Note This is a lightly edited fork of the original repo.
Welcome to RobotSearch, software for filtering RCTs from a search result as described in our paper in the Journal of Research Synthesis Methods.
We offer RobotSearch free of charge, but we'd be most grateful if you would cite us if you use it. We're academics, and thrive on links and citations! Getting RobotSearch widely used and cited helps us obtain the funding to maintain the project and make RobotSearch better.
It also makes your methods transparent to your readers, and not least we'd love to see where RobotSearch is used! :)
- To use the docker image you'll need to install Docker
- Pull the repo onto your machine, using whatever method you like for this.
cdyour way into the cloned repo.- Build the docker image with
docker build -t robotsearch .. Expect this to take a couple of minutes. - Run the app with
./start.sh. You don't need to run the docker image -./start.shwill take care of this. - Navigate to http://localhost:5050 in your browser to use the app.
- When finished, use
docker stop robotsearchto stop the container.
- To use as a Python package you will need an install of conda. Miniconda is a good choice.
- Pull the repo onto your machine, using whatever method you like for this.
cdyour way into the cloned repo.- Run
conda env create -f tmp/rs_env.ymlto create the environment with the required packages. - Activate the conda environment
conda activate robotsearch. - Run
python setup.py install. - You should now be able to run
robotsearch path_to_risto convert files, or import as a module.
RobotSearch uses machine learning as an alternative to string-based study design filters.
It works with MEDLINE searches exported from either PubMed or Ovid.
- You should conduct your search as normal (NB do not use any search terms or filters to restrict to RCTs at this stage!).
- Then export your results in RIS format (see more detailed instrutions below on how to do this in PubMed and Ovid)
- From the Command Prompt/Terminal, run the robotsearch command:
robotsearch my_file.ris - Your search results will be saved as
my_file_robotreviewer_RCTs.ris
By default, RobotSearch runs a sensitive search (i.e. very high likelihood that all RCTs will be retrieved, at expense of sometimes including non-RCTs) - this is suitable for a systematic review.
To run a precise search (i.e. the retrieved articles have a very high likelihood of being RCTs, but at the expense of missing a tiny proportion), run with an extra -p flag, e.g.:
robotsearch my_file.ris -p
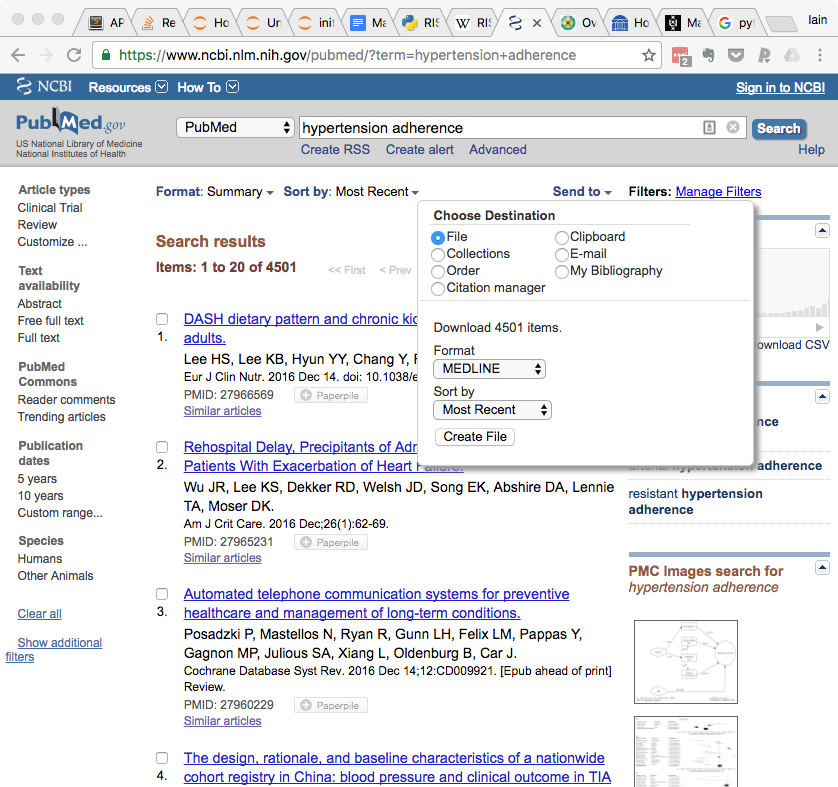
- Select 'Send to' (located in the upper left of the search results)
- Under 'Choose Destination' select File
- Under 'Format', select 'MEDLINE' from the pulldown menu
- Click the 'Create File' button
 (Endnote format includes the 'publication type' field, the RIS format does not)
(Endnote format includes the 'publication type' field, the RIS format does not)
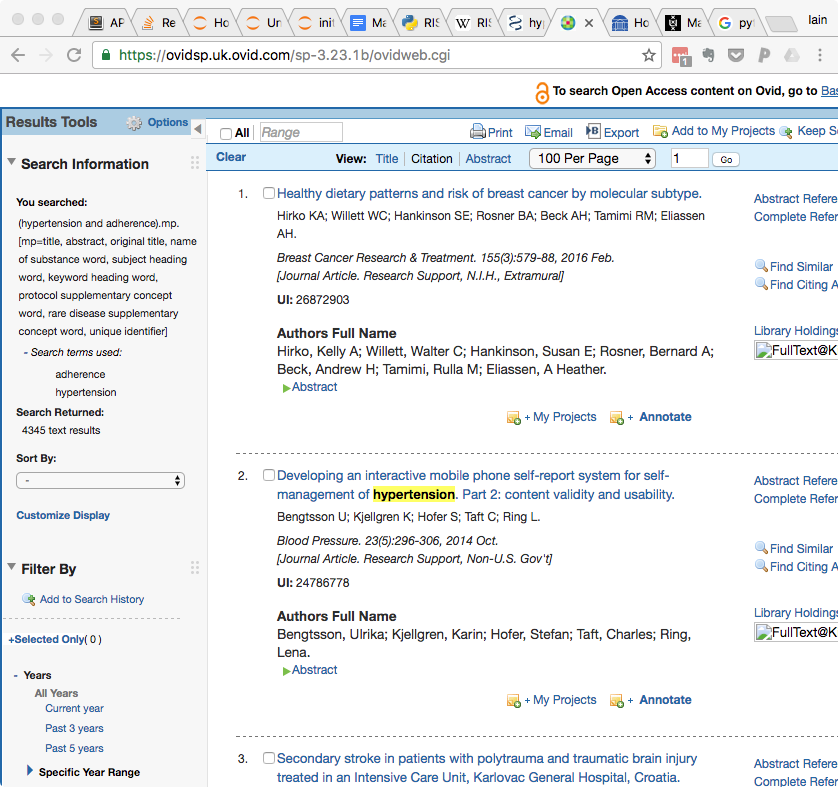
- Click the tickbox next to 'All' above the search results on the left hand side.
- Click on Export
- In the 'Export to' pulldown menu, select 'RIS'
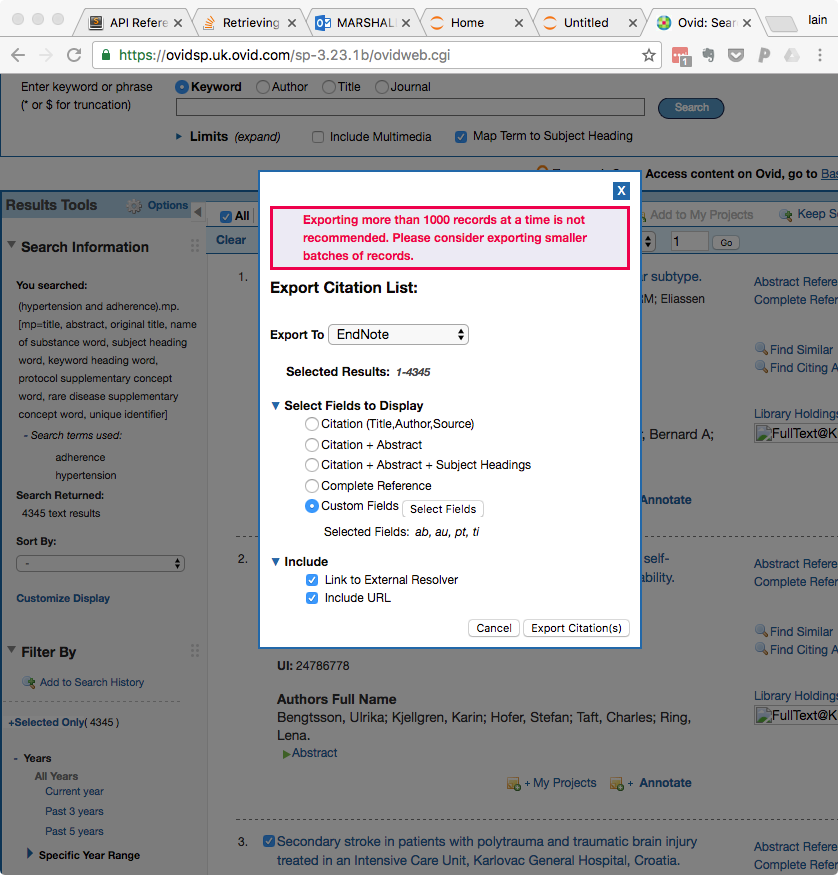
- Under 'Select Fields to Display' select 'Custom Fields', then click the 'Select Fields' button
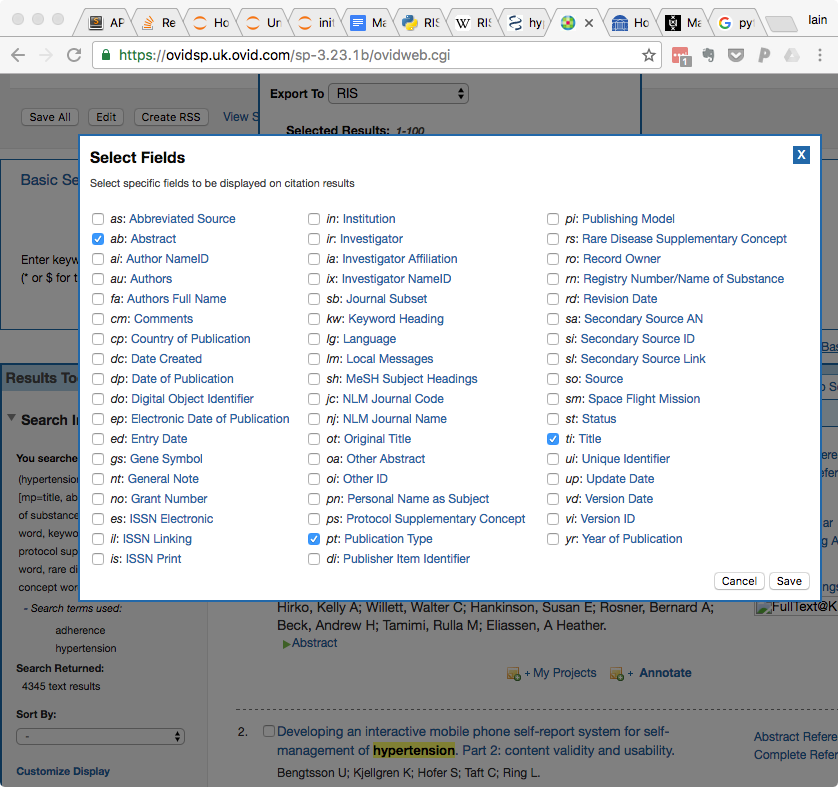
- In the Select Fields box, select the following fields: ab: Abstract, pt: Publication Type, and ti: Title. You may deselect any others.
- Click 'Save' in the bottom left
- Click 'Export Citation(s)' in the bottom right
- The citations will be exported, but there may be a wait of a minute or two.
RobotSearch has a optional test mode, which runs through a standardised search result, and double checks that the software is returning the same results as in the validation study. NB this takes around 5--10 minutes to run, depending on the speed of your machine.
To run this, type:
robotsearch -t
We would love software developers, and people who make biblographic databases to integrate this method into their systems. All the software is open source under the GNU GPL v3. Please contact us (mail@ijmarshall.com) to discuss further.
We also welcome contributions from the community; please contact us (or submit an issue via Github) if you are interested in improving the software.
RobotSearch may be called as a Python module, from within the root directory. See the example IPython notebook for how to do this.
This work is dependent on the work of the Cochrane Crowd, for whom we'd like to express enormous gratitude for their work, and in making their data available for training our machine learning models.
This work is supported by: National Institutes of Health (NIH) under the National Library of Medicine, grant R01-LM012086-01A1, "Semi-Automating Data Extraction for Systematic Reviews", and by NIH grant 5UH2CA203711-02, "Crowdsourcing Mark-up of the Medical Literature to Support Evidence-Based Medicine and Develop Automated Annotation Capabilities", and the UK Medical Research Council (MRC), through its Skills Development Fellowship program, grant MR/N015185/1
If you use RobotSearch, we'd love it if you could cite our paper, and also let us know! (you can email mail@ijmarshall.com)