mirrord lets developers run local processes in the context of their cloud environment. It’s meant to provide the benefits of running your service on a cloud environment (e.g. staging) without actually going through the hassle of deploying it there, and without disrupting the environment by deploying untested code. It comes as a Visual Studio Code extension, an IntelliJ plugin and a CLI tool. You can read more about it here.
mirrord uses your machine's default kubeconfig for access to the Kubernetes API.
Get the extension here.
- Click "Enable mirrord" on the status bar
- Start debugging your project
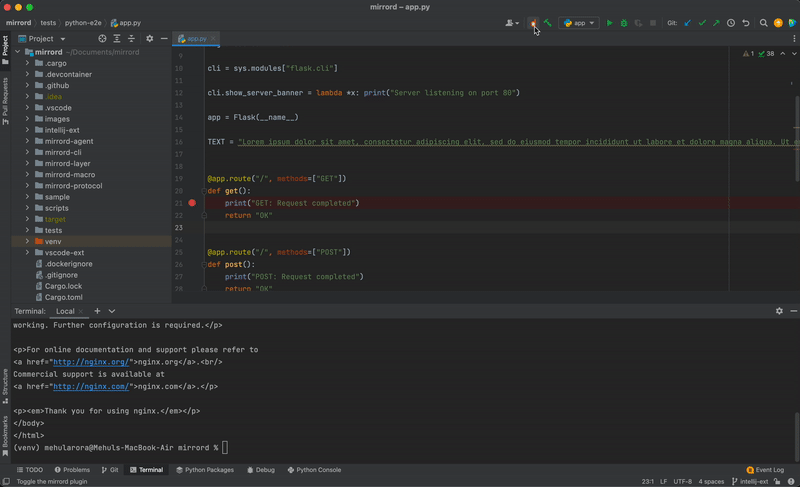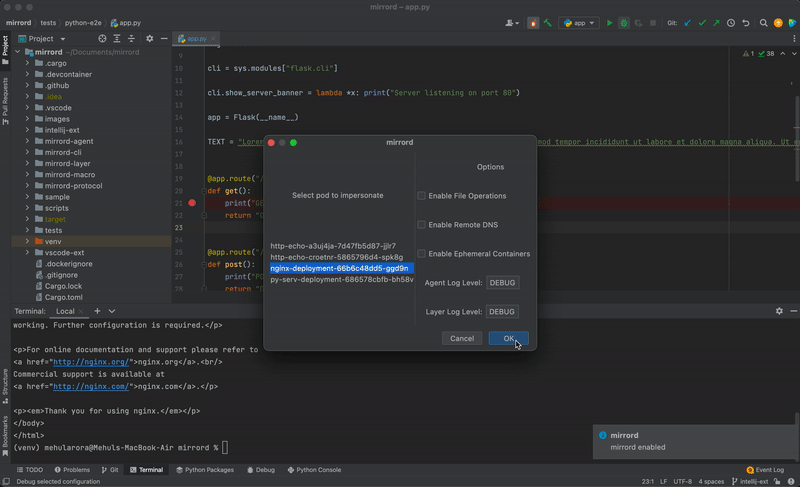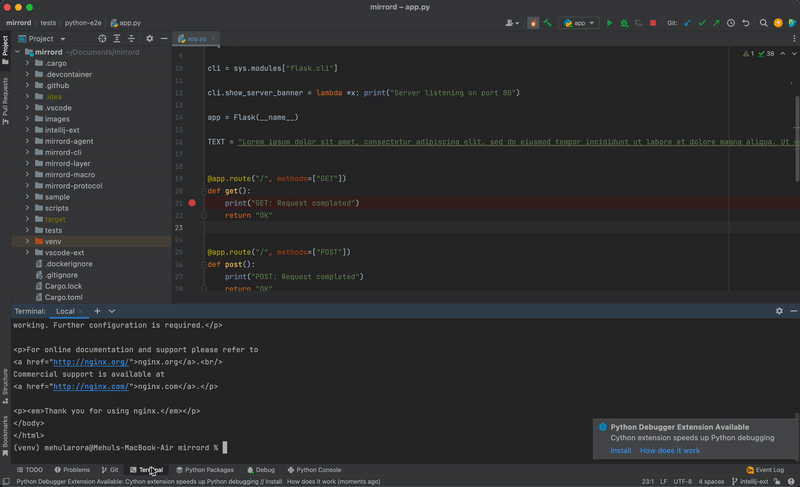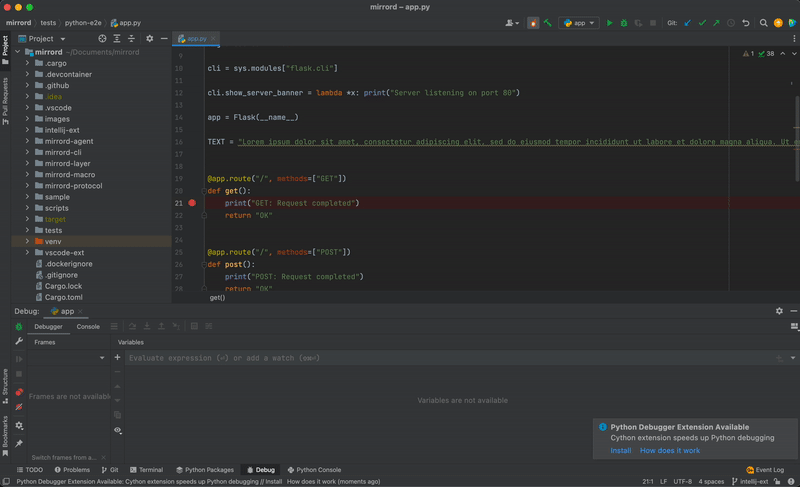
- Choose pod to mirror traffic from
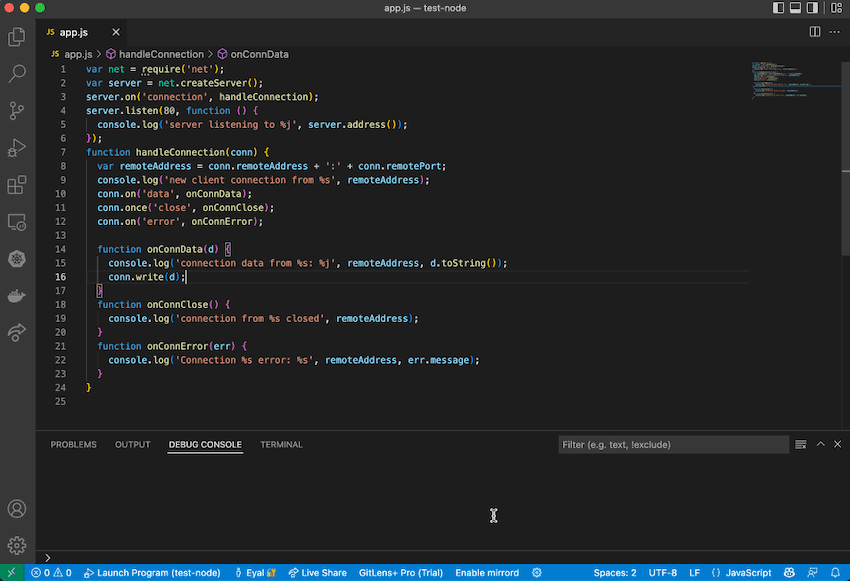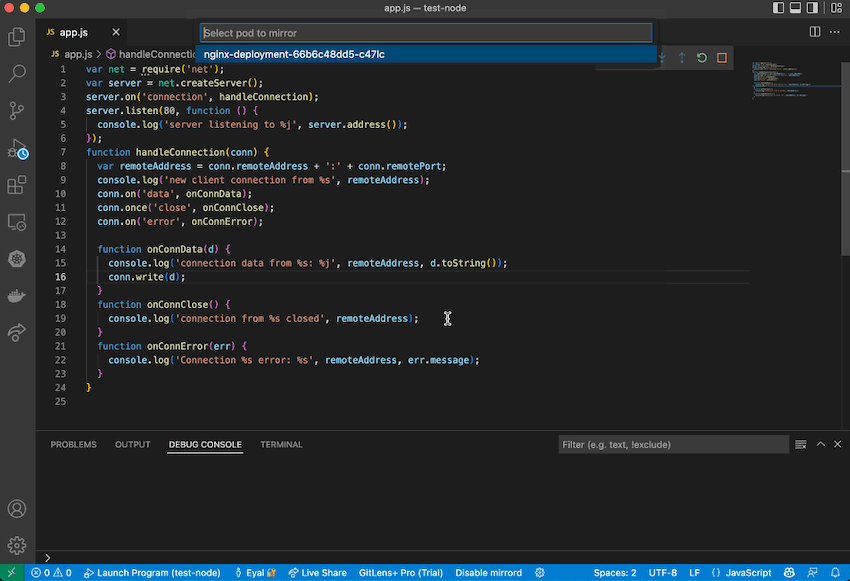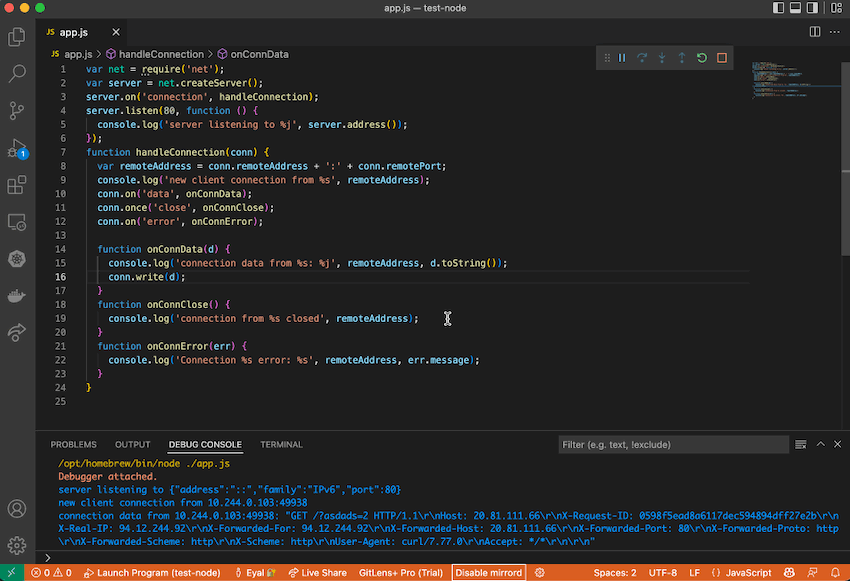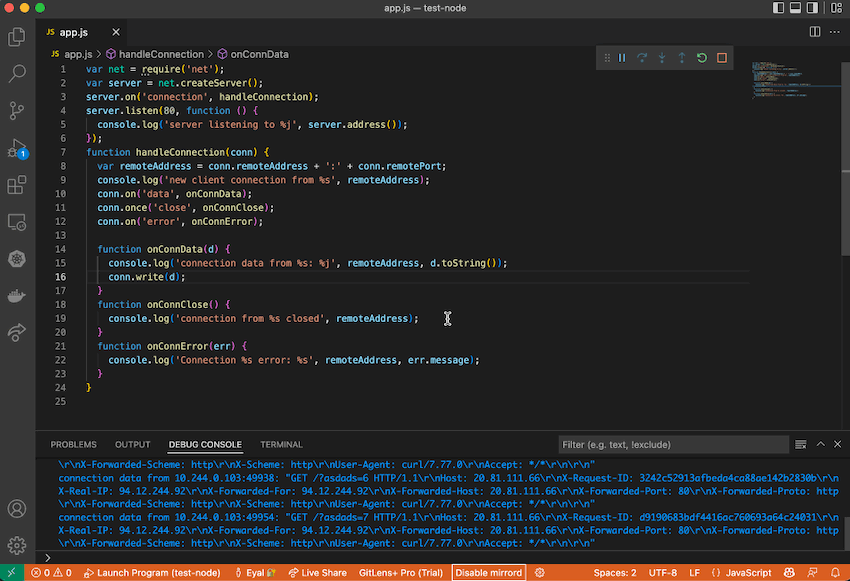
- The debugged process will be plugged into the selected pod by mirrord
Get the plugin here.
- Click the mirrord icon in the Navigation Toolbar
- Start debugging your project
- Choose a namespace and pod to impersonate
- The debugged process will be plugged into the selected pod by mirrord
curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/metalbear-co/mirrord/main/scripts/install.sh | bash- Windows isn't currently supported (you can use WSL)
mirrord exec <process command> --pod-name <name of the pod to impersonate>e.g.
mirrord exec node app.js --pod-name my-podWhen you select a pod to impersonate, mirrord launches a privileged pod on the same node as the pod you selected. The new pod is then used to connect your local process and the impersonated pod: it mirrors incoming traffic from the pod to your process, routes outgoing traffic from your process through the pod, and does the same for file reads, file writes, and environment variables. You can read more about it here.
Contributions are much welcome. Start by checking out issues. If you wish to work an issue, please comment so you can be assigned.
Read our development guide here.
Join our Discord Server for questions, support and fun.
We take our community seriously and we are dedicated to providing a safe and welcoming environment for everyone. Please take a few minutes to review our Code of Conduct.