- Key Features
- Contents
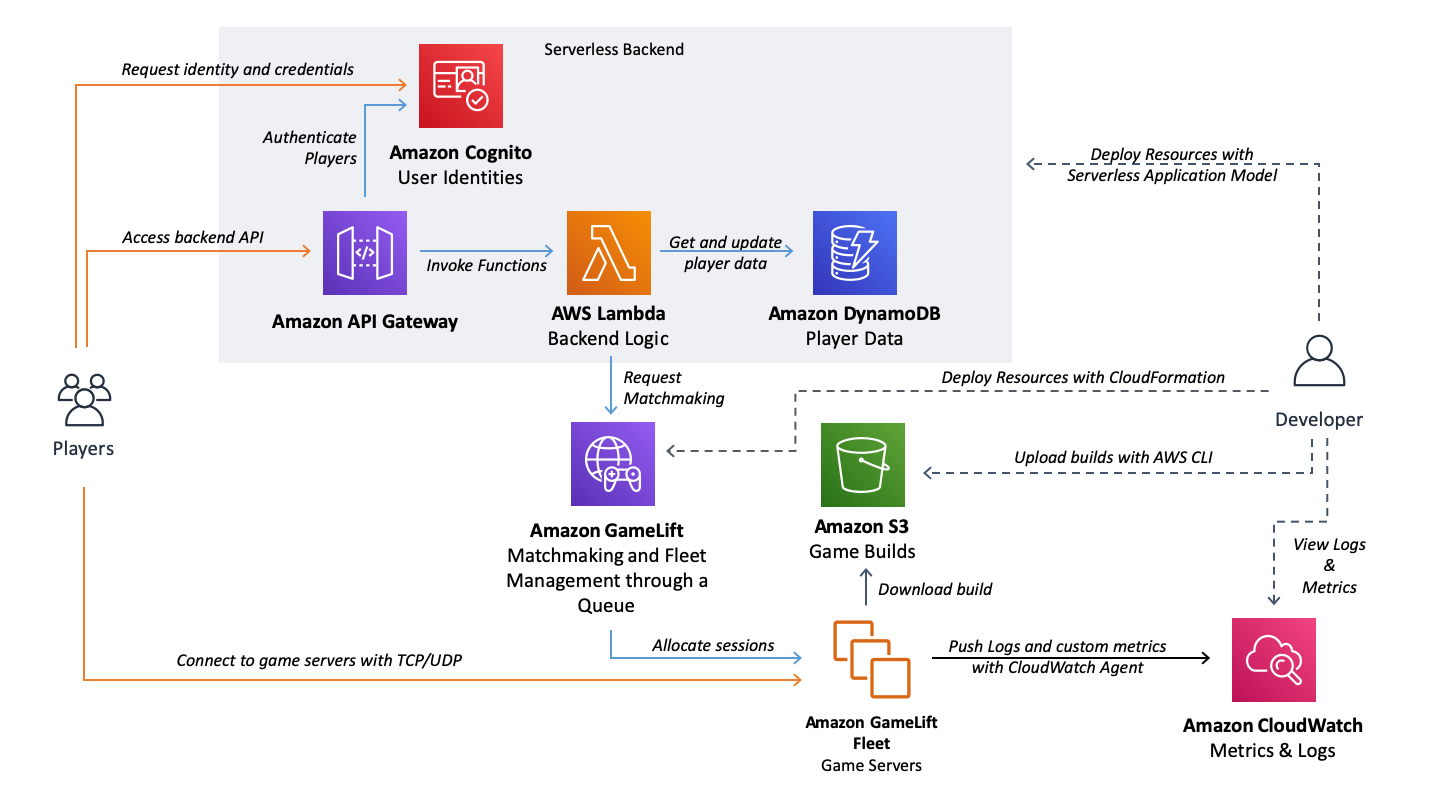
- Architecture Diagram
- Preliminary Setup
- Deployment
- Implementation Overview
- License
This repository contains a simple 3D game GameLift example with a backend service designed especially for getting started with MacOS and mobile development and leveraging deployment automation.
- Uses CloudFormation to automate the deployment of all resources
- Uses a Serverless API to initiate matchmaking built with Serverless Application Model
- Leverages FlexMatch matchmaking
- Runs on Amazon Linux 2 on the GameLift service
- Uses Cognito Identity Pools to store user identities and authenticate them against the backend
- Deployed with shell scripts
- Includes configuration to push custom logs and metrics to CloudWatch with CloudWatch Agent
- Client works on mobile platforms
- Uses Unity engine for server and client
The project is a simple "game" where 2-10 players join the same session and move around with their 3D characters. The movements are sent through the server to other players and the characters created and removed as players join and leave.
The project contains:
- A Unity Project that will be used for both Client and Server builds (
GameLiftExampleUnityProject) - A Backend Project created with Serverless Application Model (SAM) to create and API backend for matchmaking requests (
GameServiceAPI) - Fleet deployment automation leveraging AWS CloudFormation to deploy all GameLift resources (
FleetDeployment) - A build folder for the server build which includes a set of pre-required files for configuration and where you will build your Linux server build from Unity (
LinuxServerBuild)
- Install and configure the AWS CLI
- Follow these instructions to install: AWS CLI Installation
- Configure the CLI: AWS CLI Configuration
- Install Unity3D 2019
- Use the instructions on Unity website for installing: Unity Hub Installation
- Install SAM CLI
- Follow these instructions to install the Serverless Application Model (SAM) CLI: SAM CLI Installation
- Install Node.js
- Required for the SAM build: Node.js Downloads
- Install external dependencies
- GameLift Server SDK: Download and build the GameLift Server SDK (4.5) and copy all of the dll files to
GameLiftExampleUnityProject/Assets/Dependencies/GameLiftServerSDK/folder. Visual Studio is the best tool to build the project with. - Mobile SDK for Unity: Download the Mobile SDK for Unity and add the package AWSSDK.IdentityManagement.versionnumber.unitypackage to the Unity Project. NOTE: You need to have the Unity Project found in the
GameLiftExampleUnityProjectopen in order to do this. Open Unity Hub, add the GameLiftExampleUnityProject and open it (Unity 2019.2.16 or higher recommended). - Signature Calculation Example: Download the S3 example for signing API Requests and copy the folders
SignersandUtiltoGameLiftExampleUnityProject/Assets/Dependencies/folder. We will use these to sign the requests against API Gateway with Cognito credentials. After this you should not see any errors in your Unity console.
- GameLift Server SDK: Download and build the GameLift Server SDK (4.5) and copy all of the dll files to
- Select deployment Region
- The solution can be deployed in any AWS Region that supports Amazon GameLift FlexMatch. For details see the Amazon GameLift FAQ and look for "In which AWS Regions can I place a FlexMatch matchmaker?"
- Deploy the Pre-Requirements (
FleetDeployment/deployPreRequirements.sh)- Open file FleetDeployment/deployPreRequirements.sh in your favourite text editor
- Set the region variable in the script to your selected region
- Run the script (
cd FleetDeployment && sh deployPreRequirements.sh && cd ..)
- Set the role to CloudWatch Agent configuration (
LinuxServerBuild/amazon-cloudwatch-agent.json)- Open file LinuxServerBuild/amazon-cloudwatch-agent.json in your favourite text editor
- Replace the
role_arnvalue with role provided as output by the previous script - You can also find the ARN in the CloudFormation stack, in IAM console or as output of Step 1
- Deploy the Backend API with SAM (
GameServiceAPI/deploy.sh)- Make sure you have the SAM CLI installed
- Open file GameServiceAPI/deploy.sh in your favourite text editor
- Modify the script to set the
regionvariable to your selected region - Modify the script to set the
deploymentbucketnameto a globally unique name for the code deployment bucket - Run the script to deploy the backend API (
cd GameServiceAPI && sh deploy.sh && cd ..)
- Set the API endpoint to the Unity Project
- Open Unity Hub, add the GameLiftExampleUnityProject and open it (Unity 2019.2.16 or higher recommended)
- Set the value of
static string apiEndpointto the endpoint created by the backend deployment inGameLiftExampleUnityProject/Assets/Scripts/Client/MatchmakingClient.cs - You can find this endpoint from the
gameservice-backendStack Outputs in CloudFormation or from the API Gateway console (make sure to have the/Prod/in the url)
- Set the Cognito Identity Pool configuration (
GameLiftExampleUnityProject/Assets/Scripts/Client/MatchmakingClient.cs)- Set the value of
static string identityPoolIDto the identity pool created by the Pre-Requirements deployment - You can also find the ARN in the CloudFormation stack, in the Amazon Cognito console or as the output of Step 1
- Set the value of
public static string regionStringandpublic static Amazon.RegionEndpoint regionto the values of your selected region - NOTE: At this point, this part of the code is not compiled because we are using Server build configuration. The code might show up greyed out in your editor.
- Set the value of
- Build the server build
- In Unity go to "File -> Build Settings"
- Go to "Player Settings" and find the Scripting Define Symbols ("Player settings" -> "Player" -> "Other Settings" -> "Scripting Define Symbol")
- Replace the the Scripting Define Symbol with
SERVER. Remember to press Enter after changing the value. C# scripts will use this directive to include server code and exclude client code - Close Player Settings and return to Build Settings
- Switch the target platform to
Linux. If you don't have it available, you need to install Linux platform support in Unity Hub. - Check the box
Server Build - Build the project to the
LinuxServerBuildfolder (Click "Build" and in new window choose "LinuxServerBuild" folder, enter "GameLiftExampleServer" in "Save as" field and click "Save")
- Deploy the build and the GameLift resources (
FleetDeployment/deployBuildAndUpdateGameLiftResources.sh)- Open file FleetDeployment/deployBuildAndUpdateGameLiftResources.sh in your favourite text editor
- Set the region variable in the script to your selected region
- Run the script (
cd FleetDeployment && sh deployBuildAndUpdateGameLiftResources.sh && cd ..) - This will take some time as the fleet instance AMI will be built and all the GameLift resources deployed
- You should see all the resources created in the GameLift console (Fleet, Alias, Build, Queue, Matchmaking Rule Set and Matchmaking Configuration) as well as in CloudFormation
- Build and run two clients
- Set the the Scripting Define Symbol
CLIENTin the Player Settings in the Unity Project (File -> "Build Settings" -> "Player settings" → "Player" → "Other Settings" → "Scripting Define Symbol" → Replace completely to "CLIENT") - Open the scene "GameWorld" in Scenes/GameWorld
- Open Build Settings (File -> Build Settings) in Unity and set target platform to
Mac OSX(or whatever the platform you are using) and uncheck the boxServer Build - Build the client to any folder (Click "Build", select your folder and click "Save")
- You can run two clients by running one in the Unity Editor and one with the created build. This way the clients will get different Cognito identities. If you run multiple copies of the build, they will have the same identity (and hence same player ID) and will NOT be matched.
- You will see a 10 second delay in case you connect only 2 clients. This is because the matchmaking expects 4 clients minimum and will relax the rules after 10 seconds
- The clients need to connect within 20 seconds as this is the timeout value for the matchmaking
- Set the the Scripting Define Symbol
GameLift resources are deployed with CloudFormation templates. Two CloudFormation Stacks are created by the shell scripts: GameLiftExamplePreRequirements with prerequirements.yaml template and GameliftExampleResources with gamelift.yaml template.
- an IAM Role for the GameLift Fleet EC2 instances that allows access to CloudWatch to push logs and custom metrics
- a Cognito Identity Pool that will be used to store player identities and the associated IAM Roles for unauthenticated and authenticated users that clients use to access the backend API through API Gateway. We don't authenticate users in the example but you could connect their Facebook identitities for example or any custom identities to Cognito
- a FlexMatch Matchmaking Rule Set that defines a single team with 4 to 10 players and a requirement for the player skill levels to be within a distance of 10. All players will have the same skill level in the example that is stored in DynamoDB by the backend service. There is also an expansion to relax the rules to minimum of 2 players after 10 seconds. When you connect with 2 clients, you will see this 10 second delay before the expansion is activated.
- a FlexMatch Matchmaking Configuration that uses the Rule Set and routes game session placement requests to the Queue.
- a GameLift Queue that is used to place game sessions on the GameLift Fleet. In the example we have a single fleet but you could have multiple Fleets within the Region (for example a Spot Fleet and a failover On-Demand Fleet for cost optimization) as well as Fleets in different Regions to support players globally.
- a GameLift Fleet that sits behind the Queue and uses the latest game server build uploaded by the
deployBuildAndUpdateGameLiftResources.shscript. The fleet runs on Amazon Linux 2 and there are two game server processes running on each instance. The ports for the processes are defined as parameters to the game server process and matching ports are enabled for inbound traffic to the fleet. You can pack more game servers on each instance based on the instance size and the resource requirements of your server. Our example uses C5.Large instance type which is a good starting point for compute intensive workloads.
The backend service is Serverless and built with Serverless Application Model. The AWS resources are defined in the SAM template template.yaml within the GameServiceAPI folder. SAM CLI uses this template to generate the gameservice.yaml template that is then deployed with CloudFormation. SAM greatly simplifies defining Serverless backends.
The backend contains two key Lambda functions: RequestMatchmakingFunction and RequestMatchStatusFunction defined as Node.js scripts within the gameservice folder. These functions are called by the API Gateway defined in the template that uses AWS_IAM authentication. Only signed requests are allowed and the clients use their Cognito credentials to sign the requests. This way we also have their Cognito identity available within Lambda which is used to securely identify users and access their data in DynamoDB.
The SAM template defines IAM Policies to allow the Lambda functions to access both GameLift to request matchmaking as well as DynamoDB to access the player data. It is best practice to never allow game clients to access these resources directly as this can open different attack vectors to your resources.
Both the client and server are using Unity. The server is built with SERVER scripting define symbol which is used in the C# scripts to enable and disable different parts of the code.
Key code files:
Scripts/Server/GameLift.cs: Here we will initialize GameLift with the GameLift Server SDK. The port to be used is extracted from the command line arguments and the port is also used as part of the log file to have different log files for different server processes. Game session activations, health checks and other configuration follow closely the examples provided in the GameLift Developer Guide. Game sessions are defined as "started" once 2 players at least have joined (done in theServer.csscript) and terminated when players have left or in case players don't join within 5 seconds after new game session info is received.Scripts/Server/Server.cs: Here we will start a TCP Server listening to the port defined in the command line arguments to receive TCP connections from clients. We will handle any messages from clients and direct them to other clients in the game where appropriate. Messages use a binary format with BinaryFormatter that serializes and deserializes the SimpleMessage class directly to the network stream. It is recommended to use a binary format instead of a text format to minimize the size or your packets. BinaryFormatter is not the most optimal in size and you might want to consider options such as Protocol Buffers to reduce the packet size. BinaryFormatter is used to keep the example simple and clean. Sending and receiving messages is done with theScripts/NetworkingShared/NetworkProtocol.csclass that is used by both the client and the server.Scripts/Server/SimpleStatsdClient.csis used to send custom game session specific metrics to CloudWatch through the CloudWatch Agent running on the instances. These metrics are tagged with the game session which will be presented as a Dimension in CloudWatch. As StatsD is used with UDP traffic within localhost, collecting metrics is fast and has low CPU footprint in the game server process.
CloudWatch Agent
CloudWatch agent is initialized in the install.sh script when a Fleet is created. This will start the agent on each individual instance with the configuration provided in LinuxServerBuild/amazon-cloudwatch-agent.json. We will send game session log files from both the server processes with the fixed file names based on the ports. We will also start a StatsD client to send custom metrics to CloudWatch Metrics.
A key thing to notice is that we need to define the Instance Role to be used by the agent. The IAM Role provided by the instance metatadata will not send metrics and logs correctly as it is a role in the GameLift service accounts.
The game client is using Unity and is tested on MacOS and iOS platforms but should work on any platform. The input for the player character is arrow keys or WASD so there is no input option on iOS currently. The client is built with CLIENT scripting define symbol which is used in the C# scripts to enable and disable different parts of the code.
Connection Process
Client uses AWS Mobile SDK for Unity to request a Cognito Identity and connects to the Serverless backend with HTTPS and signs the requests to API Gateway with the credentials provided by Cognito. After the matchmaking is done, the client will use the connection info provided by the serverless backend (which it receives from GameLift FlexMatch) to connect directly to the server with a TCP connection. The client sends the PlayerSessionID it receives from the Serverless backend to the server and the server validates this ID with the GameLift service.
Key code files:
Scripts/Client/Client.cs: This is the main class of the client that initiates the matchmaking and connects to the server. It also processes all messages received from the server and updates the associated enemy player entities based on them. Enemy players will be spawned and removed as they join and leave and their movement will be interpolated based on the position messages received. We will also send position updates for our local player to the server here.Scripts/Client/MatchMakingClient.cs: This is the HTTPS client to the backend service that makes the signed requests to request matchmaking and request the status of a matchmaking ticket.Scripts/Client/NetworkClient.cs: This is the TCP Client class that manages the TCP connection to the server and sending/receiving of messages. It uses NetworkProtocol inNetworkProtocol.csto serialize and deserialize messages in a binary format in the same way as the server.
This example is licensed under the Apache 2.0 License. See LICENSE file.