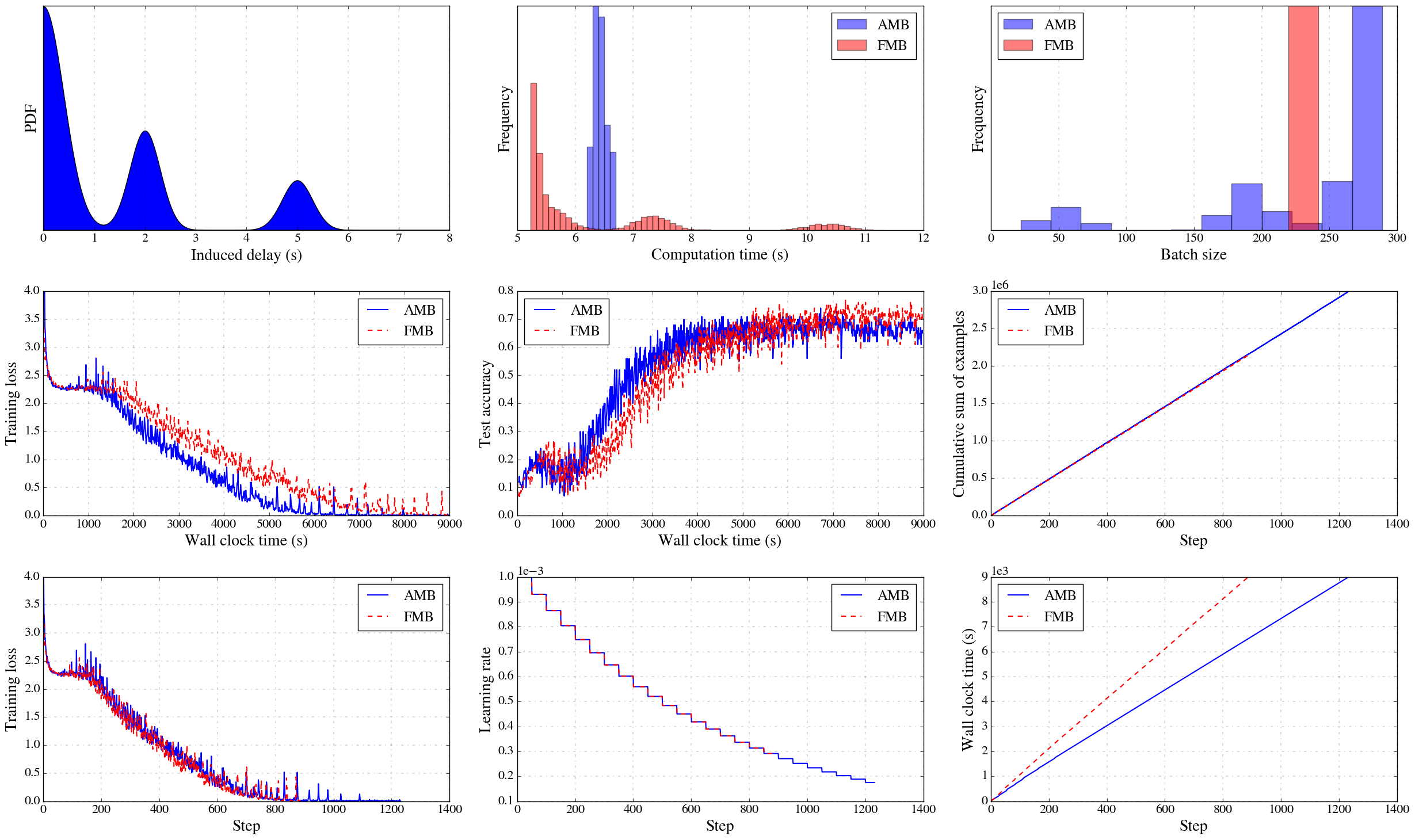
The repository contains the TensorFlow-based implementations of Anytime Mini-Batch (AMB) and Fixed Mini-Batch (FMB). The codebase uses MPI for process management (e.g. spawn master and workers in master-worker system) and inter-process communication (e.g. communication between master and workers).
The AMB and FMB implementations can be used to recreate results presented in
- Anytime Stochastic Gradient Descent: A Time to Hear from all the Workers (Paper) and
- Asynchronous delayed optimization with time-varying minibatches (Paper). See this repository for the commands needed to recreate results therein.
run_sample_code.pyincludes a sample code. See the comments therewithin.- Run the code with
mpirun -n 3 python -u run_sample_code.py(master and two workers). If it doesn't run (probably due to limited memory), try with-n 1. - Toggle
is_distributedboolean to run in distributed or non-distributed manner.
- Execute following commands to check the versions of
python,numpy,mpi4pyandtensorflow.
python --version
python -c 'import numpy; print(numpy.__version__)'
python -c 'import mpi4py; print(mpi4py.__version__)'
python -c 'import tensorflow; print(tensorflow.__version__)'
- The sample code is tested and works on two systems that have following versions.
python: 3.7.0
numpy: 1.16.3
mpi4py: 3.0.0
tensorflow: 1.13.1
python: 3.5.2
numpy: 1.16.4
mpi4py: 3.0.2
tensorflow: 1.14.0
- Generate FMB data using the following command:
mpirun -n 2 python -u run_perf_amb.py cifar10 fmb rms 242 --test_size 100 --cuda cpu_master--cuda cpu_masterruns the master node on cpu, and one worker node on GPU. Remove this argument if running on multiple GPUs.cifar10: CIFAR10 datasetfmb rms 242: FMB approach with RMS-prop optimizer and a mini-batch size 242- See in
run_perf_amb.pyfor other applicable arguments.
- Generate AMB data with following command:
mpirun -n 2 python -u run_perf_amb.py cifar10 amb rms 356 --amb_time_limit 6.2 --amb_num_partitions 16 --test_size 100 --cuda cpu_master
- If necessary can induce stragglers by adding the argument
--induce niagara.- Stragglers are induced by calling
sleepfor a random amount of time before the computations. The sleep time is sampled from a mixture of 1d Gaussian distributions as defined below. For example,niagaraspecifies one mixture distribution comprising of four components. See for details the definition ofniagarainrun_perf_amb.py. In each component the first argument specifies the mean, second the standard deviation, and the third the weight of the component.
- Stragglers are induced by calling
- After generating data, plot the results as follows.
python plot_perf_amb.py- See the arguments within
plot_perf_amb.pyfor applicable arguments.
- Create an MPI cluster - StarCluster may be helpful.
- Sample commands:
mpi1 python -u run_perf_amb.py mnist fmb rms 64
mpi4 python -u run_perf_amb.py mnist amb adm 64 --amb_time_limit 9.2 --amb_num_partitions 64 --starter_learning_rate 0.001
mpi4 python -u run_perf_amb.py cifar10 amb adm 64 --amb_time_limit 9.2 --amb_num_partitions 64 --starter_learning_rate 0.001 --test_size 100
mpi4 python -u run_perf_amb.py mnist amb rms 4096 --amb_time_limit 9.2 --amb_num_partitions 64 --starter_learning_rate 0.001 --induce
mpiall python -u run_perf_amb.py mnist amb rms 1024 --amb_time_limit 1.9 --amb_num_partitions 16
mpi11 python -u run_perf_amb.py cifar10 amb rms 256 --amb_time_limit 5.5 --amb_num_partitions 16 --test_size 100 --induce > $SCRATCH/anytime/output_amb 2>&1
mpi11 python -u run_perf_amb.py cifar10 fmb rms 256 --test_size 100 --induce > $SCRATCH/anytime/output_fmb 2>&1- Here,
mpi1,mpi4andmpiallare aliases. For examplempi4translates tompirun -host master,node001,node002,node003. - If running on Niagara use
srun -n 1in place ofmpi1. - For CIFAR10 it is important to set a low value for
test_size. Otherwise master will use all 10,000 samples in the test dataset to evaluate the model. As a result workers will have to wait to send updates to the master. - A sample log line printed by a worker looks like
Sending [256] examples, compute_time [5.63961], last_idle [0.267534], last_send [0.244859].sleep_time: time spent sleeping in the current step ifinduceis true (inducing stragglers).last_send: in the last step, time spent sending the update to the master.last_idle: in the last step, time spent after sending an update till starting computations for the next step (includes receiving time from the master as well).
- Generate all plots using
python plot_perf_amb.py --save. Training loss plot is generated by the loss evaluated at the master in each step using abatch_sizeminibatch. - Point to a specific directory and plot only a subset of axes using
python plot_perf_amb.py --data_dir /desired/directory --type panel_main --subset accuracy_vs_time loss_vs_step.
- AMB implementation in this code uses
tf.while_loopto partition minibatches. - The input minibatch is partitioned into
amb_num_partitions'micro' batches, each of sizebatch_size/amb_num_partitions. The gradients of partitions are then calculated in a loop, starting from the first while the elapsed time>amb_time_limit. When the condition fails the worker sends the gradients (summed across the processed partitions) to master. - The execution speed for
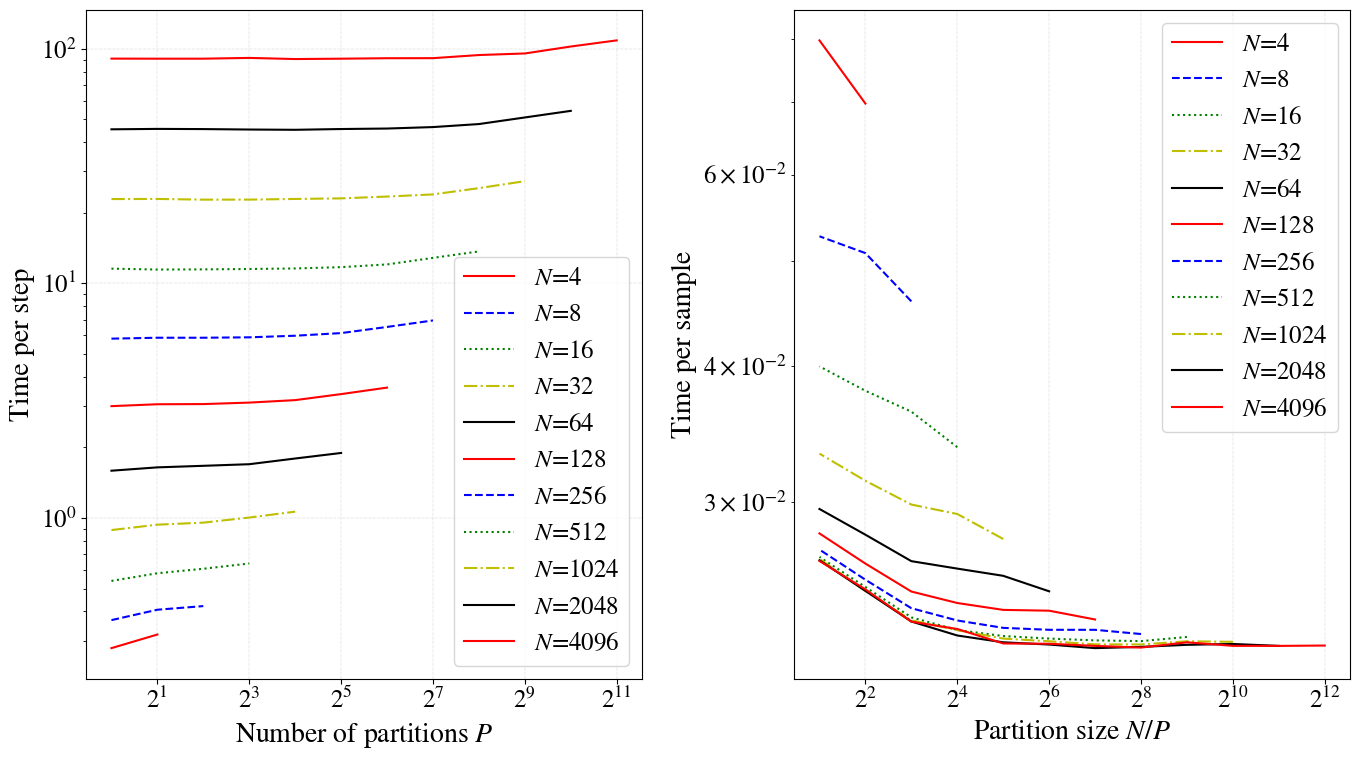
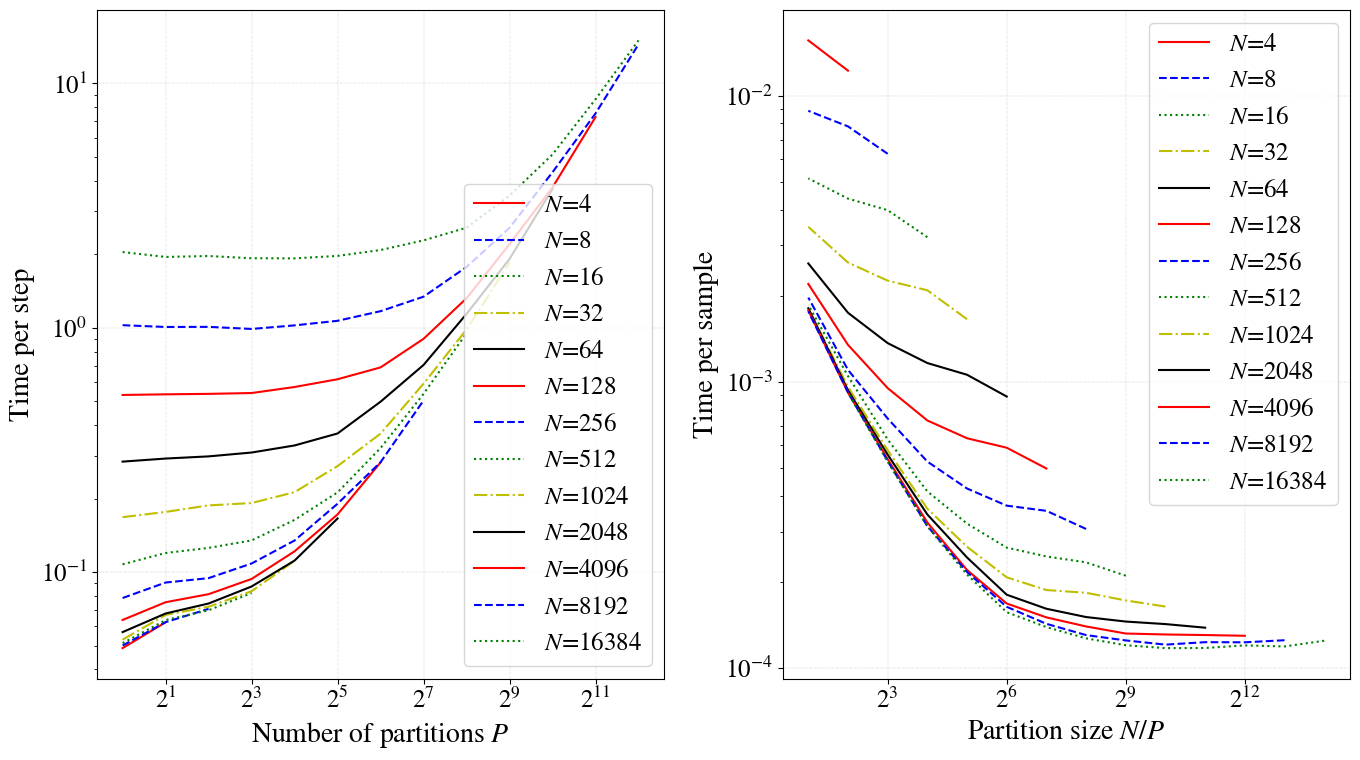
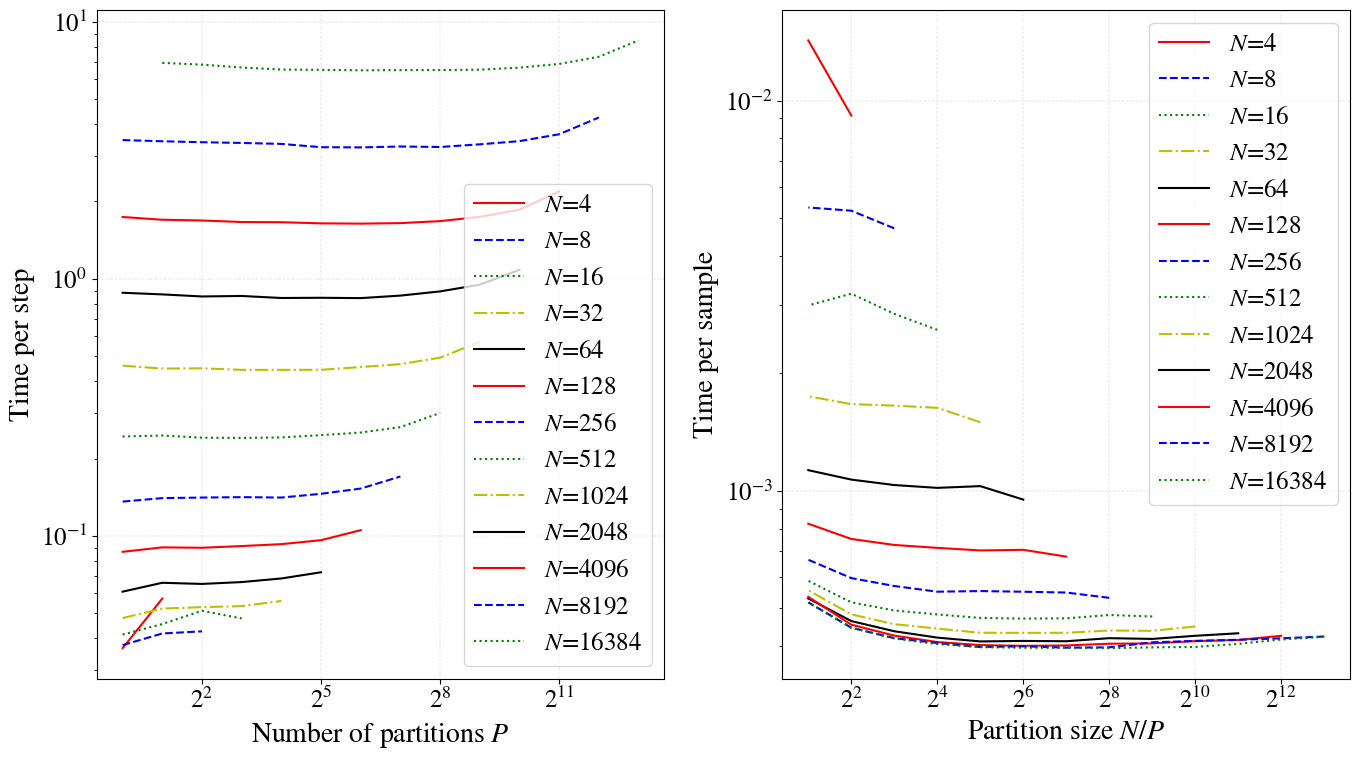
amb_num_partitions=10is lower than that foramb_num_partitions=1even for the samebatch_size. Can measure execution speed drop on different platforms (EC2, Compute Canada), NN architectures (fully-connected, convolutional). - Following plots are produced using
test_perf_partitions.pywhich includes data generating and plotting commands. - The CIFAR10 model used in this code produces following output on EC2.
- Number of partitions:
amb_num_partitions - Partition size:
batch_size/amb_num_partitions - Time per step: Time taken to go through all the partitions (covering the whole batch)
- Time per sample: Time per step divided by batch size
- Number of partitions:
- When
amb_num_partitions=1AMB has same performance as FMB. Whenamb_num_partitionsincreasese the performance decreases.
- Conclusion: For CIFAR10, if
batch_size> 512, maintaining a partition size > 32 (2^5) will cause a minimal impact on the execution time. - This means for
batch_size=512 setamb_num_partitions=512/32=16. - Below is another example for fully connected (top) vs convolutional (bottom) network for a toy dataset. Note that the while loop has a lower impact for convolutional nets. This is because the matrix multiplication in fully connected nets is well supported in modern hardware.
- Sample commands:
python -u test_perf_partitions.py batch toy_model
python -u test_perf_partitions.py plot --save --silent --ext png pdf
python -u test_perf_partitions.py eval mnist --batch_size 64 --num_partitions 2
python -u test_perf_partitions.py eval cifar10 --batch_size 64 --num_partitions 2- Modify and run
test_bandwidth.shto generate data. - Use command
python plot_perf_amb.py --type master_bandwidth --data_dir data/test_bandwidth/4_reduce_arr/bandwidth__1024to plot the results.