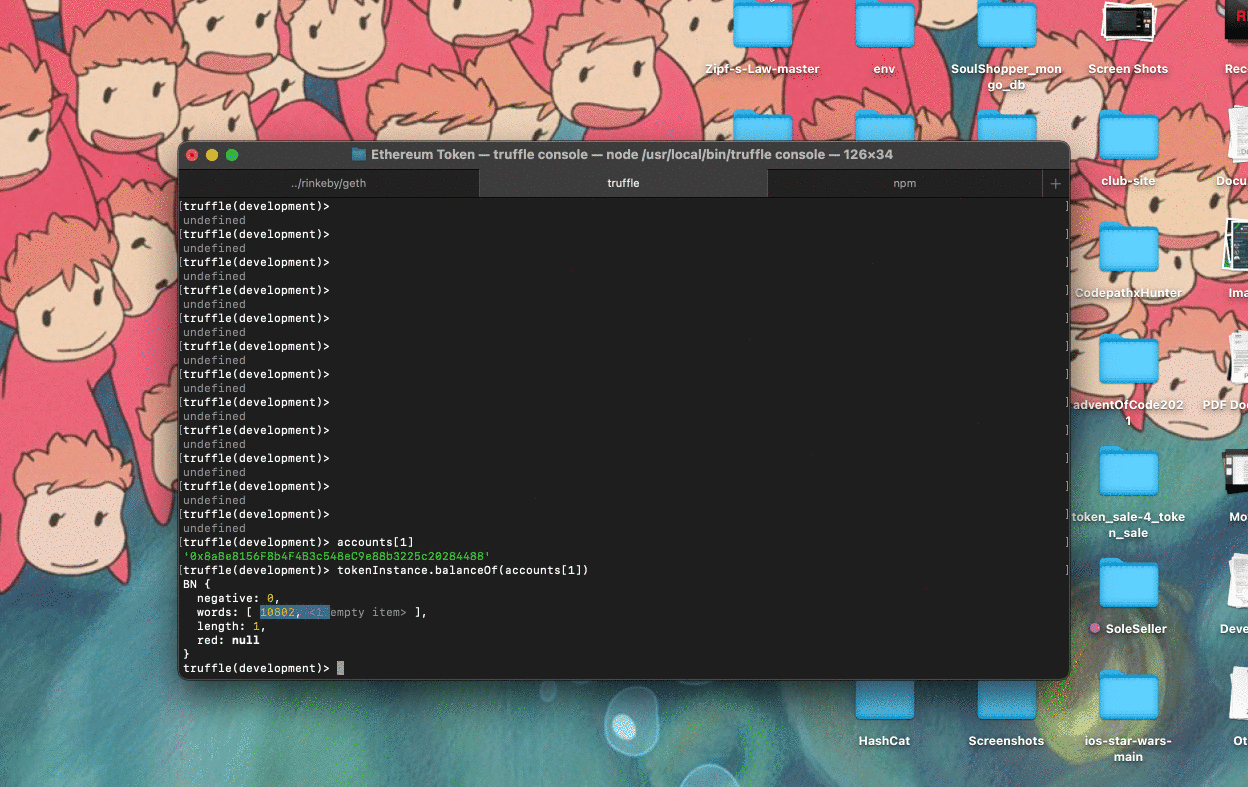
tokenAvailable = 750000.
set admin account that contains all tokens
web3.eth.getAccounts().then(function(acc){ accounts = acc });admin = accounts[0];
transfer token from admin account to tokenSale address and a receipt should print.
token.transfer(tokenSale.address, tokenAvailable, {from: admin})
After transferring tokens from admin account to tokensSaleContract, admin account should have 250000 tokens and this amount should display in our MyToken ICO SALE page.
Check balance
token.balanceOf(tokenSale.address)
Purchasing tokens on ICO website:
Showing account balance in Truffle console:
This is incomplete and still being worked on. My laptop does not have enough diskspace for me to do this.
Rinkeby Test Network With Geth
There are different test networks we can use. We will be using the Rinkeby Test Network.
First we need to connect our Geth node to the test network.
Unlike Ganache, Geth is a full blown Ethereum node and we will use it to connect to the Rinkeby test network. As a node when we are connected to the ETH network we are participating in the network.
run our Geth node with the rinkeby network by doing:
geth --rinkeby --http --http.api="personal,eth,network,web3,net" --ipcpath "~/Library/Ethereum/geth.ipc"
specify libraries that we want to use with http.api and the installation path with ipcpath. When we connect to the rinkeby network we need to get all the data and wait for it to download. So after running command for the first time there will significant activity and it will need a lot of disk space.
open the console with geth attach.
Run eth.synching, our current block number should sync up to the highest block number. That way we know our node has completely synced with the network.
create a new account on the Rinkeby network with geth --rinkeby account new this will give you an account address.
my address -> 0x59e700901aF64155015F177231b47f4E553bf017
Since we cannot mine Ether on the Rinkeby test network (since its only a test network), we need to request Ether from a Rinkeby Ether Faucet. This way we can fund our accounts to deploy our smart contracts. A faucet is a smart contract that can dispense Ether. Go to faucet.rinkeby.io to request Ether to your account address.
use eth.balanceOf(accounts[0]) to check accounts balance
Make sure to have your truffle project configured to deploy our contracts to the Rinkeby network.
we need to unlock our account in order to deploy, basically giving our account permission to deploy.
personal.unlockAccount(eth.accounts[0], null, 1200), here we use the personal library, account 0, null password (it will ask you for a password again) and the account will be unlocked for 1200 seconds.
Geth has to be done syncing in order to deploy contracts. Check using eth.syncing, it should return false.
Do truffle migrate --reset --compile-all --network rinkeby
We configured the network in our truffle-config file. So, it knows to use the rinkeby network. After our contracts migrate you should see the transactions in the Geth node sync process. They also will be reflected in our contrats .json file.
We will need to give our tokensale contrat some tokens on the Rinkeby network. So first we will need a deployed instance of our token sale contract so we can transfer tokens. We do this in the Geth console with the Web3 library.
First, open the geth console by doing geth attach, and then we keep track of our admin by var admin = eth.accounts[0].
Set var tokensAvailable = 750000. Get the tokensSale address which we can find in contracts/MyTokenSale.json. In the networks array and is the address value for the Rinkeby network port 4 key.
set var tokenSaleAddress = 0x0.
All functions and variables must follow the naming convention as shown in the ERC-20 token standard
Smart contracts are code that gets executed on the blockchain. It will be where the logic of your token and token sale will live. Reading, writing, behavior (buy, sale, transfer, etc), basic attributes (name, symbol, price, supply, etc) all exist in the contract.
To run migrations use truffle migrate on the terminal. You can use the --reset flag if needed.
Whenever you run migrations and deploy contracts to blockchain it will cost gas. Reading from Ethereum blockchain is free, writing to it will cost ETH. After deploying the contracts your new ETH balance will be reflected on Ganache. Ganache will always use the first address by default.
Just like wallets can have tokens, so can smart contracts. We have to give our token sale contract tokens.
Metamask will help our browser communicate with the blockchain because most browsers by default won't talk to the blockchain. Metamask will talk to web3, injecting an http provider into our browser that allows our browser to communicate with our client side that will talk to the blockchain.
We use truffle-contract as a dependency for our client side and it will hepl use interact with contracts. Truffle contract will know how to use our contracts JSON files and its ABI's.
Solidity v0.5.16 Documentation
"Interacting with Deployed Ethereum Contracts in Truffle"
Lots of thanks and credit to Gregory McCubbin from Dapp University for making this project possible. 🙏