mkdir scripts mkdir data
sh download_data.sh
For more information about the dataset, go to https://files.grouplens.org/datasets/movielens/ml-latest-small-README.html
In cloud shell run:
bq mk \
--project_id=[PROJECT_ID] \
--dataset_id=gcp_dataform \
--location=US
When you create your first Dataform repository, Dataform automatically generates a service account. Dataform uses the service account to interact with BigQuery on your behalf.
Your Dataform service account ID is in the following format:
service-PROJECT_NUMBER@gcp-sa-dataform.iam.gserviceaccount.com
Replace PROJECT_NUMBER with the Project Number of your Google Cloud project.
The Dataform service account requires a number of IAM roles with which to be able to execute the workflows in BigQuery and load data from the Google Cloud Storage Bucket. Add the following roles to the Dataform service account:
- BigQuery Job User role.
- BigQuery Data Editor role.
- BigQuery Data Viewer role.
- Storage Object Viewer role.
- Secret Manager Secret Accessor
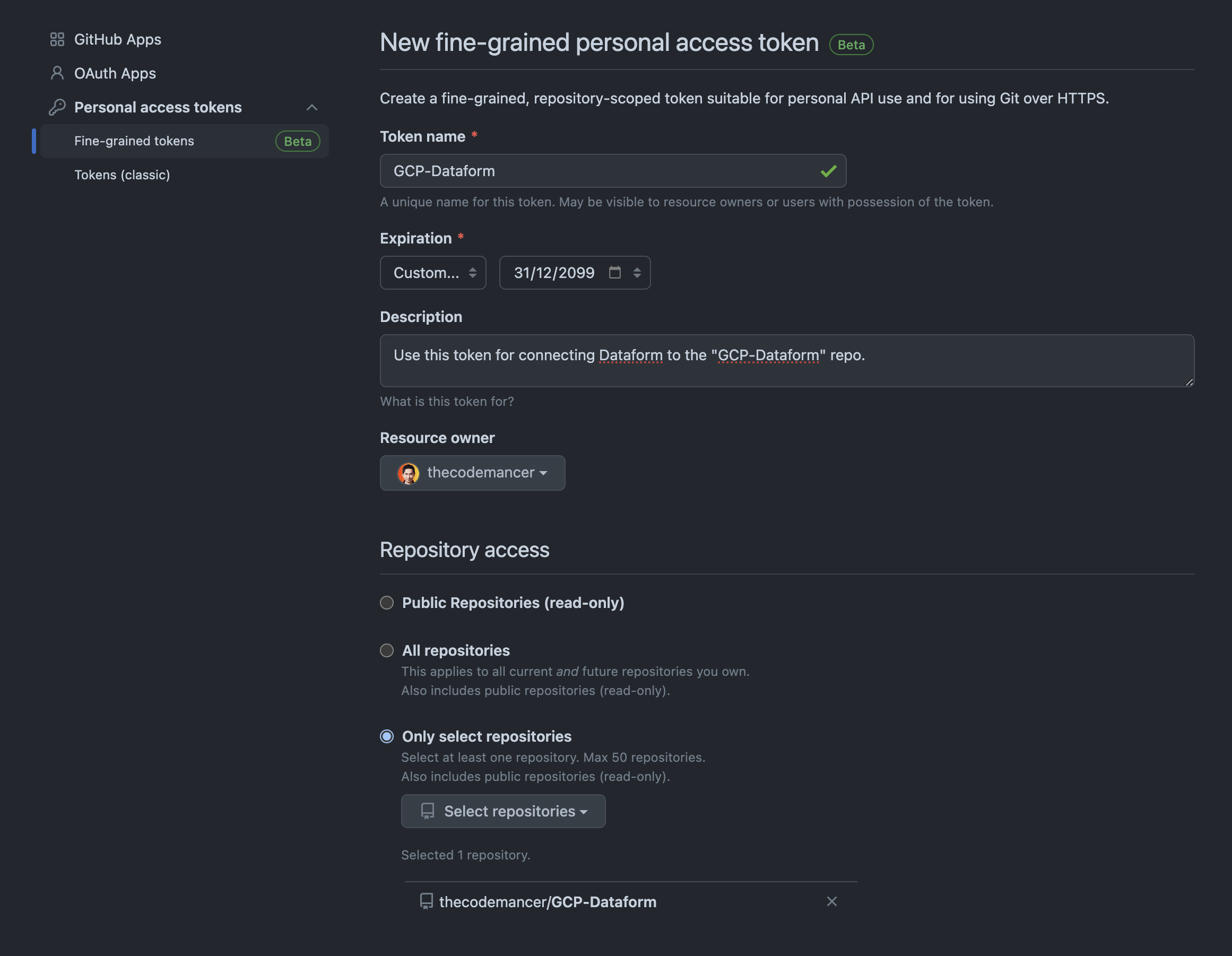
In this step, we're going to create a fine-grained personal access token. These types of tokens are fine-grained, repository-scoped tokens suitable for personal API use and for using Git over HTTPS.
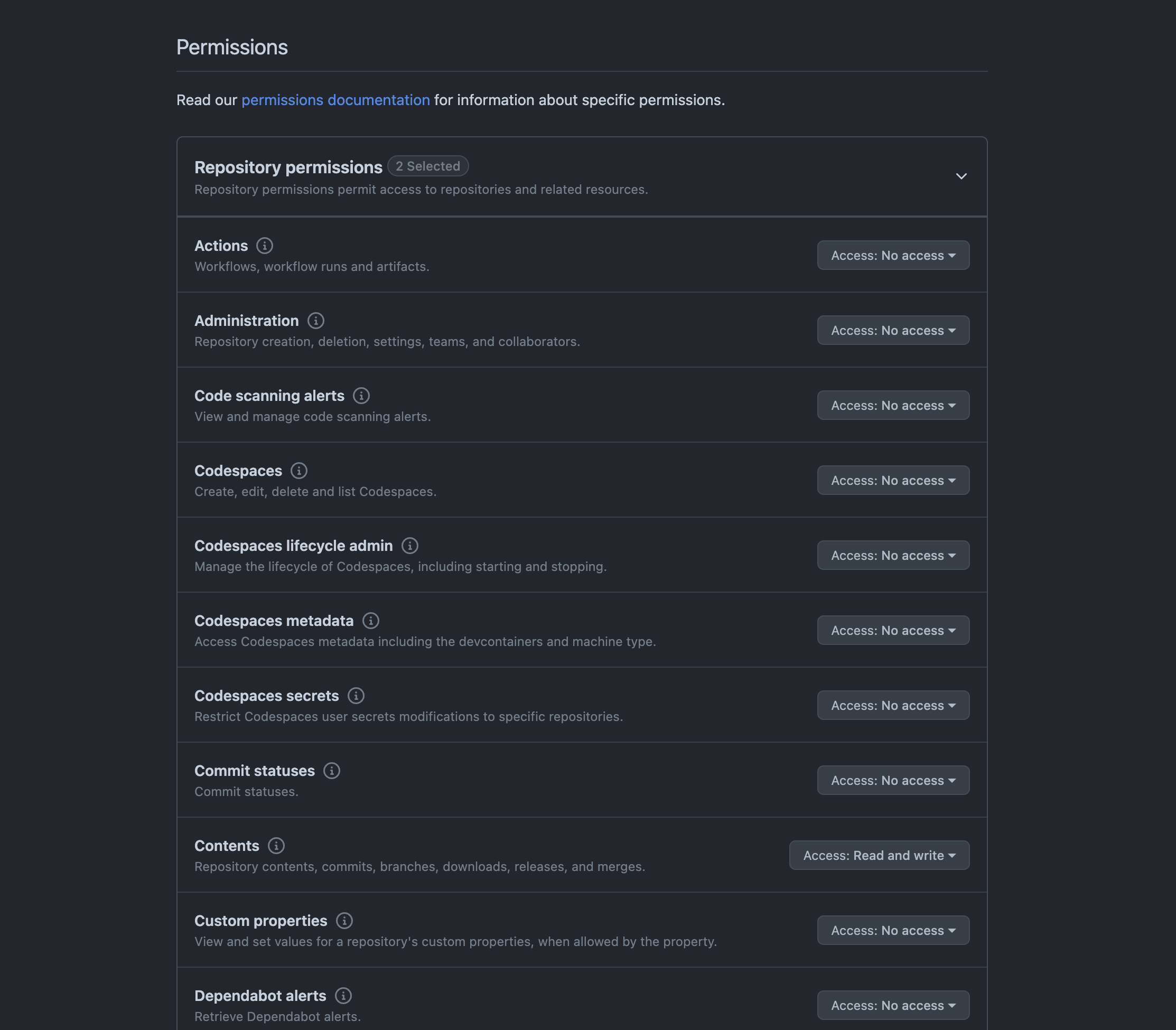
Go to Settings --> Developer Settings --> Personal access tokens. Enter a token name, expiration, description, resource owner, and repository access. In Permissions, go to contents and select Read and write. Click on Generate token.
Make sure to copy your personal access token now as you will not be able to see it again.
Secret Manager lets you store, manage, and secure access to your application secrets. In the Google Cloud console, go to the Secret Manager page and create a secret. Enter a Name and paste your GitHub token as Secret value. Leave the rest of the fields with their default values.
Repositories contain a single Dataform project that can be connected to your Git provider. Within a repository you can create workspaces for development and execute your SQL workflows against BigQuery.
New repositories start empty and can be connected to a git provider after being created.
ℹ Dataform will execute workflows as the service account service-[PROJECT_NUMBER]]@gcp-sa-dataform.iam.gserviceaccount.com. Ensure that the service account has been granted the role roles/bigquery.user in order to create datasets, tables and jobs. Also ensure that the service account has been granted access to read any datasets or tables that your workflow will consume.
Development workspaces contain an editable copy of your team's repository. Using development workspaces, you can develop code without affecting other users, commit changes, and push commits to your remote Git repository. If your repository is connected to a remote Git provider, changes from your development workspace will be pushed to a remote branch named after your development workspace. Otherwise, your changes will be pushed to your default branch.
To start developing with Dataform, first initialize your project with the required configuration files.
ℹ Dataform needs a secret containing a personal access token (for HTTPS remotes) or a user private key (for SSH remotes) for connecting to your git provider.
To link a Dataform repository to a remote Git repository, follow these steps:
-
In the Google Cloud console, go to the Dataform page.
-
Select the repository you want to connect.
-
On the repository page, click Settings > Connect with Git.
-
In the Link to remote repository pane, in the Remote Git repository URL field, enter the URL of the remote Git repository, ending with .git.
For HTTPS authentication, the URL of the remote Git repository cannot contain usernames or passwords.
For SSH authentication, the URL of the remote Git repository be in one of the following formats:
- Absolute URL:
ssh://git@{host_name}[:{port}]/{repository_path}, `port`` is optional. - SCP-like URL:
git@{host_name}:{repository_path}.
- Absolute URL:
-
In the Default remote branch name field, enter the name of the main development branch of the remote Git repository.
-
In the Secret drop-down, select your secret for the remote Git repository.
-
If you used SSH authentication for the remote repository, in the SSH public host key value field, enter a single public host key of your Git provider.
The SSH public host key value must be in the format of a known_hosts file. The value must contain an algorithm and a public key encoded in the base64 format, but without the hostname or IP, in the following format:
ALGORITHM BASE64_KEY_VALUE
For the Azure DevOps Services public host key, see Use SSH key authentication.
For the Bitbucket public host key, see Configure SSH.
For the GitHub public host key, see GitHub's SSH key fingerprints.
For the GitLab public host key, see SSH known_hosts entries.
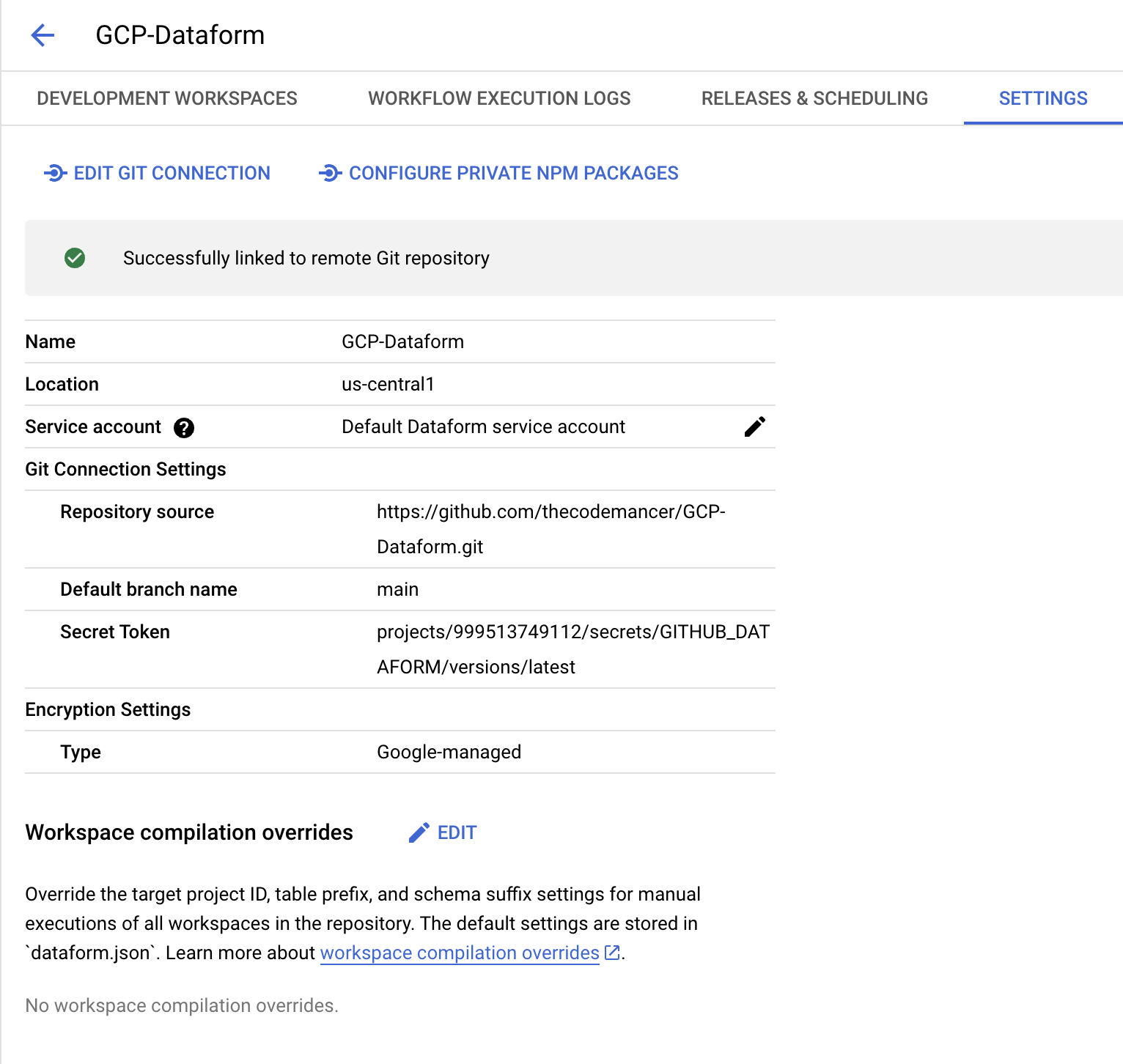
- Click Link. If you followed the steps correctly, your Repository settings should look like the following: