Leverage AutoQuery CRUD, ServiceStack Studio with User Admin module to create a multi-user ASP.NET Core Booking System from scratch within minutes with full Audit History, fine-grained permissions, declarative validation, run adhoc queries & export to Excel by just defining code-first high-performance AutoQuery CRUD Typed APIs - ServiceStack does the rest!
YouTube: youtu.be/XpHAaCTV7jE
The quickest way to run this Booking CRUD Example is to download & run it:
$ app download NetCoreApps/BookingsCrud -out BookingsCrud
$ cd BookingsCrud\Acme
$ dotnet run
Install app dotnet tool and create empty web project:
$ dotnet tool install -g app
$ app new web Acme
You can then easily layer on additional functionality to integrate with your preferred technology of your Environment's infrastructure, e.g. In order for this project to be self-hosting it utilizes the embedded SQLite database, which we can configure along with configuration to enable popular Authentication providers and an RDBMS SQLite Auth Repository with:
$ app mix auth auth-db sqlite
But if you wanted to enable Sign in with Apple and use SQL Server you'll instead run:
$ app mix auth-ext auth-db sqlserver
You can view all DB and Auth options available by searching for available mix gists by tag:
$ app mix #db
$ app mix #auth
Typically the only configuration that needs updating is your DB connection string in Configure.Db.cs, in this case it's changed to use a persistent SQLite DB:
services.AddSingleton<IDbConnectionFactory>(new OrmLiteConnectionFactory(
Configuration.GetConnectionString("DefaultConnection")
?? "bookings.sqlite",
SqliteDialect.Provider));You'll also want to create RDBMS tables for any that doesn't exist:
using var db = appHost.Resolve<IDbConnectionFactory>().Open();
db.CreateTableIfNotExists<Booking>();The beauty of AutoQuery is that we only need to focus on the definition of our Data Models using C# POCOs which OrmLite will use to create and query the RDBMS tables with whilst AutoQuery generates the Typed API implementations enabling us to build full functional high-performance systems with rich querying capabilities, declarative validation & authorization permissions and rich integrations with the most popular platforms without needing to write any logic.
The Booking class defines the Data Model whilst the remaining AutoQuery & CRUD Services define the typed inputs, outputs and behavior of each API available that Queries and Modifies the Booking table.
An added utilized feature are the [AutoApply] attributes which applies generic behavior to AutoQuery Services.
The Behavior.Audit* behaviors below depend on the same property names used in the
AuditBase.cs
class where:
Behavior.AuditQuery- adds an Ensure AutoFilter to filter out any deleted recordsBehavior.AuditCreate- populates theCreated*andModified*properties with the Authenticated user infoBehavior.AuditModify- populates theModified*properties with the Authenticated user infoBehavior.AuditSoftDelete- changes the behavior of the default Real Delete to a Soft Delete by
populating theDeleted*properties
public class Booking : AuditBase
{
[AutoIncrement]
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public RoomType RoomType { get; set; }
public int RoomNumber { get; set; }
public DateTime BookingStartDate { get; set; }
public DateTime? BookingEndDate { get; set; }
public decimal Cost { get; set; }
public string Notes { get; set; }
public bool? Cancelled { get; set; }
}
public enum RoomType
{
Single,
Double,
Queen,
Twin,
Suite,
}
[AutoApply(Behavior.AuditQuery)]
public class QueryBookings : QueryDb<Booking>
{
public int[] Ids { get; set; }
}
[ValidateHasRole("Employee")]
[AutoApply(Behavior.AuditCreate)]
public class CreateBooking
: ICreateDb<Booking>, IReturn<IdResponse>
{
public string Name { get; set; }
[ApiAllowableValues(typeof(RoomType))]
public RoomType RoomType { get; set; }
[ValidateGreaterThan(0)]
public int RoomNumber { get; set; }
public DateTime BookingStartDate { get; set; }
public DateTime? BookingEndDate { get; set; }
[ValidateGreaterThan(0)]
public decimal Cost { get; set; }
public string Notes { get; set; }
}
[ValidateHasRole("Employee")]
[AutoApply(Behavior.AuditModify)]
public class UpdateBooking
: IPatchDb<Booking>, IReturn<IdResponse>
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
[ApiAllowableValues(typeof(RoomType))]
public RoomType? RoomType { get; set; }
[ValidateGreaterThan(0)]
public int? RoomNumber { get; set; }
public DateTime? BookingStartDate { get; set; }
public DateTime? BookingEndDate { get; set; }
[ValidateGreaterThan(0)]
public decimal? Cost { get; set; }
public bool? Cancelled { get; set; }
public string Notes { get; set; }
}
[ValidateHasRole("Manager")]
[AutoApply(Behavior.AuditSoftDelete)]
public class DeleteBooking : IDeleteDb<Booking>, IReturnVoid
{
public int Id { get; set; }
}A Service can have both an IUpdateDb<T> API to define a full update where every field is updated
as well as an IPatchDb<T> API that only updates non nullable properties.
ServiceStack Studio edit Record UI will use the IUpdateDb<T> if it exists, otherwise uses the IPatchDb<T> API
and only updates changed fields.
Note: The
resetrequest param, e.g.?reset=Field1,Field2can set multiple fields toNULLinIPatchDb<T>APIs
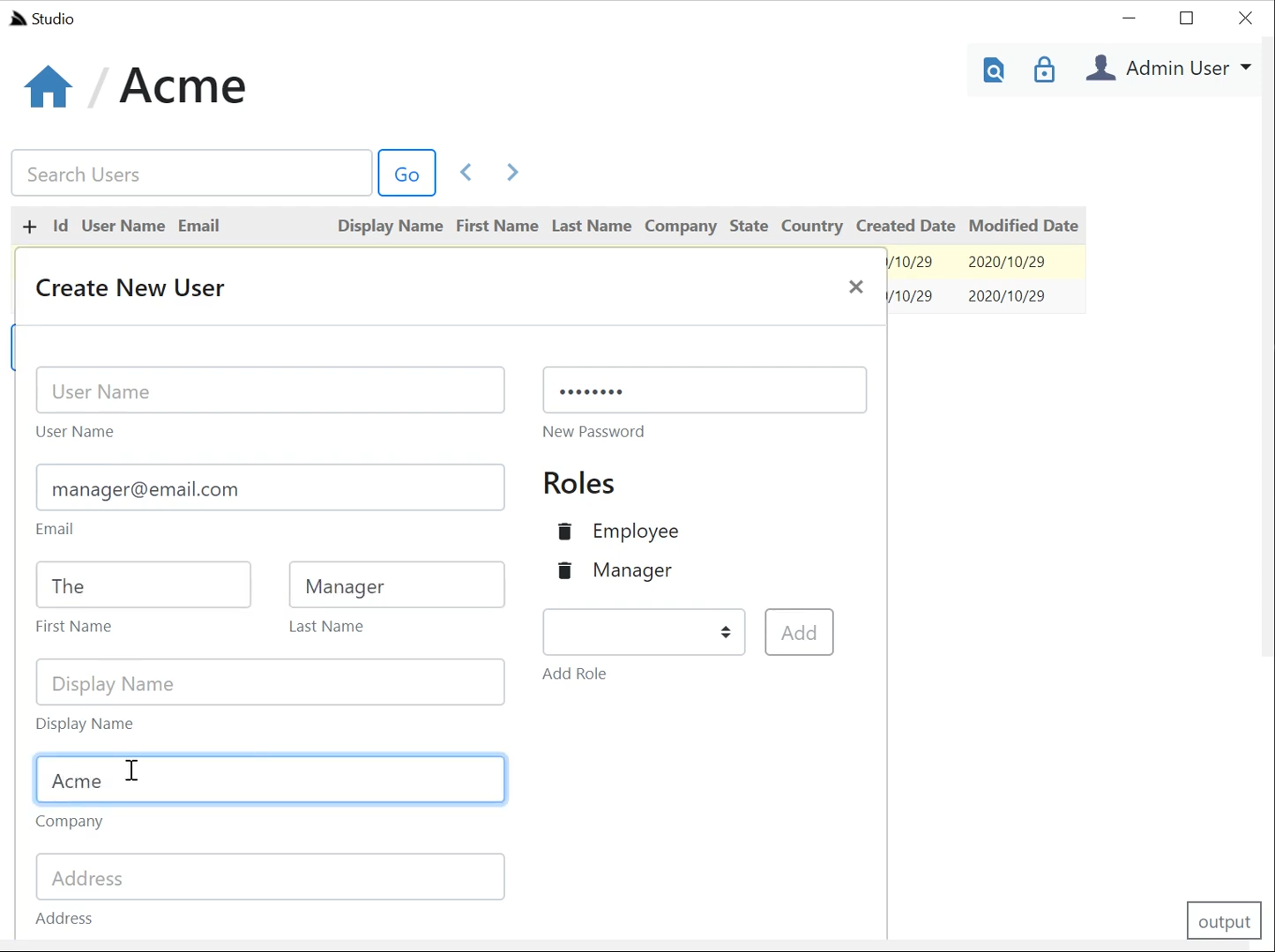
With your AutoQuery APIs created, you can run your App and use ServiceStack Studio UI to manage Bookings and Users.
Install the app dotnet tool then launch with:
YouTube: youtu.be/2FFRLxs7orU