By Youjia Zhou, Kevin Knudson and Bei Wang.
This is a demo that implements algorithms for discrete stratification Morse theory (DSMT).
The main features of our system:
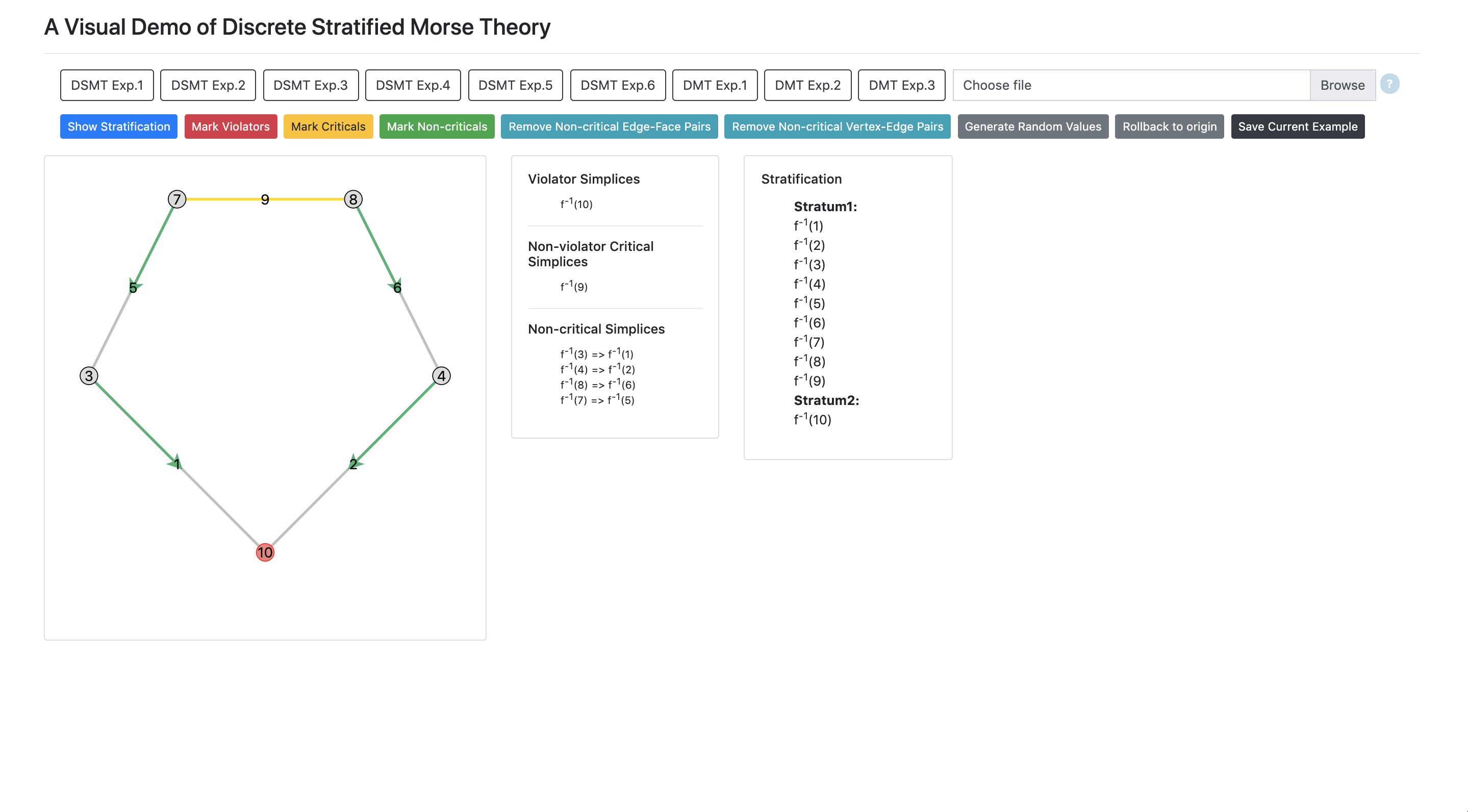
- Given a 2-dimensional simplicial complex, construct the discrete stratified Morse function and demonstrate the stratification.
- Mark violators/ criticals/ non-critical pairs.
- Perform simplification by removing non-critical pairs.
For theoretical and algorithmic details on DSMT, please refer to:
Discrete Stratified Morse Theory: Algorithms and A User's Guide. Kevin Knudson, Bei Wang. ArXiv:1801.03183, 2019.
https://arxiv.org/abs/1801.03183
An earlier version appears as an extended abstract:
Discrete Stratified Morse Theory: A User's Guide. Kevin Knudson and Bei Wang. International Symposium on Computational Geometry (SOCG), 2018.
Please download the media portfolio (video + software) for SOCG 2020 Media Exposition here.
Please view the complete user manual here.
git clone git@github.com:tdavislab/VIS-DSMT.gitcd VIS-DSMT
python3 run.py
# Hit Ctrl+c to quitYou can view the page at http://0.0.0.0:8000/.
Users can import a new example with specific data format.
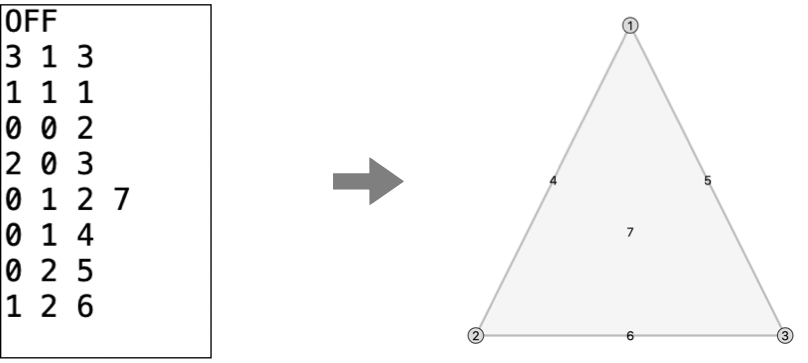
The input file should be a TXT file of the following format.
-
The second line specifies the number of vertices, faces and edges.
-
Starting from the third line, each line specifies the position and function value of a simplex. The order is to specify vertices first,then faces, and then edges.
-
For vertices, the position is represented as its x and y coordinates.For edges, the position is represented as the indices of the vertices on its two ends. For faces,the position is represented as the indices of the vertices on its boundary. For example, if a face is a triangle, the line specifying it will have the form of “u, v, w, f”, where u, v, w are the indices of its three vertices, and f is the function value of it.
-
The imported example is expected to be some planar geometric 2-dimensional simplicial complex (e.g., a planar triangulation).
Our system is web-based and can be accessed from any modern web-browser (tested using Google Chrome).
The tool is implemented in HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. The algorithm is implemented in pure JavaScript, and the module collection D3.js is used for redenring SVGs and providing interactive visualization.
This work was supported in part by the National Science Foundation (NSF) grants IIS-1513616 and DBI-1661375.
We thank Yulong Liang who worked on the first prototype of the visualization.