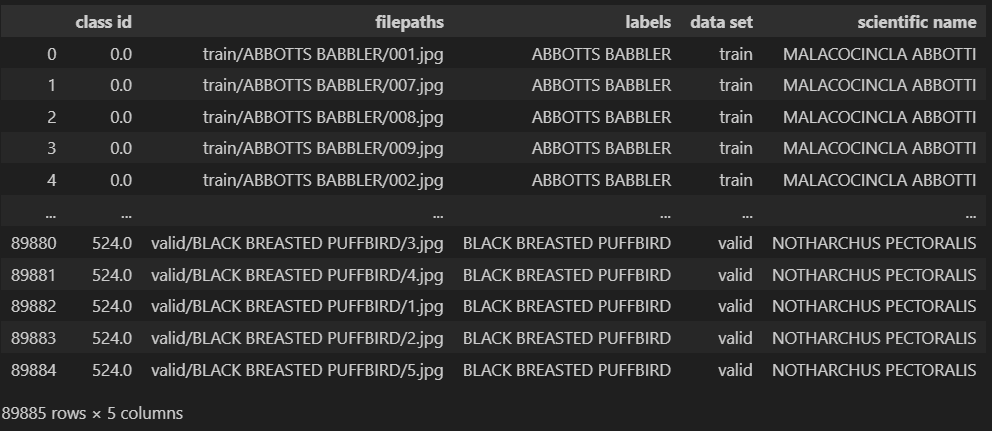
- Data set of 525 bird species from Kaggle. 84,635 training images, 2,625 test images(5 images per species) and 2,625 validation images(5 images per species). You can download the data in Kaggle. Since the data files are too large, I have NOT uploaded the dataset here. It includes train/valid/test dataset, a csv file, and a trained model from the owner of the dataset. We would NOT use the model because we will train it on our own.
- Objective: to use tensorflow, keras to train a model using the dataset and we can use our trained model to make a prediction
- I have used Saturn Cloud free tier for this project
- All training details are in
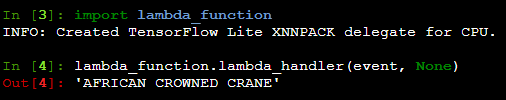
birds-classification-model-training.ipynb - Use AWS Lambda function to predict the category
- TensorFlow and keras for deep learning
- Use pre-trained models xception for general image classification
- Convolutional layers - turn an image into a vector
- Dense layers - use the vector to make the predictions
- use transfer learning and re-use - already trained convolutional layers
- First, train a small model (150x150) before training a big one (299x299)
- Tune learning rate - how fast the model trains; tune inner-layer
- Save the best model using callbacks and checkpointing
- To avoid overfitting, use dropout and augmentation
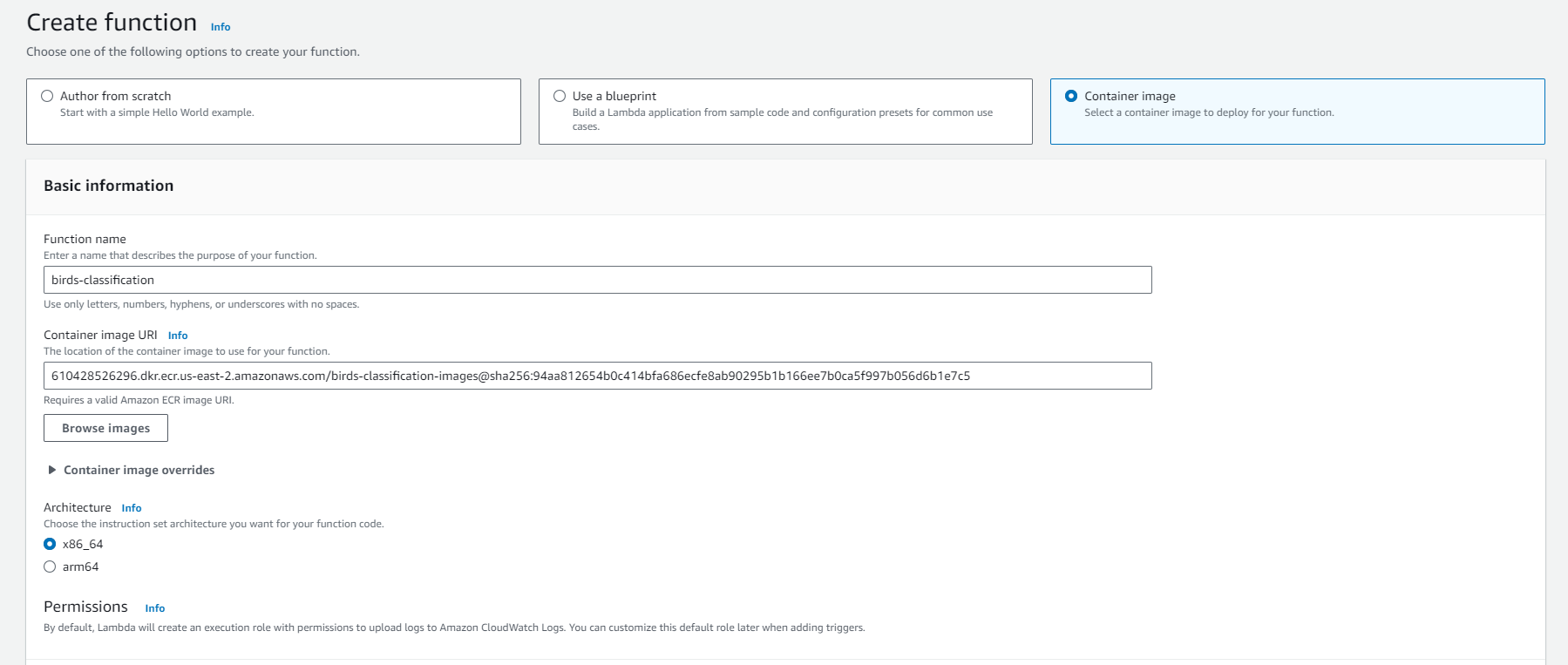
- Use AWS Lambda API to make a prediction
- US AWS S3 to save the images
- Build a frontend with Streamlit
Explore the dataset
# read data file
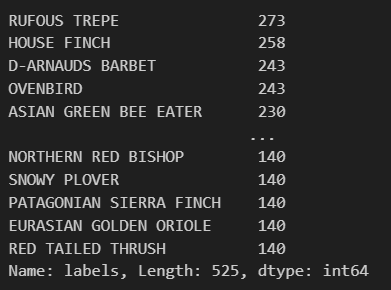
data = pd.read_csv("birds.csv")data.info()data["labels"].value_counts()# to load an image
path = "./train/ABBOTTS BABBLER"
name = "001.jpg"
fullname = f"{path}/{name}"
img = load_img(fullname, target_size=(299, 299))# convert the image to numpy arry
x = np.array(img)# check the shape of the image
x.shape- use Xception
from tensorflow.keras.applications.xception import Xception
from tensorflow.keras.applications.xception import preprocess_input
from tensorflow.keras.applications.xception import decode_predictions
# load the model
model = Xception(weights="imagenet", input_shape=(299, 299, 3))# convert all the images to numpy
X = np.array([x])
# preprocess images
X = preprocess_input(X)
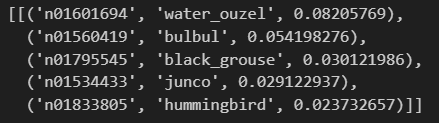
pred = model.predict(X)
# decode the prediction
decode_predictions(pred)- Load the data
train_gen = ImageDataGenerator(preprocessing_function=preprocess_input)
train_ds = train_gen.flow_from_directory(
"./train",
target_size=(150, 150),
batch_size=32
)
val_gen = ImageDataGenerator(preprocessing_function=preprocess_input)
val_ds = val_gen.flow_from_directory(
"./valid",
target_size=(150, 150),
batch_size=32,
shuffle=False
)- Load the base model
# base model
base_model = Xception(
weights="imagenet",
include_top=False,
input_shape=(150, 150, 3)
)
# freeze
base_model.trainable = False# train the top
inputs = keras.Input(shape=(150, 150, 3))
# 3D
base = base_model(inputs, training=False)
# => 2D
pooling = keras.layers.GlobalAveragePooling2D()
# => vector
vectors = pooling(base)
# add class layer
outputs = keras.layers.Dense(525)(vectors)
model = keras.Model(inputs, outputs)preds = model.predict(X)
# the output does not make sense without training
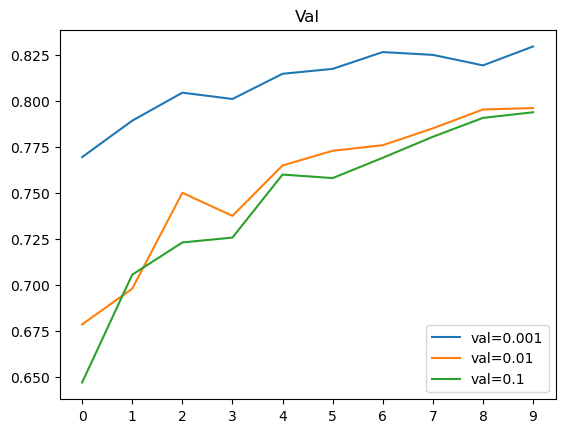
preds[0]- turning with different learning rate [0.001, 0.01, 0.1], 0.001 is the BEST
def make_model(learning_rate=0.01):
base_model = Xception(
weights='imagenet',
include_top=False,
input_shape=(150, 150, 3)
)
base_model.trainable = False
#########################################
inputs = keras.Input(shape=(150, 150, 3))
base = base_model(inputs, training=False)
vectors = keras.layers.GlobalAveragePooling2D()(base)
outputs = keras.layers.Dense(525)(vectors)
model = keras.Model(inputs, outputs)
#########################################
optimizer = keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=learning_rate)
loss = keras.losses.CategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True)
model.compile(
optimizer=optimizer,
loss=loss,
metrics=['accuracy']
)
return model- use checkpoint to save the best model during training
model.save_weights('model_v1.h5', save_format='h5')
checkpoint = keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint(
'xception_v1_{epoch:02d}_{val_accuracy:.3f}.h5',
save_best_only=True,
monitor='val_accuracy',
mode='max'
)learning_rate = 0.001
model = make_model(learning_rate=learning_rate)
history = model.fit(
train_ds,
epochs=15,
validation_data=val_ds,
callbacks=[checkpoint]
)Due to the limited space in github, all the models have not been uploaded.
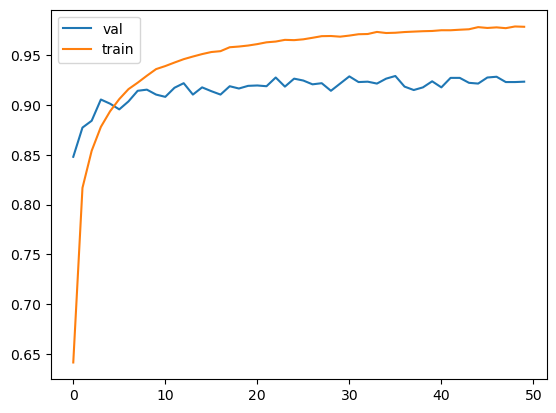
The best one is from epoch#13, val_accuracy = 0.8415
- adding more layers
- add this code to the original make_model function
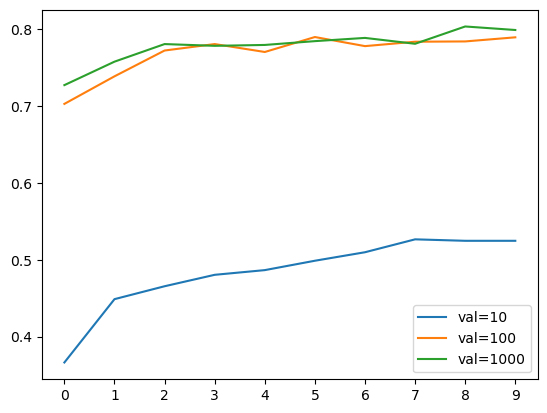
inner = keras.layers.Dense(size_inner, activation="relu")(vectors) - turning the inner-size layer with [10, 100, 1000]
- innser_size=1000 is the best
-
Regularizing by freezing a part of the network
-
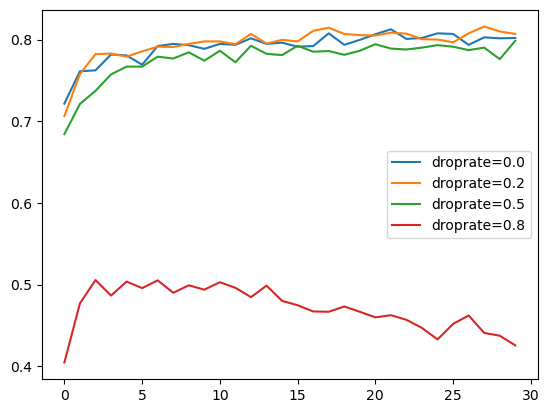
Adding dropout to our model
-
Experimenting with different values
-
add this code
drop = keras.layers.Dropout(droprate)(inner) -
The best droprate is 0.2.
- Different data augmentations
- Training a model with augmentations
- Only use it when the accuracy is better. Only added to the train data, you can pick one or a few together. Need to do your own experiment to decide which one to pick.
train_gen = ImageDataGenerator(
preprocessing_function=preprocess_input,
rotation_range=30,
width_shift_range=10,
height_shift_range=10,
shear_range=10,
zoom_range=0.1
vertical_flip=True
)
train_ds = train_gen.flow_from_directory(
"./train",
target_size=(150, 150),
batch_size=32
)
# val dataset keep the same
val_gen = ImageDataGenerator(preprocessing_function=preprocess_input)
val_ds = val_gen.flow_from_directory(
"./valid",
target_size=(150, 150),
batch_size=32,
shuffle=False
)After the augmentation, the accuracy is close to what we have before. It does not improve the result.
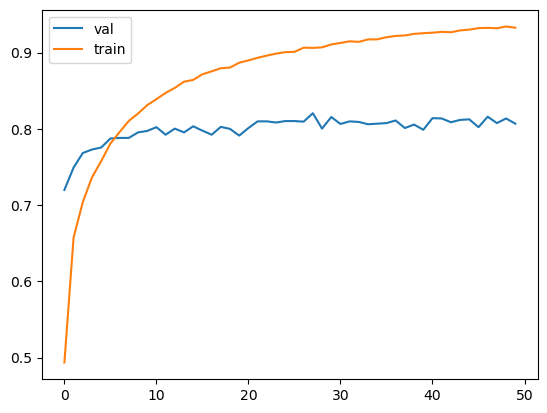
Initially 150x150 size was used to turn the model. After the best parameters are picked, we can train a larger model with the size of 299x299
- use the same make_model function with
learning_rate = 0.0005
size = 100
droprate = 0.2
input_size = 299# load the model
model = keras.models.load_model("xception_v4_36_0.929.h5")
# evaludate the model - accuracy: 0.9345
model.evaluate(test_ds)path = "./test/ALBATROSS/1.jpg"
img = load_img(path, target_size=(299, 299))
x = np.array(img)
X = np.array([x])
X = preprocess_input(X)
pred = model.predict(X)
classes = list(test_ds.class_indices.keys()) #classes list
class_pred_dict = dict(zip(classes, pred[0]))
max_class = max(class_pred_dict, key=class_pred_dict.get) # => 'ALBATROSS', it matches the real result.Since the model is large, when you git the file, an error might prompt
this exceeds GitHub's file size limit of 100.00 MB remote: error: GH001: Large files detected. You may want to try Git Large File Storage - https://git-lfs.github.com.
Solution:
- download from https://git-lfs.github.com
- use the below command one by one
git lfs version
git lfs install
git lfs track "*.h5"
git add --all
git commit -m "Add large .h5 files"
git push- if you still have a problem, try
git lfs migrate info
git lfs migrate import --include="*.h5" --include-ref=refs/heads/main
git push origin main- use TF-Lite to do the prediction
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras
model = keras.models.load_model("xception_v4_36_0.929.h5")
converter = tf.lite.TFLiteConverter.from_keras_model(model)
tflite_model = converter.convert()
with open('xception_v4_36_0.929.tflite', 'wb') as f_out:
f_out.write(tflite_model)- install the packages
!pip install keras-image-helper
!pip install --extra-index-url https://google-coral.github.io/py-repo/ tflite_runtime- load the model
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras
model = keras.models.load_model("xception_v4_36_0.929.h5")
converter = tf.lite.TFLiteConverter.from_keras_model(model)
tflite_model = converter.convert()
with open('xception_v4_36_0.929.tflite', 'wb') as f_out:
f_out.write(tflite_model)- get the classes
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator
train_gen = ImageDataGenerator(preprocessing_function=preprocess_input)
train_ds = train_gen.flow_from_directory(
"./train",
target_size=(150, 150),
batch_size=32
)
classes = list(train_ds.class_indices.keys())- get predictions
import tflite_runtime.interpreter as tflite
from keras_image_helper import create_preprocessor
interpreter = tflite.Interpreter(model_path="xception_v4_36_0.929.tflite")
interpreter.allocate_tensors()
input_index = interpreter.get_input_details()[0]["index"]
output_index = interpreter.get_output_details()[0]["index"]
preprocessor = create_preprocessor("xception", target_size=(299, 299))
path = "./test/AFRICAN CROWNED CRANE/1.jpg"
X = preprocessor.from_path(path)
interpreter.set_tensor(input_index, X)
interpreter.invoke()
preds = interpreter.get_tensor(output_index)
class_pred_dict = dict(zip(classes, preds[0]))
max_class = max(class_pred_dict, key=class_pred_dict.get)- test the lambda function
- In the termianl, run
python3 flask_predict.pyto start your server. You might just needpython yourfilename.py - open another terminal to run your
test.pywithpython3 test.py. Or you might just needpython test.py. If it shows the category of the bird, the model and server are working. Ctrl + cto end the server
- to build a virtual environment, run
pip install pipenv - install packages
pipenv install numpy flask requests pandas matplotlib tensorflow keras tflite_runtime keras_image_helper - now we have
PipfileandPipfile.lock
# Dockerfile
FROM public.ecr.aws/lambda/python:3.9
RUN pip install keras-image-helper
RUN pip install https://github.com/alexeygrigorev/tflite-aws-lambda/raw/main/tflite/tflite_runtime-2.7.0-cp39-cp39-linux_x86_64.whl
COPY xception_v4_36_0.929.tflite .
COPY lambda_function.py .
CMD ["lambda_function.lambda_handler"]docker build -t birds-classification-model .- terminal
docker run -it --rm -p 8080:8080 birds-classification-model:latest- create a new test file
# test.py
import requests
url = "http://localhost:8080/2015-03-31/functions/function/invocations"
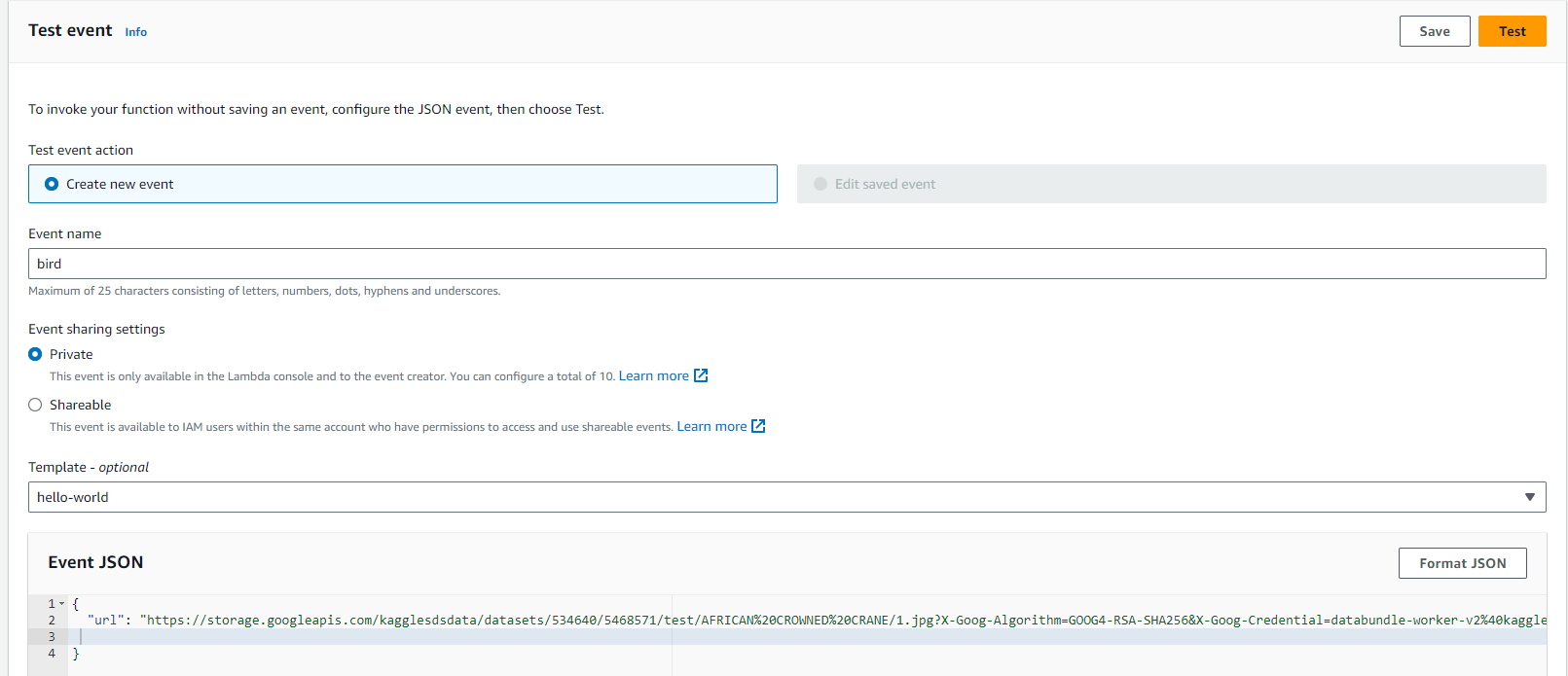
data = {"url": "https://storage.googleapis.com/kagglesdsdata/datasets/534640/5468571/test/AFRICAN%20CROWNED%20CRANE/1.jpg?X-Goog-Algorithm=GOOG4-RSA-SHA256&X-Goog-Credential=databundle-worker-v2%40kaggle-161607.iam.gserviceaccount.com%2F20231226%2Fauto%2Fstorage%2Fgoog4_request&X-Goog-Date=20231226T050028Z&X-Goog-Expires=345600&X-Goog-SignedHeaders=host&X-Goog-Signature=7a161e5f38cdca1a22757b9d75a41205257cb574919481a903f5ecaf8f2e4c083e9584767b0dc7b7c5e2a64e1b3f27d3aaea3e0cbbec38f0ea372f15635e21b85982bb29e8449e5acc676ec393f9a058e715219f4885e99c6e4feb08cb849bde7181b170b44c8584d246ae5f85833f5f2d9ee2048a5e475d535dad0dfef96ccfa42dff0a0ead93634da47f746cfd4d4e6ca74afde6a6f2f92ca1be88aa579d0e738bb3d8c25eb8fe765e775f12bc0fe84aaace72fd6756947238edec02271ba2c6f9fa3e237bfb66857fa380dd9bd8b74ea46bb41ec03e864467ab3fe5ad541512ec63f3786d672004f9618783df3dbf173b3266b1b9eca2b35b28829970f70b"}
result = requests.post(url, json=data).json()
print(result)- aws cli
# install awscli if you dont have it
pip install awscli
# create image
aws ecr create-repository --repository-name birds-classification-imagesReturn:
{
"repository": {
"repositoryArn": "arn:aws:ecr:us-east-2:610428526296:repository/birds-classification-images",
"registryId": "610428526296",
"repositoryName": "birds-classification-images",
"repositoryUri": "610428526296.dkr.ecr.us-east-2.amazonaws.com/birds-classification-images",
"createdAt": 1703568201.0,
"imageTagMutability": "MUTABLE",
"imageScanningConfiguration": {
"scanOnPush": false
},
"encryptionConfiguration": {
"encryptionType": "AES256"
}
}
}- login
aws ecr get-login --no-include-email | sed 's/[0-9a-zA-Z=]\{20,\}/PASSWORD/g'Return:
docker login -u AWS -p PASSWORD https://610428526296.dkr.ecr.us-east-2.amazonaws.com- execute login
$(aws ecr get-login --no-include-email)Return:
Login Succeeded
# copy below to terminal
ACCOUNT=610428526296
REGION=us-east-2
REGISTRY=birds-classification-images
PREFIX=${ACCOUNT}.dkr.ecr.${REGION}.amazonaws.com/${REGISTRY}
TAG=birds-classification-model-xception-v4-001
REMOTE_URI=${PREFIX}:${TAG}- run the image
docker run -it --rm birds-classification-model:latest- Stop ctrl+c
- tag
docker tag birds-classification-model:latest ${REMOTE_URI}- push to ecr
docker push ${REMOTE_URI}-
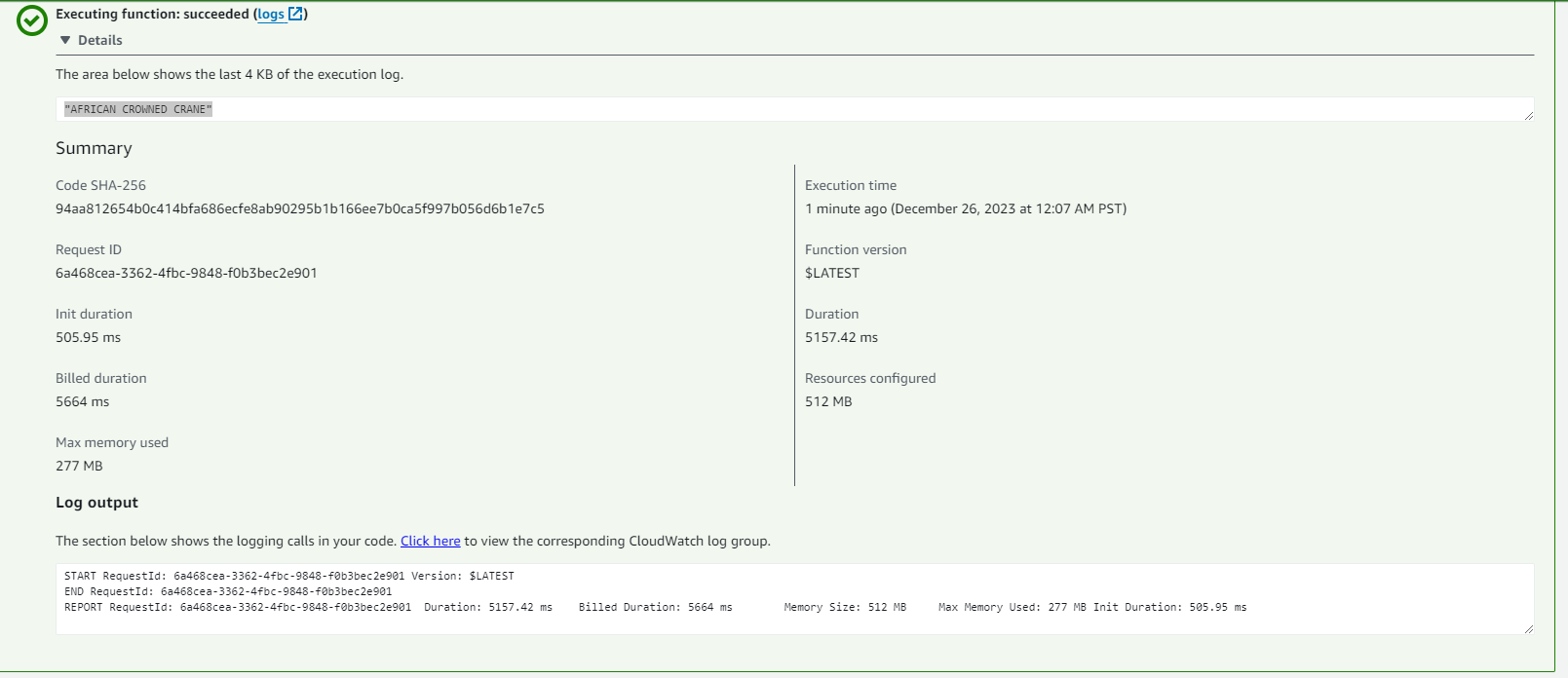
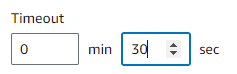
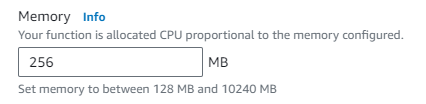
timeout error "errorMessage": "2023-12-26T06:08:51.451Z 0ef69c65-21d9-437b-89d8-50c8c3c04f23 Task timed out after 3.08 seconds"
-
to fix the error -> configuration -> general config-> timeout/memory timeout: 2min 30 seconds memory: 512MB
- create a POST resource with the Lambda function as the trigger
- test
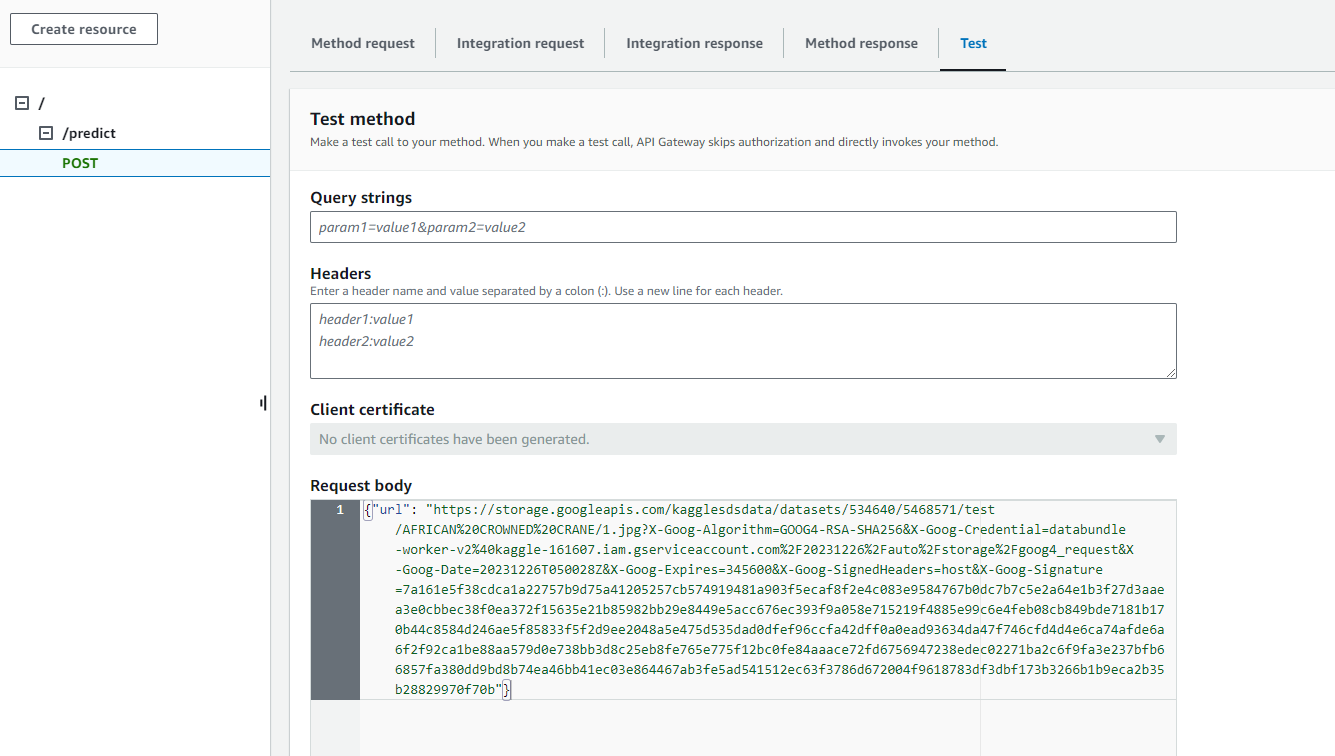
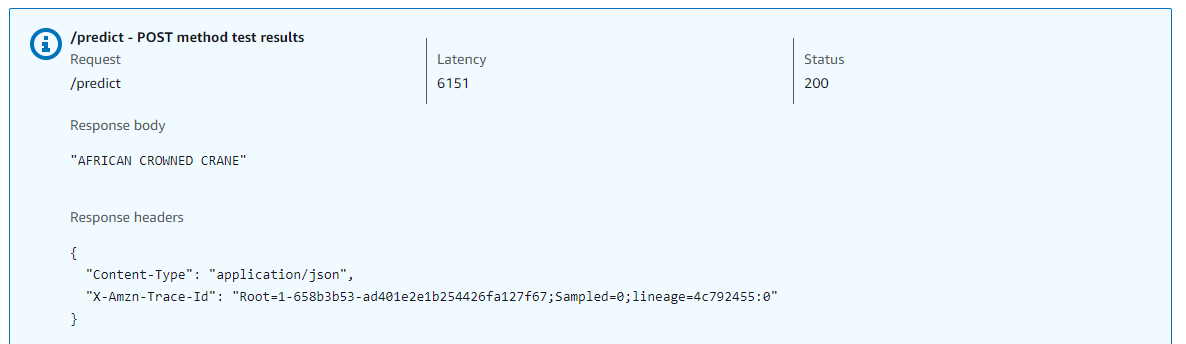
- deploy
- new stage -> name a new stage (eg: beta or test) -> deploy
- Dashboard -> URL
- update your test.py with the new url+predict
- run the test again
python3 test.py - return the result
- to hide your endpoint
- create
.envfile -> write your AWS_LAMBDA_URL="https://......../predict" - in
test.pyfile
from dotenv import load_dotenv import os
- create
l oad_dotenv() url = os.getenv("AWS_LAMBDA_URL") ```
pip install streamlitinstall streamlit- import other packages in app.py
- write a tile
st.write - create a title, header
st.title,st.header - upload file
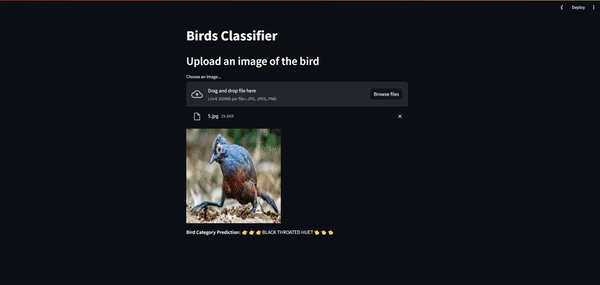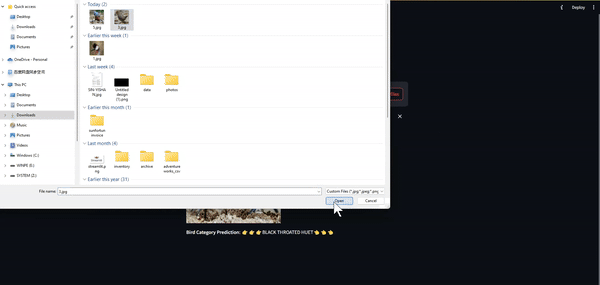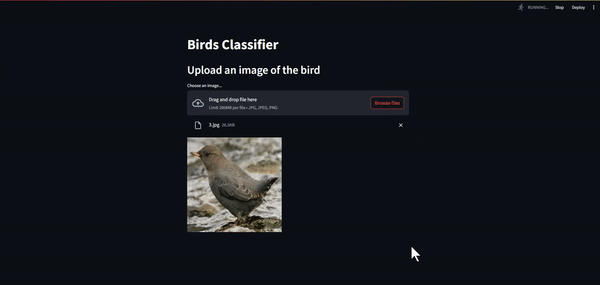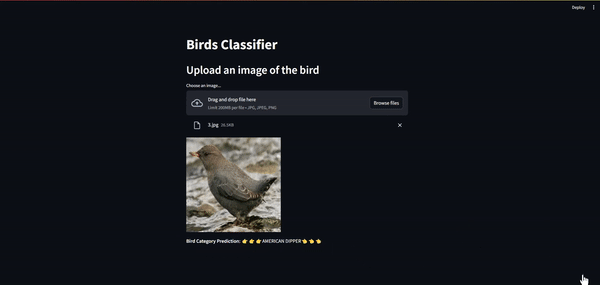
st.file_uploader - display the image
image = Image.open(uploaded_file).convert('RGB') st.image(image, use_column_width=True)
- upload the image to a cloud storage (eg: aws s3)
s3 = boto3.client('s3') with open("temp.jpg", "rb") as data: s3.upload_fileobj(data, 'birds-classification', 'myimage.jpg')
- call the Lambda function and show the result
- run
streamlit run app.pyto start the server - register an account in streamlit
- push your code in github
- click "Deploy" button when viewing your app at the up-right corner
- confirm your github folder, you main app name, for example app.py
- if you have credentail errors, go to setting to add all your secrets
AWS_LAMBDA_URL="your_url" S3_BUCKET_URL="your_bucket_url" AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID = "key" AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY = "secret_key" AWS_REGION = "region"
- Congrats! Your app is live 🎊 Birds Clissifier