gradle-eclipse-aar-plugin
Gradle plugin to use Android AAR libraries on Eclipse.
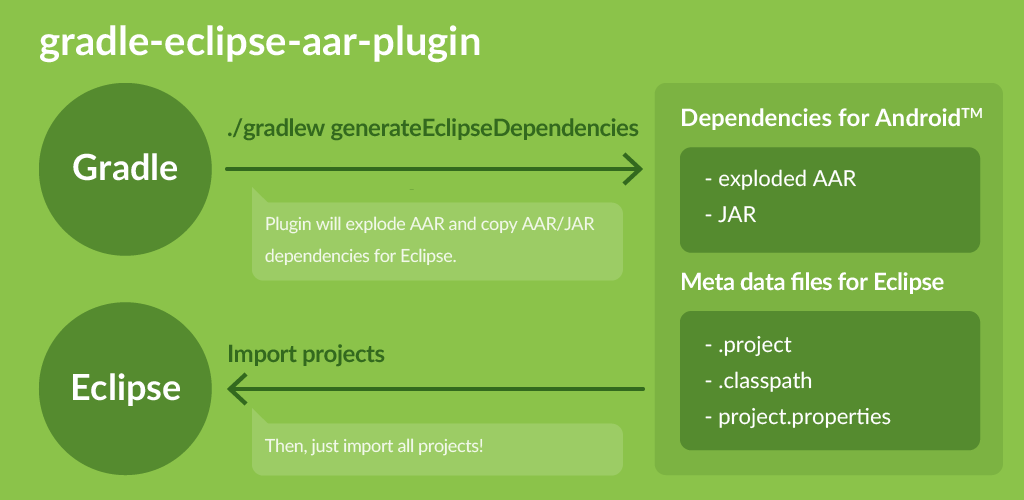
With this plugin, you can manage dependencies with Gradle and build app on Eclipse.
Android Studio has been officially released, but some of you still want/are forced to use Eclipse ADT for some reasons. Android Studio has much better build system by integrating Gradle, and many of the remarkable features are unavailable in Eclipse. In particular, many Android libraries are provided with AAR format recently, so it's now big disadvantage for Eclipse to manage these dependencies. This plugin will explode AAR libraries and create "Android Library Project"s or copy JARs for your project by executing just one command, and you just import these projects in Eclipse.
Originally I was inspired by this article, then rewrote almost all of it and added many improvements to automate conversion process and to cover several dependency/project conditions.
Prerequisites
This plugin is tested under these conditions.
Usage
Prepare build.gradle
If your project already uses Gradle and Android Studio,
just apply this plugin and configure it in eclipseAar closure.
buildscript {
repositories {
mavenCentral()
// Enable this if you use SNAPSHOT
//maven {
// url uri('https://oss.sonatype.org/content/repositories/snapshots/')
//}
}
dependencies {
classpath 'com.android.tools.build:gradle:1.0.0'
classpath 'com.github.ksoichiro:gradle-eclipse-aar-plugin:0.1.1'
}
}
apply plugin: 'com.android.application'
// Apply this plugin
apply plugin: 'com.github.ksoichiro.eclipse.aar'
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
// Write your dependencies
dependencies {
compile 'com.android.support:appcompat-v7:21.0.2'
compile 'com.nineoldandroids:library:2.4.0'
compile 'com.melnykov:floatingactionbutton:1.0.7'
compile 'com.github.ksoichiro:android-observablescrollview:1.5.0'
}
// Configure eclipse-aar plugin
eclipseAar {
// See "Configurations" for details
androidTarget = 'android-21'
aarDependenciesDir = 'aarDependencies'
}
// Configure android plugin
// (Even if you don't develop with Gradle, write following at least)
android {
compileSdkVersion 1
// Source directory is 'src/main/java' by default.
// This will be added as a classpath entry in .classpath file.
// If you'd like to set src directory other than that,
// override it with sourceSets.main.java.srcDirs like this.
sourceSets {
main {
java.srcDirs = [ 'src' ]
}
}
}Prepare Gradle or Gradle wrapper
Install Gradle 2.2.1+.
Or copy Gradle wrapper files into your project. If you use Gradle wrapper, you don't have to install Gradle.
gradlegradlewgradlew.bat
Generate dependencies
$ ./gradlew generateEclipseDependenciesJAR dependencies will be copied to libs directory,
and AAR dependencies will be exploded and copied to aarDependencies directory by default.
Import projects to Eclipse and build app
- Launch Eclipse.
- Select
File>Import. - Select
General>Existing Projects into Workspaceand clickNext. - Click
Browseand select project root directory. - Check
Search for nested projects. - Select all projects and click next.
Note that if you've imported projects in Eclipse before, there might bebindirectories and they might be recognized as projects, but don't select them. - Some warning messages might be generated, but ignore them and wait until build finishes.
Run the app
- Confirm your device is connected.
- Right click your main project and select
Run As>Android Application.
project.properties?
Eclipse ADT plugin uses project.properties file to manage library project dependencies.
If you don't have project.properties file, this plugin will create it.
If you have project.properties file but don't have the required AAR dependency entries in it, this plugin will add these entries, too.
Therefore you don't have to care about them.
But please note that if you have file dependencies (libs/xxx.jar),
you should manually add entries for them to project.properties file.
.classpath files?
Eclipse has .classpath files to manage dependencies.
For Android apps, each library projects must be declared as <classpathentry> tags in .classpath file.
If you don't have .classpath file, this plugin will create it.
If you have .classpath file but don't have <classpathentry>s for the required libraries in it, this plugin will add these entries, too.
Therefore you don't have to care about them.
But please note that if you have file dependencies (libs/xxx.jar),
you should manually add entries for them to .classpath file.
.project files?
Eclipse has .project files to manage project description.
If you don't have .project file, this plugin will create it, so you don't have to care about them.
Configurations
Configurations for this plugin are written in eclipseAar closure.
| Configuration | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| androidTarget | android-21 |
target value in dependency projects' project.properties |
| aarDependenciesDir | aarDependencies |
Directory to explode AARs |
| jarDependenciesDir | (null) | Directory to locate JAR. |
| projectNamePrefix | (Empty) | Project name prefix for AAR dependencies |
| projectName | (Target project name) | Base project name for AAR dependencies |
| cleanLibsDirectoryEnabled | false |
Set to true if you want libs directory to be cleaned before files are generated. |
| targetConfigurations | ['compile', 'debugCompile'] |
Configurations that dependency JAR/AAR will be aggregated from |
Samples
See samples directory.
Each projects refer to samples/repo directory as a Maven repository.
You must generate it before using samples with following command:
$ cd /path/to/this/project/root/
$ ./gradlew clean assemble uploadArchivesAfter that, you can try this plugin in each projects.
Example:
$ cd ./samples/example/
$ ./gradlew generateEclipseDependenciesLicense
Copyright 2015 Soichiro Kashima
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License.