DVR and a fastest path algorithm implemented using Go channels. Created by Taylor Flatt and Arjun Yelamanchili
- Get the source code by running
git clone github.com/taylorflatt/remote-shell - Inside the directory, there is the routing (network map) file. Populate this with any assortment of network configurations. See below for more detailed instructions.
- Run the program by typing
go run main.go. - Then input which router you would like to watch to see the table change after each exchange.
- Finally, if you would like to compute the fastest path between any two routers, enter those into the source and destination.
- To exit, hit
ctrl+c.
A sample network map is included. The format goes as follows:
TABLE DESTINATION COST
The following is required:
- Each router is mentioned at least once as
TABLE. - Each path is mentioned at least once.
For instance, if I want to add a few paths to router A's table, I could add the following to routers.txt:
A B 5
A C 2
A D 6
A E 15
Will produce:
Router A's Initial Table
Desintation Next Cost
A A 0
B B 5
C C 2
D D 6
E E 15
This would create a network map in which A is connected to B, C, D, and E. You can add any other routers that you wish as well.
(Source: BYU.edu)
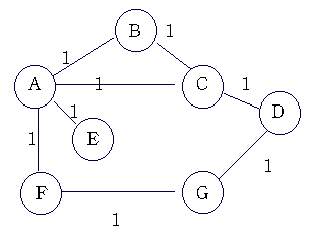
The routers.txt file would look like:
A B 1
A C 1
A E 1
A F 1
B C 1
C D 1
D G 1
F G 1
E A 1
All of the routers (A,B,C,D,E,F,G) are mentioned at least once for TABLE. Also note that E has only a route to A. I could exclude A's mention of E (A E 1) and simply use (E A 1) to define both the router E and the path from A to E. So the 3rd line is not necessary.