Base R ships with a lot of functionality useful for time series, in particular in the stats package. However, these features are not adapted to most archaeological time series. These are indeed defined for a given calendar era, they can involve dates very far in the past and the sampling of the observation time is (in most cases) not constant.
aion provides a system of classes and methods to represent and work with such time-series (and time intervals). Dates are represented as rata die (Reingold and Dershowitz 2018), i.e. the number of days since 01-01-01 (Gregorian), with negative values for earlier dates. This allows to represent dates independently of any calendar: it makes calculations and comparisons easier.
Once a time series is created with aion, any calendar can be used
for printing or plotting data (defaults to Gregorian Common Era; see
vignette("aion")).
aion does not provide tools for temporal modeling. Instead, it offers a simple API that can be used by other specialized packages (see kairos or ananke).
To cite aion in publications use:
Frerebeau N (2024). “aion: An R Package to Represent Archaeological Time Series.” Journal of Open Source Software, 9(96). doi:10.21105/joss.06210 https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.06210.
Frerebeau N, Roe J (2024). aion: Archaeological Time Series. Université Bordeaux Montaigne, Pessac, France. doi:10.5281/zenodo.8032278 https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8032278, R package version 1.2.0, https://packages.tesselle.org/aion/.
This package is a part of the tesselle project https://www.tesselle.org.
You can install the released version of aion from CRAN with:
install.packages("aion")And the development version from GitHub with:
# install.packages("remotes")
remotes::install_github("tesselle/aion")## Load package
library(aion)Time-series of ceramic counts:
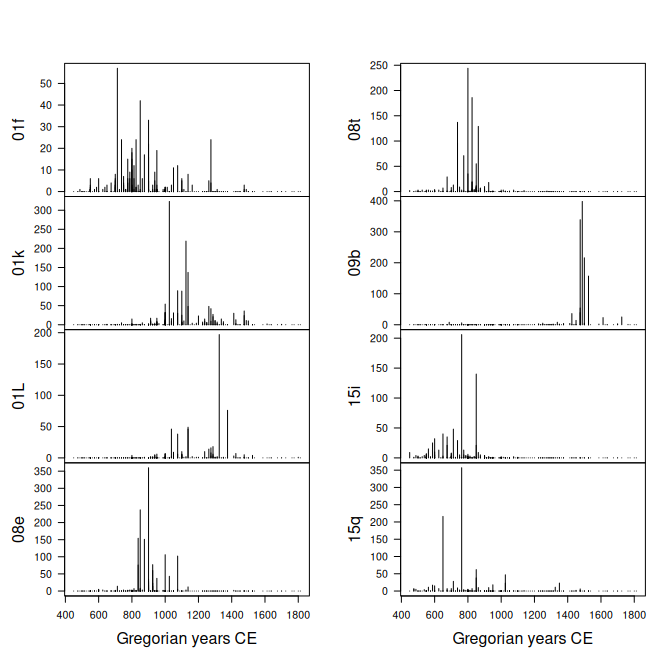
## Get ceramic counts (data from Husi 2022)
data("loire", package = "folio")
## Keep only variables whose total is at least 600
keep <- c("01f", "01k", "01L", "08e", "08t", "09b", "15i", "15q")
## Get time midpoints
mid <- rowMeans(loire[, c("lower", "upper")])
## Create time-series
X <- series(
object = loire[, keep],
time = mid,
calendar = AD()
)
## Plot (default calendar)
plot(
x = X,
type = "h" # histogram like vertical lines
)Plot time ranges:
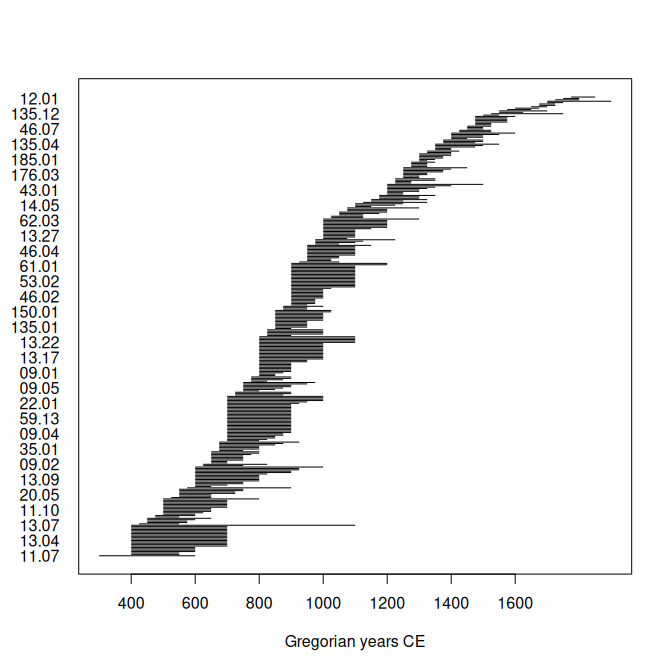
## Create time intervals
Y <- intervals(
start = loire$lower,
end = loire$upper,
names = rownames(loire),
calendar = AD()
)
## Plot (default calendar)
plot(x = Y)This package provides translations of user-facing communications, like
messages, warnings and errors, and graphical elements (axis labels). The
preferred language is by default taken from the locale. This can be
overridden by setting of the environment variable LANGUAGE (you only
need to do this once per session):
Sys.setenv(LANGUAGE = "<language code>")Languages currently available are English (en) and French (fr).
- era provides a consistent representation of year-based time scales as a numeric vector with an associated era.
Please note that the aion project is released with a Contributor Code of Conduct. By contributing to this project, you agree to abide by its terms.
Reingold, Edward M., and Nachum Dershowitz. 2018. Calendrical Calculations: The Ultimate Edition. 4th ed. Cambridge University Press. https://doi.org/10.1017/9781107415058.