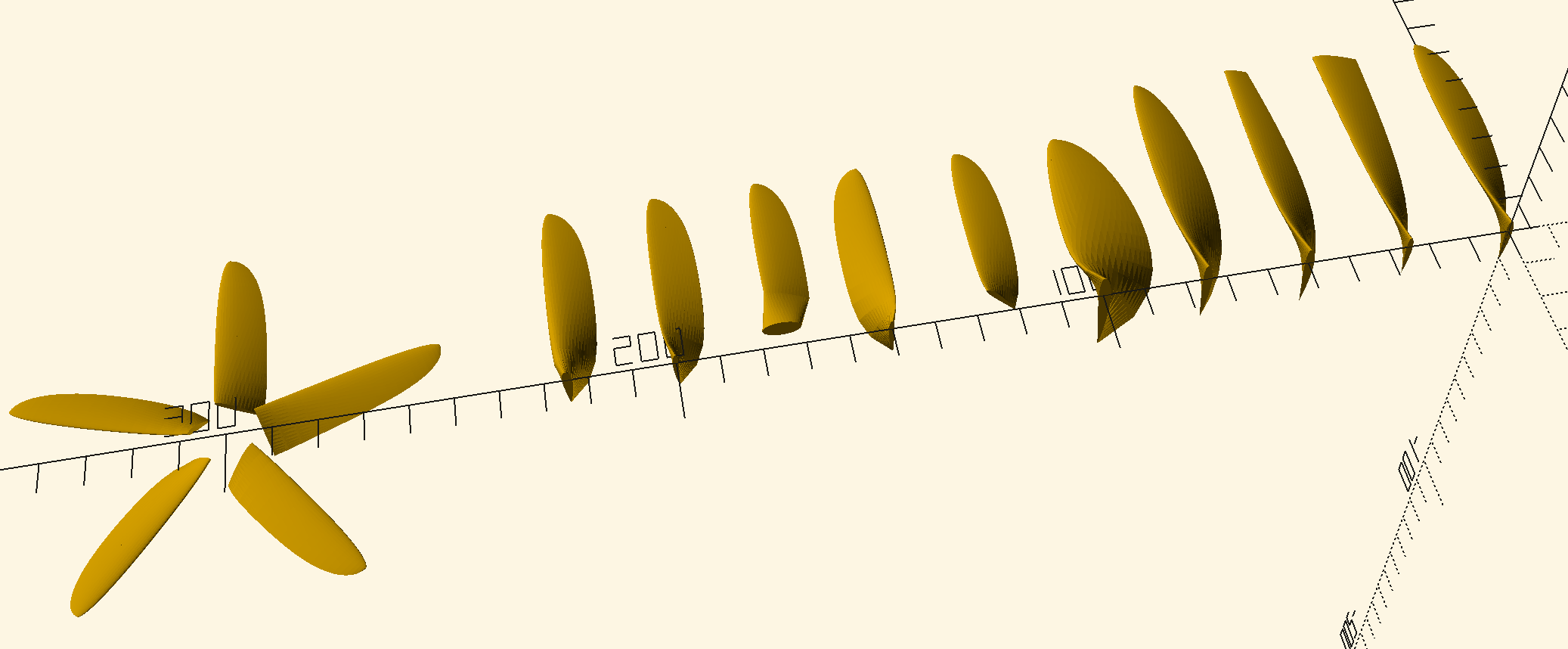
Generate propeller blades in OpenSCAD.
What can it do?
- Create propeller blades
- Use any four digit NACA profiles
- Specify size and pitch
- Specify elliptical lift outline or trapezoidal outlines
- Make propeller or turbine blades
- Finish the blade at the root
- The blades can rotate clockwise or counterclockwise
- You can specify the aspect ratio of the blade
- You can specify different wing profiles for each blade section, with interpolation
- You can plug in your own outline
- Specify accuracy for quick or precise output
Note the propellers and turbine blades generated by this code is not at all tested in real life scenarios and may be totally wrong, though probably they are ok.
To use bladegen, you should put the bladegen folder from the git libraries
folder to the OpenSCAD library folder that you will find in the File menu of
OpenSCAD. Additionally you will need to install the DiscreteOpenSCAD library
BOSL2 also in the library folder.
use <bladegen/bladegen.scad>
INCH_MM = 25.6;
translate([0, 0, 0]) bladegen(pitch = 4 * INCH_MM, diameter = 5 * INCH_MM);
translate([0, 25, 0]) bladegen(pitch = 4 * INCH_MM, diameter = 5 * INCH_MM, outline = rectangular_outline());
translate([0, 50, 0]) bladegen(pitch = 4 * INCH_MM, diameter = 5 * INCH_MM, outline = rectangular_outline(taper_tip = 0.5));
translate([0, 75, 0]) bladegen(pitch = 4 * INCH_MM, diameter = 5 * INCH_MM, outline = elliptical_outline(exponent = 5));
translate([0, 100, 0]) bladegen(pitch = 40, diameter = 100, outline = elliptical_outline(aspect_ratio = 3));
translate([0, 125, 0]) bladegen(pitch = 40, diameter = 100, inner_radius = 0.10);
translate([0, 150, 0]) bladegen(pitch = 40, diameter = 100, ccw = true);
translate([0, 175, 0]) bladegen(pitch = 40, diameter = 100, inner_radius = 0.30, root = ellipse_root(radius = 0.1));
translate([0, 200, 0]) bladegen(pitch = 40, diameter = 100, turbine = true);
translate([0, 225, 0]) bladegen(pitch = 40, diameter = 100, wing_sections = naca_wing_sections([[0.0, 2440], [0.5, 2420], [1.0, 0010]]));
translate([0, 250, 0]) bladegen(pitch = 40, diameter = 100, wing_sections = naca_wing_sections([[0.0, 2440, 8], [0.5, 2420, 8], [1.0, 0010, 0]]));
translate([0, 325, 0]) bladegen(pitch = 40, diameter = 100, inner_radius = 0.15, blades = 5);
If you prefer, open the file demo.scad to run the above commands.
Lengths are given in the OpenSCAD unit which normally is mm. Some other values
are specified in % of blade length, 0.0 being at the root and 1.0 at the tip.
The root shape in particular should be scaled so that a width of 1.0 will be as
wide as the chord where the blade ends (inner_radius).
To make a hub, it must be done manually by a code something like
use <bladegen/bladegen.scad>
diameter = 200;
hub_r = 15;
hub_h = 12;
hole_d = 6;
root = ellipse_root(r = [0.2, 0.08], rotate = 40.0, radius = 0.10);
difference() {
union() {
bladegen(diameter = 200, pitch = 150, inner_radius = 0.3, root = root, blades = 5);
translate([0, 0, -1]) cylinder(r = hub_r, h = hub_h, center = true);
}
cyl(d = hole_d, h = 99, center = true, $fn = 30);
}This code also demontrates ending the blade near the root. Any shape can be supplied.
If you don't supply a diameter parameter, the diameter will be 1.0 long and the pitch is specified as number of diameters advancement per revolution. It may sometimes be easier to work in this manner and then just scale the propeller to the correct diameter after. If you do this, the relative pitch remains constant with different sizes. Normally, pitch and diameter are dependent on each other.
The library is built around the bladegen function. All parameters are
supplied with default values, but you may want to change these.
The bladegen will calculate a number of points along the blade radius called
nodes. You can adjust the accuracy and speed of the blade generation by
supplying the segments parameter to bladegen.
The outline is calculated as a chord length at each node point. You would
normally generate an outline with the function elliptical_outline(...) or
rectangular_outline(...). These functions return new functions, which may
supply an outline based on the node position.
You may also supply your custom outline literal function like this:
custom_outline = function (radius) (0.5 * (1 - radius)^2 + 0.5) / 5;
bladegen(outline = custom_outline);The function should return a chord length based on the radius going from 0.0 to 1.0. The chord length must also take the desired aspect ratio into consideration.
The wing section profile is done much the same as the outline calculation. To
use a single NACA profile supply a parameter outline = naca_wing() to the
bladegen call. Like for the outlines, the function returns a new function
that is called later with the correct radius parameter for the nodes. You can
also specify different wing sections by using the function
naca_wing_sections(...). The NACA profiles are interpolated at each node. The
parameter to the function receives a list of lists of two or three elements
each. The first is the radial position along the blade 0 to 1, the second the
four digit NACA profile and the last one is an optional angle of attack to
rotate the profile.
Custom wing section distributions may be made like custom outlines, but it is
harder to achieve. An example in the code is the function naca_wing_sections.
bladegen(wing_sections = naca_wing(2408));
bladegen(wing_sections = naca_wing_sections([[0.0, 2430, 8.0], [1.0, 2408, 10.0]]));