I make this repo to practice data Structures concepts as well as C and CPP. My goal here is to implement data Structures concepts in both language, and also using different paradigms.
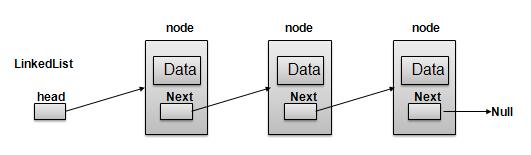
A linked list is a linear data structure, in which the elements are not stored at contiguous memory locations. The elements in a linked list are linked using pointers as shown in the below image.
- LinkedList contains elements called Nodes.
- Each Node carries a data field and a Link Field called next.
- Each Node is linked with anothe Node using its next link.
- Last Node carries a next as NULL to mark the end of the list.
- Append - Add an Node at the beginning of the list.
- Insert - Add an Node at a given position position.
- Print - Print the entire list to stdout.
- Delete - Delete an Node at a given position.
- DeleteValue - Delete a Node that has the given value.
- get - Get the data of a node at given position.
- (free) - I use Free function only in C, to free the allocated memory in the program.
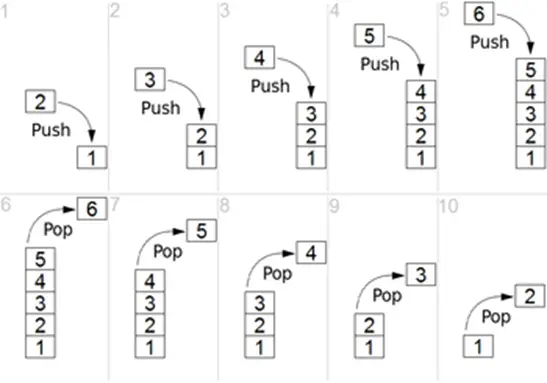
A stack is an abstract data type with a predifined capacity or size. It is a simple data structure that allows adding and removing elements in a particular order.
- 1-Stack is an ordered list of similar data type.
- 2-Stack is a LIFO(Last in First out) structure.
- 3-push() function is used to insert new element into the stack.
- 4-pop() function is used to remove an element from the stack. Both insertion and deletion are allowed only on top of the stack
- 5-Stack is in Overflow state when it is completely full, and is said in Underflow state if it is completely empty.
- Push - Add an element at the top of the stack.
- Pop - Remove an element from the top of the stack.
- Top - Get the element at the top of the stack.
- isEmpty - Check whether the stack is empty or not.
- Print - Prints the stack to the stdout.
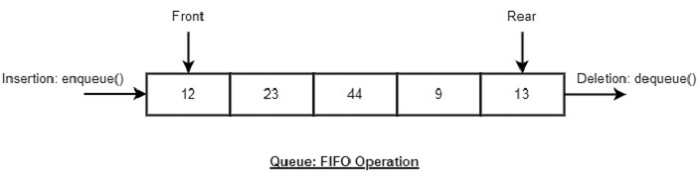
Queue is like stack, is also an abstract data structure. The difference between queue and stack is queue is open at both its ends. Hence it follows FIFO structure, i.e. the data inserted first will accessed and removed first. The data is inserted into the queue through one end (rear) and deleted from it using other end (front).
- Push/Enqueue - Add an element at the rear of the queue.
- Pop/Dequeue - Remove an element from the front of the queue.
- Top/Peek - Get the element at the top of the queue.
- Print - Prints the queue to the stdout.
- isEmpty - Check whether the queue is empty or not.
Trees are abstract data types, that represent a hierarchical tree structured with a sef of connected nodes. Each node in the tree can be conneted to many other nodes called children, and chilren must be connected to exacltly one parent.
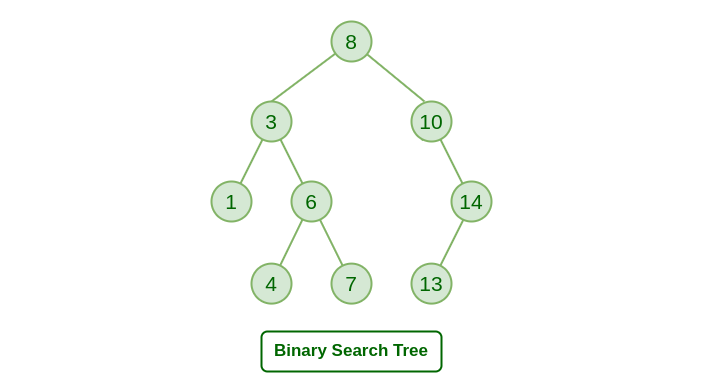
In this repo we are gonna see the BST or Binary Search Tree, is type of trees, but with different propreties.
- The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys lesser than the root node key.
- The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys greater than the root node key
- The left and right subtree each must be a binary tree.
- addNode - Add a node to the tree.
- search - Search for a node in the tree.
- max - finds the maximum node in the tree.
- min - finds the minimum node in tree.
- height - finds the height of the tree.
- levelOrder - prints the tree in level-order.
- delete - Delete a node from a tree. (The hardest)
In computer science, tree traversal (also known as tree search and walking the tree) is a form of graph traversal and refers to the process of visiting (e.g. retrieving, updating, or deleting) each node in a tree data structure, exactly once. Such traversals are classified by the order in which the nodes are visited. The following algorithms are described for a binary tree, but they may be generalized to other trees as well.
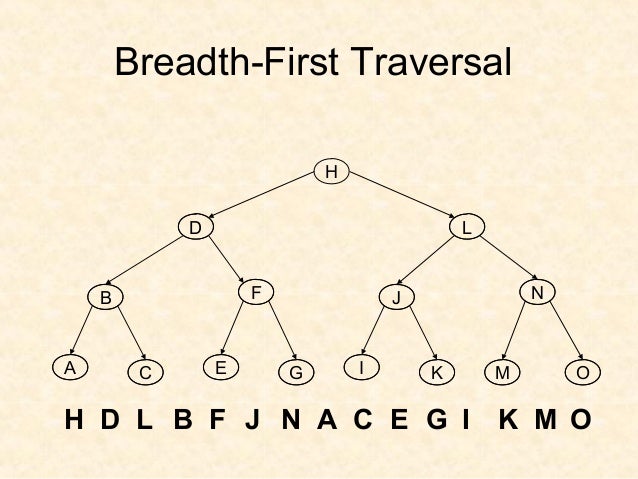
In breadth-first search (BFS) or level-order search, the search tree is broadened as much as possible before going to the next depth.
- Level-order: H, D, L, B, F, J, N, A, C, E, G, I, K, M, O.
- Preorder
- Inorder
- Postorder