- Lightweight, python only, logstash alternative
- Exports systemd journald logs to an external service, eg cloudwatch, elasticsearch
- Use with a cron job
- Python 3.4+
# Fedora/RHEL/CentOS
$ dnf install python-systemd python3-systemd
OR
# Debian/Ubuntu/Mint
$ apt-get install python-systemd python3-systemd
$ pip install systemdlogger
$ systemdlogger -h
usage: systemdlogger [-h] config
Exports systemd logs to different storage backends, eg
cloudwatch/elasticsearch.
positional arguments:
config path to config file
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exitSee example config files below.
$ systemdlogger config.json
*/1 * * * * . /etc/webserver.env; export ENV=$NODE_ENV; /usr/local/bin/systemdlogger /path/to/config.json >/etc/logs/systemdlogger.log 2>&1
Full example config that includes extra optional properties.
{
"systemd": {
"unit": "webserver"
},
"backends": {
"cloudwatch": {
"log_group_name": "log_group_name",
"log_stream_name": "log_stream_name"
}
}
}If the elasticsearch endpoint does not use port 9200 you need to explicitly state it as shown below:
{
"systemd": {
"unit": "webserver"
},
"backends": {
"elasticsearch": {
"doctype": "webserver",
"hosts": ["search-applogs-blahiy7jyhmqwerfnrfg9trdz4.eu-west-1.es.amazonaws.com:80"]
}
}
}Environment variables will be interpolated when the config is loaded.
$ ENV=uat FOO=bar systemdlogger config.json
// config.json
{
"systemd": {
"unit": "webserver"
},
"backends": {
"cloudwatch": {
"log_group_name": "$ENV-myapp",
"log_stream_name": "$FOO-myservice"
}
}
}Is loaded as:
...
"cloudwatch": {
"log_group_name": "uat-myapp",
"log_stream_name": "bar-myservice"
}Appends EC2 instance id to logstream name, eg:
Log Groups > webapp-uat > webapp-i-06e2a5d847e0d532f
Creates daily indexes for logs in logs-YYYY-MM-DD format, eg:
logs-16-08-25
logs-16-08-26
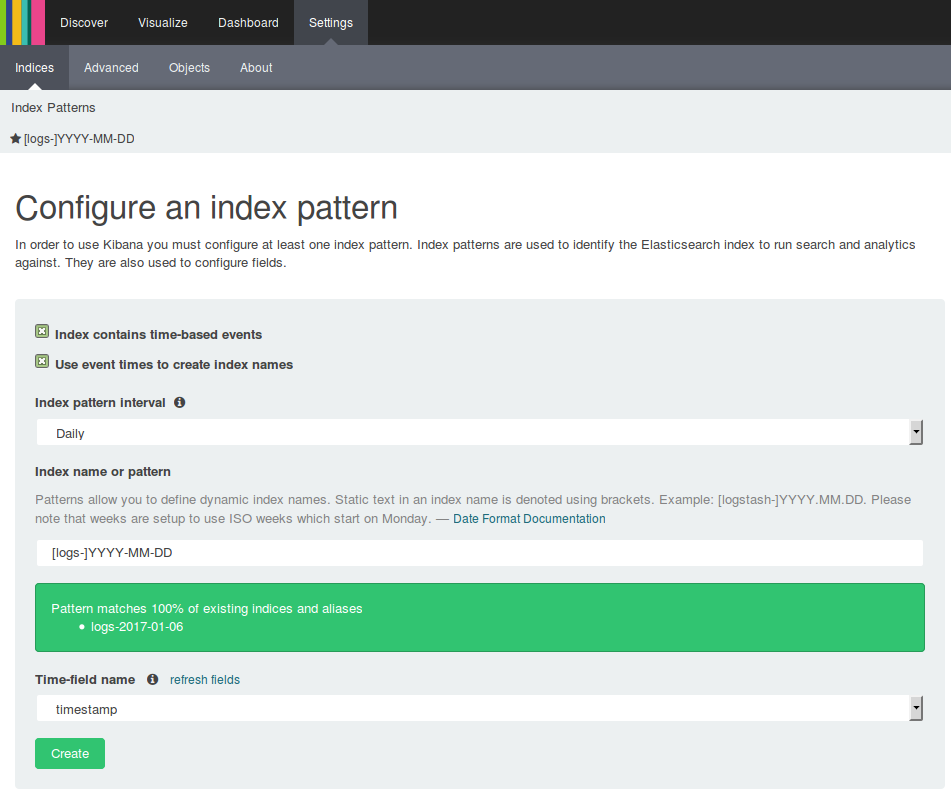
Configure Kibana index pattern:
- Go to Kibana index settings URL eg,
http://<your_elasticsearch_domain>/_plugin/kibana/#/settings/indices/?_g=() - Select both checkboxes.
- Set
Index pattern intervaltoDaily - Enter
[logs-]YYYY-MM-DDfor the index name - Select
timestampfor the timestamp field - Click on
Create
$ make setup
$ source env/bin/activate
$ make deps
$ pip install -r requirements.txt
$ make test
Run against elasticsearch docker container.
$ docker-compose up -d
$ make test-integration