Tao Tang · Longfei Gao · Guangrun Wang · Yixing Lao · Peng Chen · Hengshuang Zhao · Dayang Hao · Xiaodan Liang* · Mathieu Salzmann · Kaicheng Yu
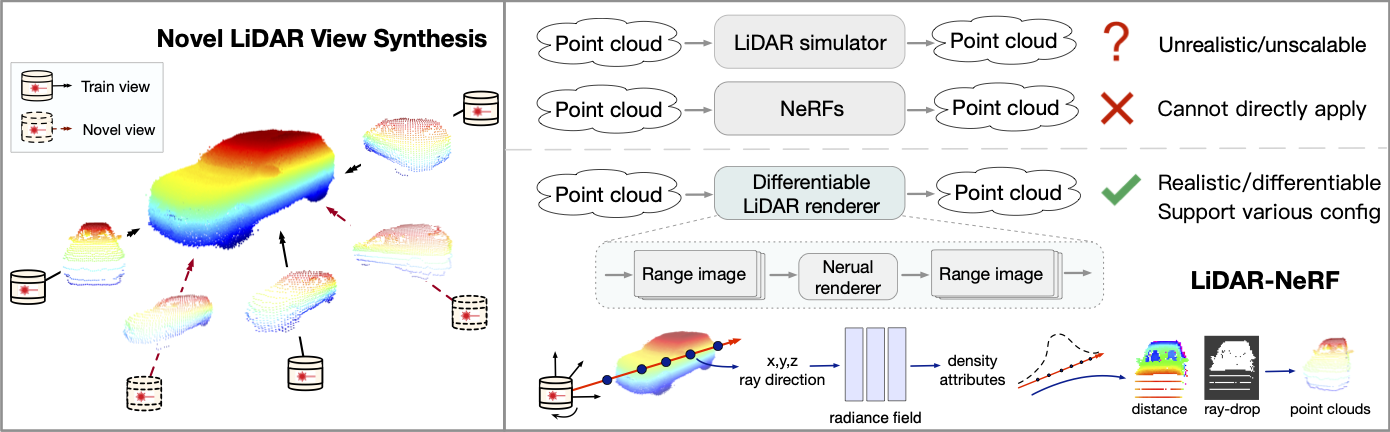
This paper introduces a new task of novel LiDAR view synthesis and proposes a differentiable framework called LiDAR-NeRF with a structural regularization, as well as an object-centric multi-view LiDAR dataset called NeRF-MVL.
- We formulate the first differentiable framework, LiDAR-NeRF, for novel LiDAR view synthesis, which can render novel point clouds with point intensity and ray-drop probability without explicit 3D reconstruction.
- We propose a structural regularization method to effectively preserve local structural details, thereby guiding the model towards more precise geometry estimations, leading to more faithful novel LiDAR view synthesis.
- We establish the NeRF-MVL dataset from LiDAR sensors of real autonomous vehicles to evaluate the object-centric novel LiDAR view synthesis.
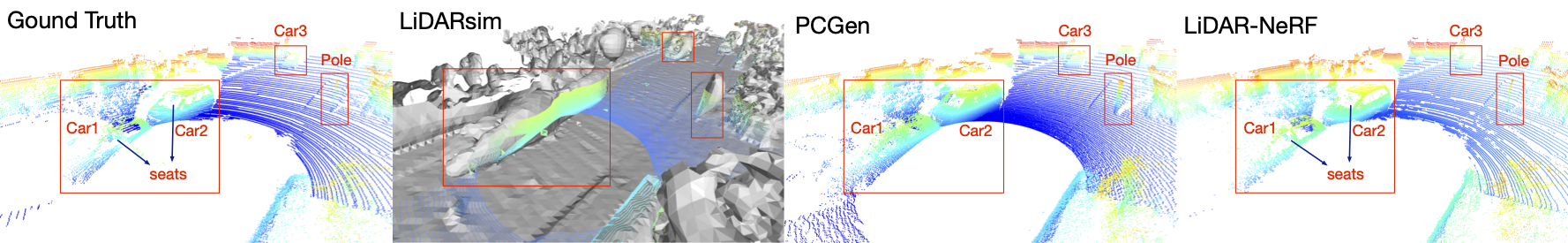
- We demonstrate the effectiveness of our LiDAR-NeRF quantitatively and qualitatively in both scene-level and object-level novel LiDAR view synthesis.
- [2023/07/14] LiDAR-NeRF v0.1.0 released. NeRF-MVL dataset released.
conda create -n lidarnerf python=3.9
conda activate lidarnerf
# Dependencies
pip install -r requirements_torch.txt
pip install -r requirements.txt
# tiny-cuda-nn
# This may take a while, please refer to the official documentation
pip install git+https://github.com/NVlabs/tiny-cuda-nn/#subdirectory=bindings/torch
# camtools
pip install git+https://github.com/yxlao/camtools.git
# Install lidar-nerf
pip install -e .
python -c "import lidarnerf; print(lidarnerf.__version__)"First, download KITTI-360 dataset from
here and put the dataset
into data/kitti360. Your folder structure should look like this:
data
└── kitti360
└── KITTI-360
├── calibration
├── data_2d_raw
├── data_3d_raw
└── data_posesNext, run KITTI-360 dataset preprocessing:
# Generate train range images
python preprocess/generate_train_rangeview.py --dataset kitti360
# Generate jsons
python preprocess/kitti360_to_nerf.py
# Calculate center pose (optional) can directly use our config
python preprocess/cal_centerpose_bound.pyAfter preprocessing, your folder structure should look like this:
data
└── kitti360
├── train
├── KITTI-360
│ ├── calibration
│ ├── data_2d_raw
│ ├── data_3d_raw
│ └── data_poses
├── transforms_{sequence_id}test.json
├── transforms_{sequence_id}train.json
└── transforms_{sequence_id}val.jsonFirst, download our NeRF-MVL dataset from here. Your folder structure should look like this:
$ tree data -l -L 2
data
└── nerf_mvl
└── nerf_mvl_7k
└── {class_name}
├── {frame_id}.npy
└── lidar2world.txtNext, run NeRF-MVL dataset preprocessing:
# If you only download raw nerf_mvl_7k, you need convert it to nerf_mvl_7k_pano(optional)
# or directly download our processed dataset in https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1pwnIjBUMIYg0fmLaeLj-sKfVcnBexlMq?usp=sharing
# Generate train range images
python preprocess/generate_train_rangeview.py --dataset nerf_mvl
# Generate jsons
python preprocess/nerfmvl_to_nerf.pyAfter preprocessing, your folder structure should look like this:
data
└── nerf_mvl
├── dataset_bbox_7k.npy
├── nerf_mvl_7k
│ └── {class_name}
│ ├── {frame_id}.npy
│ └── lidar2world.txt
├── nerf_mvl_7k_pano
│ └── {class_name}
│ ├── {frame_id}.npy
│ └── lidar2world.txt
├── transforms_{class_name}_test.json
├── transforms_{class_name}_train.json
└── transforms_{class_name}_val.json# kitti360
python main_lidarnerf.py -L --workspace log/kitti360_lidar
# nerf_mvl
python main_lidarnerf.py --config configs/nerf_mvl.txt -L --workspace log/trial_nerf_nerf_mvlYou can download our pre-trained models here.
- Support multi-modality, e.g., RGB & LiDAR
- Support more datasets, e.g, nuScenes, Waymo
- Support more implicit geometry representation, e.g., SDF
We welcome all forms of community contributions, including issues, bug fixes, new features, and more. Please format the code before submitting a pull request.
If you find our code or paper helps, please consider citing:
@article{tao2023lidar,
title = {LiDAR-NeRF: Novel LiDAR View Synthesis via Neural Radiance Fields},
author = {Tao, Tang and Gao, Longfei and Wang, Guangrun and Lao, Yixing and Chen, Peng and Zhao hengshuang and Hao, Dayang and Liang, Xiaodan and Salzmann, Mathieu and Yu, Kaicheng},
journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.10406},
year = {2023}
}This code is built on top of the super-useful torch-ngp implementation.
@misc{torch-ngp,
author = {Jiaxiang Tang},
year = {2022},
note = {https://github.com/ashawkey/torch-ngp},
title = {Torch-ngp: a PyTorch implementation of instant-ngp}
}The raydrop-mlp code for PCGen is borrowed from nerf-pytorch.
@misc{lin2020nerfpytorch,
title = {NeRF-pytorch},
author = {Yen-Chen, Lin},
publisher = {GitHub},
journal = {GitHub repository},
howpublished = {\url{https://github.com/yenchenlin/nerf-pytorch/}},
year = {2020}
}