This is a main repository for the Serverless REST API in .NET 6 with AWS Lambda course.
| Project | Description |
|---|---|
| SimpleApi | Simple REST API with AWS Lambda |
| MinimalLambda | Minimal API (using Controller) with AWS Lambda |
| SimpleApiWithDynamoDb | Simple REST API with AWS Lambda and DynamoDB |
This is a very quick demo of how to create a serverless rest API using AWS Lambda and .NET 6. The project is created using the dotnet new command and the Amazon.Lambda.Templates NuGet package.
Install the AWS Lambda templates for .NET 6 using the following command:
dotnet new -i Amazon.Lambda.TemplatesIf already installed check the installed templates using the following command:
dotnet new --listInstall Amazon.Lambda.Tools Global Tools if not already installed.
dotnet tool install -g Amazon.Lambda.ToolsIf already installed check if new version is available.
dotnet tool update -g Amazon.Lambda.Tools| Template Name | Short Name | Language | Tags |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lambda Empty Serverless | serverless.EmptyServerless | [C#],F# | AWS/Lambda/Serverless |
We will create a new project using the serverless.EmptyServerless template.
dotnet new serverless.EmptyServerless --name SimpleApi --output dotnet-rest-api-with-lambdaThis project's purpose is only demostrating how to create a serverless rest API using AWS Lambda and .NET 6.
We don't need serverless.template file. So, we can delete it.
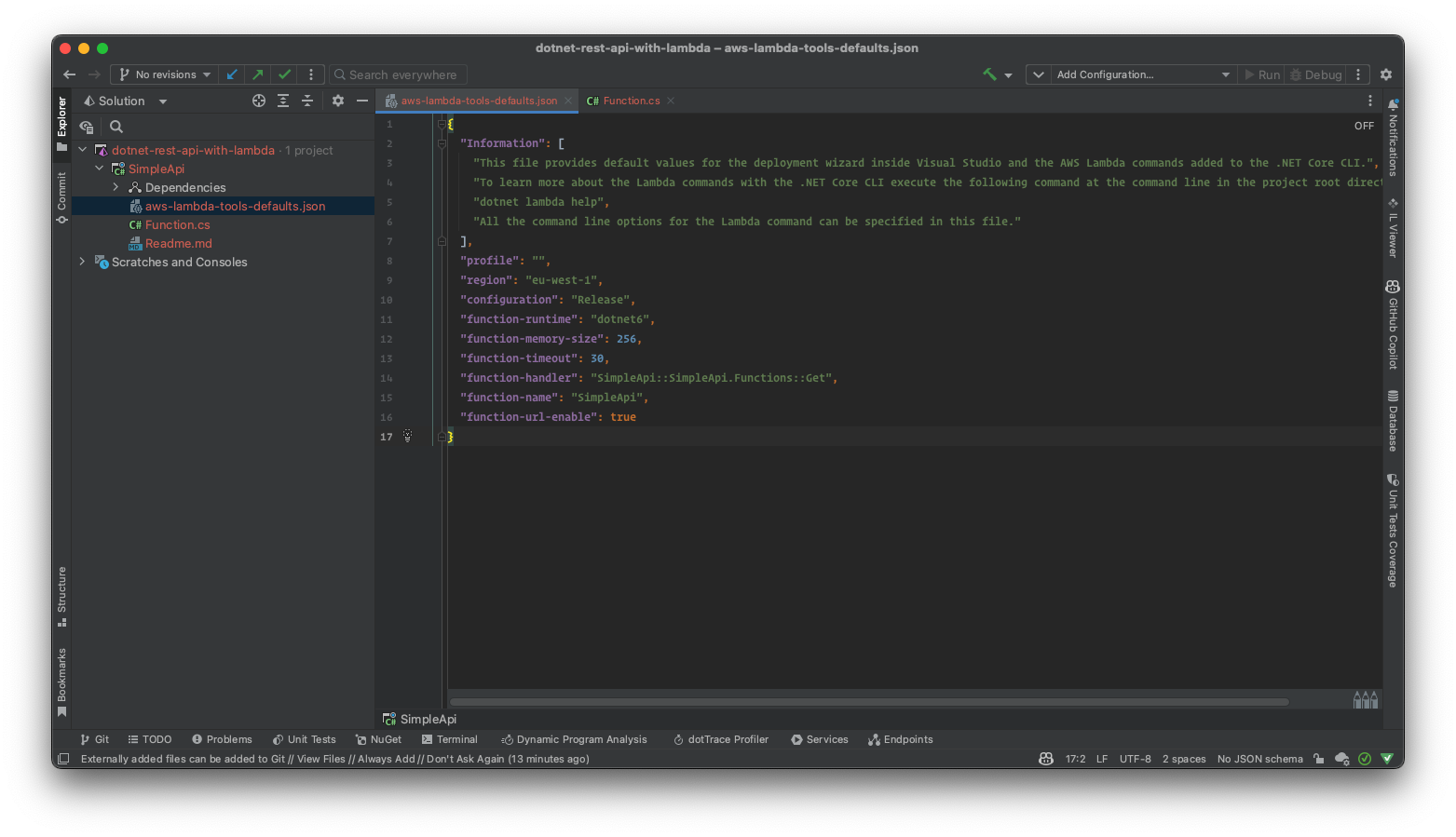
Now we need to configure aws-lambda-tools-defaults.json file.
We must set function-runtime to dotnet6, function-memory-size to 256 and function-timeout to 30.
function-handler is the name of the class that will handle the request. In this project, we will use SimpleApi::SimpleApi.Functions::Get as the handler.
First part is the assembly name, second part is the namespace and the class name. Last part is the method name.
We have a Get method in Functions class. This method will handle the request.
public APIGatewayProxyResponse Get(APIGatewayProxyRequest request, ILambdaContext context)
{
return new APIGatewayProxyResponse
{
StatusCode = 200,
Body = "Hello World!",
Headers = new Dictionary<string, string> { { "Content-Type", "text/plain" } }
};
}Now that we have created the project, we can deploy it to AWS Lambda. Go to the project directory and run the following command:
dotnet lambda deploy-functionWe need to configure the Lambda function on AWS Console.
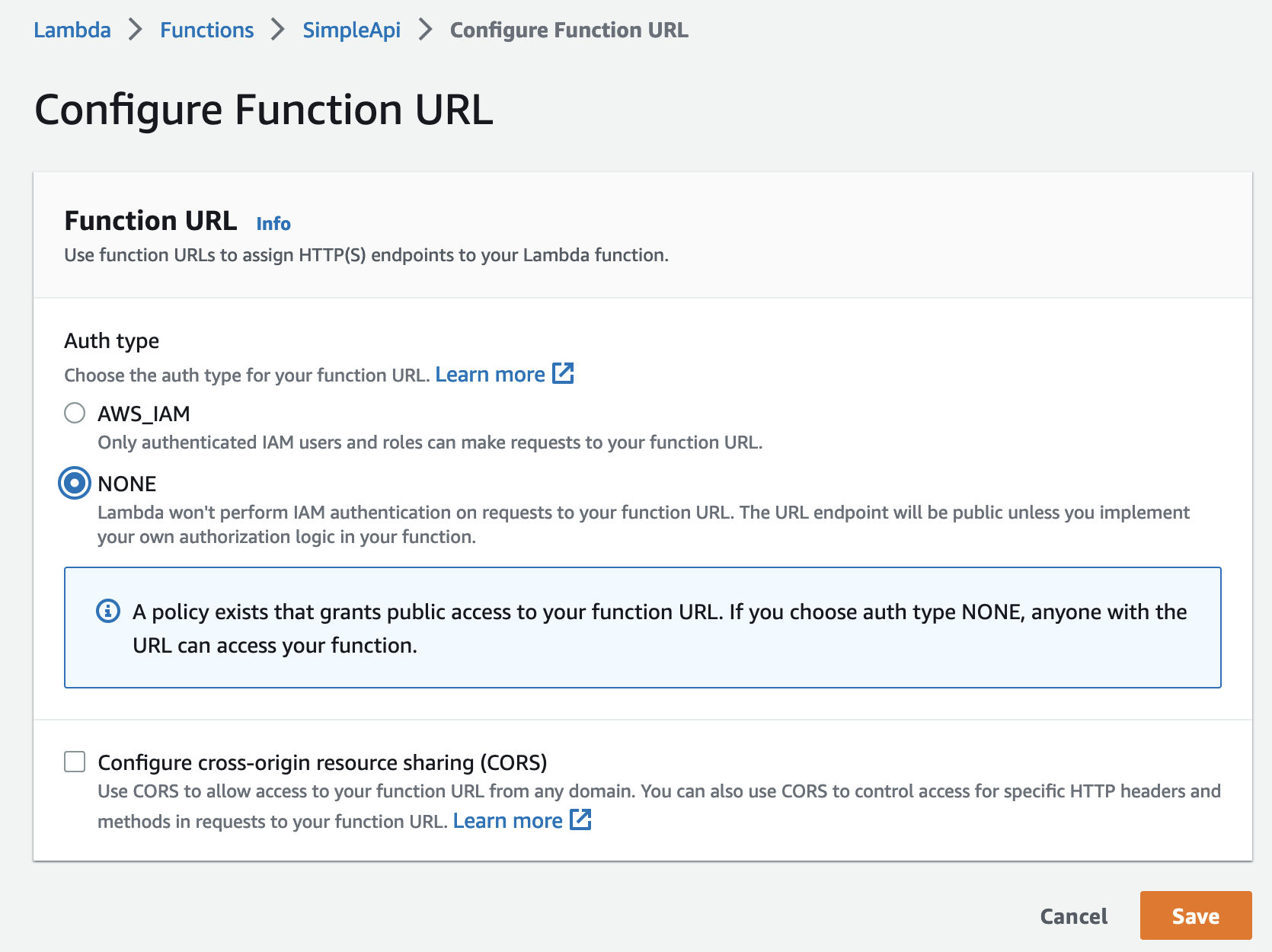
In the Configuration tab, we need to create a new Function URL.
The auth type should be NONE. Then click on Save.
You have created a serverless rest API using AWS Lambda and .NET 6.
We will create a minimal API using AWS Lambda and .NET 6. It will be a simple API with a single MapGet method and a single controller which is a simple calculator class with four methods.
We are going to use the serverless.AspNetCoreMinimalAPI template. You can create a new project using the following command:
dotnet new serverless.AspNetCoreMinimalAPI --name MinimalLambda --output MinimalLambdaor using the Rider IDE.
We need to configure aws-lambda-tools-defaults.json file.
This time we will use function-handler as MinimalLambda. Then we can remove serverless.template file.
In the Program.cs file, we have a CreateHostBuilder method. This method will create a new IHostBuilder instance.
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Add services to the container.
builder.Services.AddControllers();
// Add AWS Lambda support. When application is run in Lambda Kestrel is swapped out as the web server with Amazon.Lambda.AspNetCoreServer. This
// package will act as the webserver translating request and responses between the Lambda event source and ASP.NET Core.
builder.Services.AddAWSLambdaHosting(LambdaEventSource.RestApi);
var app = builder.Build();
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.MapControllers();
app.MapGet("/", () => "Welcome to running ASP.NET Core Minimal API on AWS Lambda");
app.Run();LambdaEventSource.RestApi is the event source that will be used to handle the request. If we change it to LambdaEventSource.HttpApi, we will be able to use the new HTTP API.
builder.Services.AddAWSLambdaHosting(LambdaEventSource.HttpApi);In the Controllers folder, we have a CalculatorController.cs file. This file contains a Calculator class with four methods. We can use these methods to perform simple calculations.
Now that we have created the project, we can deploy it to AWS Lambda. Go to the project directory and run the following command:
dotnet lambda deploy-functionWith "function-url-enable": true in aws-lambda-tools-defaults.json file, we can get the function URL after deploying the project.
Now we can use the function URL to access the API.
They can be accessed using the following URLs:
https://<function-url>/calculator/add/1/2https://<function-url>/calculator/subtract/1/2https://<function-url>/calculator/multiply/1/2https://<function-url>/calculator/divide/1/2
With Postman, we can send a request to these URLs and get the result.
You have created a minimal API using AWS Lambda and .NET 6.
We are going to create a new project with a simple API and a DynamoDB table. We will use the serverless.AspNetCoreMinimalAPI template.
In this project we need some NuGet packages. We will use AWSSDK.DynamoDBv2 and Amazon.Lambda.AspNetCoreServer.Hosting with FastEndpoints, FastEndpoints.Swagger and ValueOf packages.
We will add a Domain folder to the project. In this folder, we will add a User class and a Common folder.
In the Common folder, we will add UserId, FullName, EmailAddress and Password classes. You can find the code for these classes in the here.
|-- Domain
|-- Common
|-- EmailAddress.cs
|-- FullName.cs
|-- Password.cs
|-- UserId.cs
|-- User.cs
We will add a Contracts folder to the project. In this folder, we will add Data, Requests and Responses folders.
In the Data folder, we will add UserDto class. In the Requests folder, we will add CreateUserRequest, DeleteUserRequest, GetUserRequest and UpdateUserRequest classes.
In the Responses folder, we will add UserResponse,GetAllUsersResponse and ValidationFailureResponse classes. You can find the code for these classes in the here.
|-- Contracts
|-- Data
|-- UserDto.cs
|-- Requests
|-- CreateUserRequest.cs
|-- DeleteUserRequest.cs
|-- GetUserRequest.cs
|-- UpdateUserRequest.cs
|-- Responses
|-- GetAllUsersResponse.cs
|-- UserResponse.cs
|-- ValidationFailureResponse.cs
We will add a Mapping folder to the project. In this folder, we will add ApiContractToDomainMapper, DomainToApiContractMapper, DomainToDtoMapper and DtoToDomainMapper classes.
You can find the code for these classes in the here.
|-- Mapping
|-- ApiContractToDomainMapper.cs
|-- DomainToApiContractMapper.cs
|-- DomainToDtoMapper.cs
|-- DtoToDomainMapper.cs
We will add a Repositories folder to the project. In this folder, we will add IUserRepository interface and UserRepository class.
You can find the code for this interface and class in the here.
|-- Repositories
|-- IUserRepository.cs
|-- UserRepository.cs
We will add a Services folder to the project. In this folder, we will add IUserService interface and UserService class.
You can find the code for this interface and class in the here.
|-- Services
|-- IUserService.cs
|-- UserService.cs
We will add a Endpoints folder to the project. In this folder, we will add CreateUserEndpoint, DeleteUserEndpoint, GetUserEndpoint and UpdateUserEndpoint classes.
You can find the code for these classes in the here.
|-- Endpoints
|-- CreateUserEndpoint.cs
|-- DeleteUserEndpoint.cs
|-- GetUserEndpoint.cs
|-- UpdateUserEndpoint.cs
We will add a Summaries folder to the project. In this folder, we will add CreateUserSummary, DeleteUserSummary, GetUserSummary and UpdateUserSummary classes.
You can find the code for these classes in the here.
|-- Summaries
|-- CreateUserSummary.cs
|-- DeleteUserSummary.cs
|-- GetUserSummary.cs
|-- UpdateUserSummary.cs
We will add a Validation folder to the project. In this folder, we will add CreateUserRequestValidator, UpdateUserRequestValidator and ValidationExceptionMiddleware classes.
You can find the code for these classes in the here.
|-- Validation
|-- CreateUserRequestValidator.cs
|-- UpdateUserRequestValidator.cs
|-- ValidationExceptionMiddleware.cs
We need to enable Lambda hosting in Program.cs file.
builder.Services.AddAWSLambdaHosting(LambdaEventSource.HttpApi);Now we add FastEndpoints and swagger services.
builder.Services.AddFastEndpoints();
builder.Services.AddSwaggerDoc();We need to configure DynamoDB in Program.cs file. We will use AmazonDynamoDBClient to connect to DynamoDB.
builder.Services.AddSingleton<IAmazonDynamoDB>(_ => new AmazonDynamoDBClient(RegionEndpoint.EUWest1));We will add UserRepository and UserService to the services.
builder.Services.AddSingleton<IUserRepository>(provider =>
new UserRepository(provider.GetRequiredService<IAmazonDynamoDB>(),
config.GetValue<string>("Database:TableName")));
builder.Services.AddSingleton<IUserService, UserService>();We will add ValidationExceptionMiddleware to the services.
app.UseMiddleware<ValidationExceptionMiddleware>();
app.UseFastEndpoints(x =>
{
x.ErrorResponseBuilder = (failures, _) =>
{
return new ValidationFailureResponse
{
Errors = failures.Select(y => y.ErrorMessage).ToList()
};
};
});We will add Database:TableName to the appsettings.json configuration file.
{
"Database": {
"TableName": "users"
}
}
We will deploy the project to AWS Lambda using the following command.
dotnet lambda deploy-function
In AWS Console, go to DynamoDB service and create a table with the name users. The table should have a part key with the name pk and type String. The table should have a sort key with the name sk and type String.
After creating the table, click the Actions button and select Create access control policy. Identity provider should be Login with Amazon and all permissions should be selected. Click Generate policy button.
The generated policy will be like this:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"dynamodb:BatchGetItem",
"dynamodb:BatchWriteItem",
"dynamodb:DeleteItem",
"dynamodb:GetItem",
"dynamodb:PutItem",
"dynamodb:Query",
"dynamodb:UpdateItem"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:dynamodb:eu-west-1:YOUR_ACCOUNT:table/users"
],
"Condition": {
"ForAllValues:StringEquals": {
"dynamodb:LeadingKeys": [
"${www.amazon.com:user_id}"
]
}
}
}
]
}
We don't need the Condition part. So we will remove it. The policy will be like this:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"dynamodb:BatchGetItem",
"dynamodb:BatchWriteItem",
"dynamodb:DeleteItem",
"dynamodb:GetItem",
"dynamodb:PutItem",
"dynamodb:Query",
"dynamodb:UpdateItem"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:dynamodb:eu-west-1:YOUR_ACCOUNT:table/users"
]
}
]
}
Now copy the policy. We will use it in the next step.
In AWS Console, go to Lambda service and select the function we created. In the Configuration tab, click the Permissions page. Click the execution role and it will open the IAM service. In the IAM service, click the Add permissions button then click the Create inline policy button.
Go to JSON tab and paste the policy we created in the previous step. Click Review policy button. Give a name to the policy and click Create policy button.
We have created a simple API with DynamoDB. You can test the API using the Postman.