mysqldump_to_AWS_S3
MySQL Database Backup Script This script is used to backup a MySQL database and upload the backup file to an AWS S3 bucket. The backup file is compressed using gzip before uploading it to S3. The script also cleans up temporary files after the backup is complete.
Prerequisites
- MySQL server is installed.
- AWS CLI is installed and configured with appropriate credentials.
- The mysqldump tool is available at /opt/bitnami/mysql/bin/mysqldump.
- The necessary permissions are granted to execute the script.
Script Option
There is two option for backup it's single & multi database backup the different is:
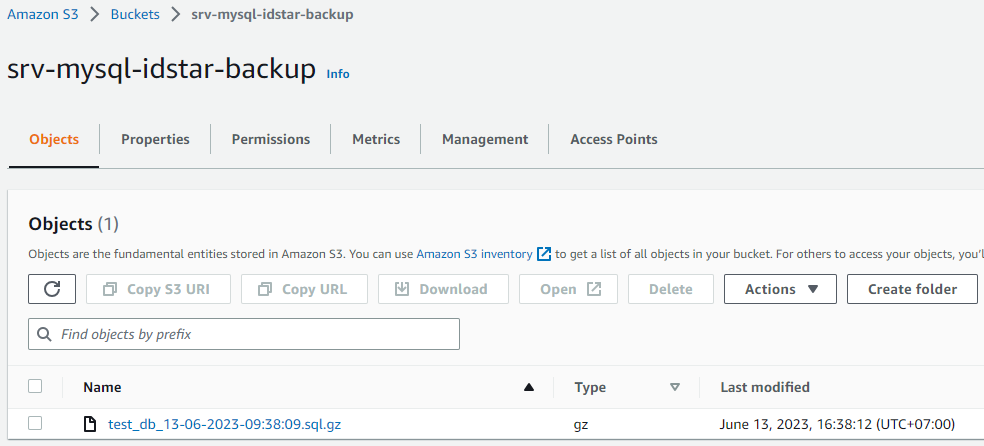
A.) Using single_mysqldump_to_aws_s3.sh if you want to backup single database, the result will look like this:
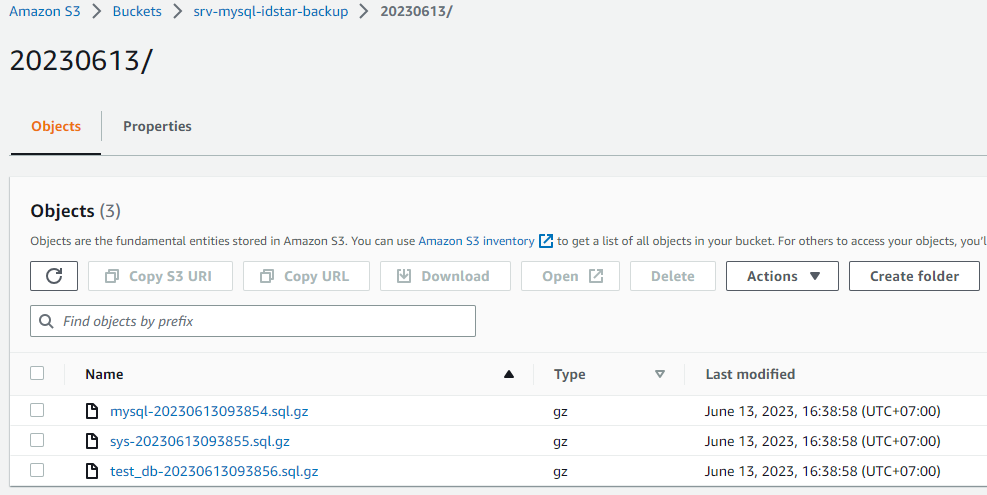
B.) Using multi_mysqldump_to_aws_s3.sh if you want to backup all database in server and it will separate by current date folder name the result will look like this:
Usage
- Install and configure AWS CLI reference and make sure your IAM Policy look like this:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "VisualEditor0",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "s3:*",
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:s3:::example-backup",
"arn:aws:s3:::example-backup/*",
]
}
]
}
Make sure you replace example-backup with your bucket name
- Set the following variables in the script according to your environment:
DB_USER: The username to access the MySQL database.
DB_PASS: The password for the MySQL database user.
DB_NAME: The name of the database to be backed up.
S3_BUCKET_NAME: The name of the AWS S3 bucket to upload the backup.
S3_BUCKET_PATH: The path within the S3 bucket where the backup will be stored.
BACKUP_DIR: The directory path where temporary backup files will be stored.
- Run the script:
$ bash backup_script.sh
- The script will generate a backup file named
{DB_NAME}_{TIME}.sql.gzin the specified BACKUP_DIR. - The backup file will be uploaded to the specified S3 bucket and path using the AWS CLI.
- Temporary backup files will be cleaned up from the BACKUP_DIR.
Notes
The script uses a credential file (mysql-credentials.cnf) to provide secure access to the MySQL database. The file is generated automatically by the script and removed after the backup is completed.
- Ensure that the script has execution permissions (chmod +x backup_script.sh) before running it.
- Make sure the AWS CLI is properly configured with the necessary credentials and permissions to access the specified S3 bucket.
- Adjust the location of mysqldump in the MYSQLDUMP variable if it is installed in a different path.
- Adjust the backup file compression method (gzip in this case) if needed.
- It's recommended to schedule regular backups using a cron job or a similar mechanism, For example, to run the backup script every day at 2:00 UTC TIME, add the following line:
Run cronjob without logging
0 2 * * * /bin/bash /path/to/backup_script.sh >/dev/null 2>&1
Run cronjob with logging
0 2 * * * /bin/bash /path/to/backup_script.sh >/path/to/backup.log 2>&1
Example
Here's an example configuration:
DB_USER="root"
DB_PASS="LKkAitdxhsj7"
DB_NAME="bitnami_example"
S3_BUCKET_NAME="example-backup"
S3_BUCKET_PATH="s3://example-backup/mysqldump/"
BACKUP_DIR="/tmp/mysqldump"
When the script is executed, it will create a backup file named bitnami_example_{timestamp}.sql.gz in the /tmp/mysqldump directory. The file will be uploaded to the example-backup S3 bucket under the mysqldump/ path.
After the backup is complete, the temporary files in /tmp/mysqldump will be deleted.
The backup file will be available at s3://example-backup/mysqldump/bitnami_example_{timestamp}.sql.gz.