Utility belt to handle data on AWS.
Contents: Use Cases | Installation | Examples | Diving Deep | Contributing
- Pandas -> Parquet (S3) (Parallel)
- Pandas -> CSV (S3) (Parallel)
- Pandas -> Glue Catalog Table
- Pandas -> Athena (Parallel)
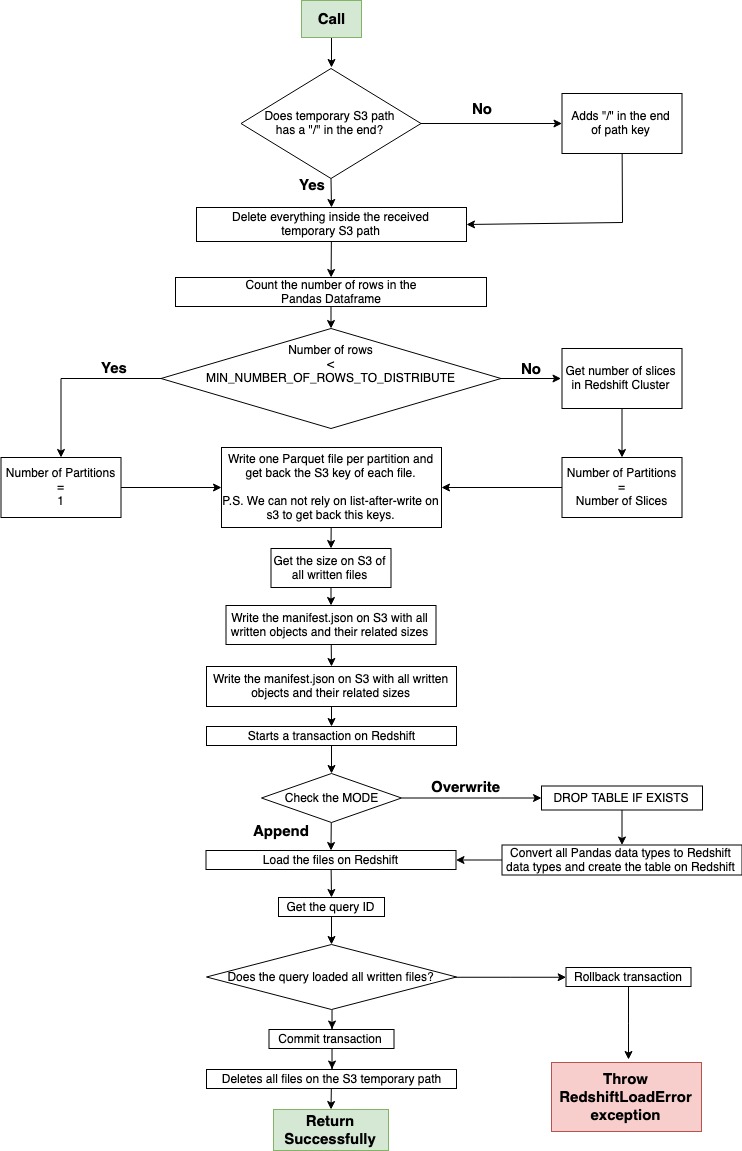
- Pandas -> Redshift (Parallel)
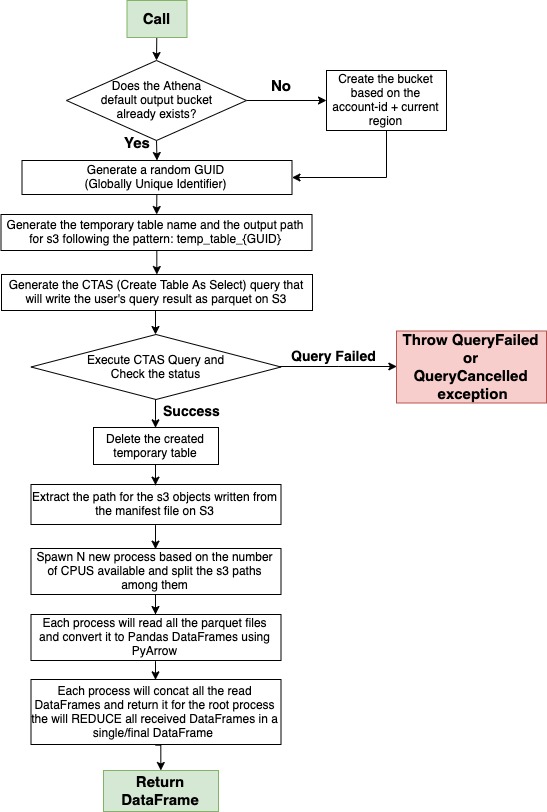
- Parquet (S3) -> Pandas (Parallel) (NEW ⭐)
- CSV (S3) -> Pandas (One shot or Batching)
- Glue Catalog Table -> Pandas (Parallel) (NEW ⭐)
- Athena -> Pandas (One shot, Batching or Parallel (NEW ⭐))
- Redshift -> Pandas (Parallel) (NEW ⭐)
- Redshift -> Parquet (S3) (NEW ⭐)
- CloudWatch Logs Insights -> Pandas
- Encrypt Pandas Dataframes on S3 with KMS keys
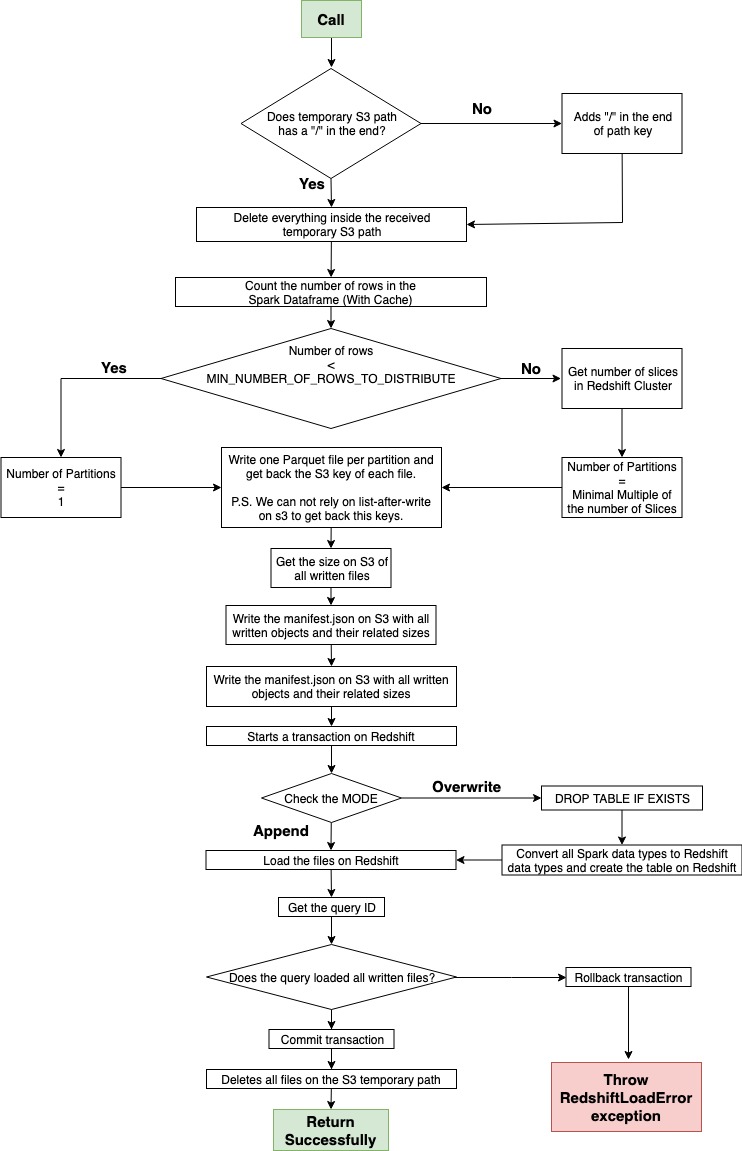
- PySpark -> Redshift (Parallel)
- Register Glue table from Dataframe stored on S3
- Flatten nested DataFrames
- List S3 objects (Parallel)
- Delete S3 objects (Parallel)
- Delete listed S3 objects (Parallel)
- Delete NOT listed S3 objects (Parallel)
- Copy listed S3 objects (Parallel)
- Get the size of S3 objects (Parallel)
- Get CloudWatch Logs Insights query results
- Load partitions on Athena/Glue table (repair table)
- Create EMR cluster (For humans)
- Terminate EMR cluster
- Get EMR cluster state
- Submit EMR step(s) (For humans)
- Get EMR step state
- Get EMR step state
- Athena query to receive the result as python primitives (Iterable[Dict[str, Any])
pip install awswrangler
Runs only with Python 3.6 and beyond.
Runs anywhere (AWS Lambda, AWS Glue Python Shell, EMR, EC2, on-premises, local, etc).
P.S. Lambda Layer's bundle and Glue's wheel/egg are available to download. It's just upload and run! 🚀
P.P.S. AWS Data Wrangler counts on compiled dependencies (C/C++) so there is no support for Glue PySpark by now.
wrangler = awswrangler.Session()
wrangler.pandas.to_parquet(
dataframe=dataframe,
database="database",
path="s3://...",
partition_cols=["col_name"],
)If a Glue Database name is passed, all the metadata will be created in the Glue Catalog. If not, only the s3 data write will be done.
extra_args = {
"ServerSideEncryption": "aws:kms",
"SSEKMSKeyId": "YOUR_KMY_KEY_ARN"
}
wrangler = awswrangler.Session(s3_additional_kwargs=extra_args)
wrangler.pandas.to_parquet(
path="s3://..."
)wrangler = awswrangler.Session()
dataframe = wrangler.pandas.read_sql_athena(
sql="select * from table",
database="database"
)wrangler = awswrangler.Session()
dataframe_iter = wrangler.pandas.read_sql_athena(
sql="select * from table",
database="database",
max_result_size=512_000_000 # 512 MB
)
for dataframe in dataframe_iter:
print(dataframe) # Do whatever you wantwrangler = awswrangler.Session(athena_ctas_approach=True)
dataframe = wrangler.pandas.read_sql_athena(
sql="select * from table",
database="database"
)wrangler = awswrangler.Session()
dataframe = wrangler.pandas.read_csv(path="s3://...")wrangler = awswrangler.Session()
dataframe_iter = wrangler.pandas.read_csv(
path="s3://...",
max_result_size=512_000_000 # 512 MB
)
for dataframe in dataframe_iter:
print(dataframe) # Do whatever you wantwrangler = awswrangler.Session()
dataframe = wrangler.pandas.read_log_query(
log_group_names=[LOG_GROUP_NAME],
query="fields @timestamp, @message | sort @timestamp desc | limit 5",
)import pandas
import awswrangler
df = pandas.read_... # Read from anywhere
# Typical Pandas, Numpy or Pyarrow transformation HERE!
wrangler = awswrangler.Session()
wrangler.pandas.to_parquet( # Storing the data and metadata to Data Lake
dataframe=dataframe,
database="database",
path="s3://...",
partition_cols=["col_name"],
)wrangler = awswrangler.Session()
wrangler.pandas.to_redshift(
dataframe=dataframe,
path="s3://temp_path",
schema="...",
table="...",
connection=con,
iam_role="YOUR_ROLE_ARN",
mode="overwrite",
preserve_index=False,
)wrangler = awswrangler.Session()
dataframe = session.pandas.read_sql_redshift(
sql="SELECT ...",
iam_role="YOUR_ROLE_ARN",
connection=con,
temp_s3_path="s3://temp_path")wrangler = awswrangler.Session(spark_session=spark)
wrangler.spark.to_redshift(
dataframe=df,
path="s3://...",
connection=conn,
schema="public",
table="table",
iam_role="IAM_ROLE_ARN",
mode="append",
)dataframe.write \
.mode("overwrite") \
.format("parquet") \
.partitionBy(["year", "month"]) \
.save(compression="gzip", path="s3://...")
wrangler = awswrangler.Session(spark_session=spark)
wrangler.spark.create_glue_table(
dataframe=dataframe,
file_format="parquet",
partition_by=["year", "month"],
path="s3://...",
compression="gzip",
database="my_database")wrangler = awswrangler.Session(spark_session=spark)
dfs = wrangler.spark.flatten(dataframe=df_nested)
for name, df_flat in dfs.items():
print(name)
df_flat.show()wrangler = awswrangler.Session()
wrangler.s3.delete_objects(path="s3://...")wrangler = awswrangler.Session()
results = wrangler.cloudwatchlogs.query(
log_group_names=[LOG_GROUP_NAME],
query="fields @timestamp, @message | sort @timestamp desc | limit 5",
)wrangler = awswrangler.Session()
wrangler.athena.repair_table(database="db_name", table="tbl_name")wrangler = awswrangler.Session()
cluster_id = wrangler.emr.create_cluster(
cluster_name="wrangler_cluster",
logging_s3_path=f"s3://BUCKET_NAME/emr-logs/",
emr_release="emr-5.27.0",
subnet_id="SUBNET_ID",
emr_ec2_role="EMR_EC2_DefaultRole",
emr_role="EMR_DefaultRole",
instance_type_master="m5.xlarge",
instance_type_core="m5.xlarge",
instance_type_task="m5.xlarge",
instance_ebs_size_master=50,
instance_ebs_size_core=50,
instance_ebs_size_task=50,
instance_num_on_demand_master=1,
instance_num_on_demand_core=1,
instance_num_on_demand_task=1,
instance_num_spot_master=0,
instance_num_spot_core=1,
instance_num_spot_task=1,
spot_bid_percentage_of_on_demand_master=100,
spot_bid_percentage_of_on_demand_core=100,
spot_bid_percentage_of_on_demand_task=100,
spot_provisioning_timeout_master=5,
spot_provisioning_timeout_core=5,
spot_provisioning_timeout_task=5,
spot_timeout_to_on_demand_master=True,
spot_timeout_to_on_demand_core=True,
spot_timeout_to_on_demand_task=True,
python3=True,
spark_glue_catalog=True,
hive_glue_catalog=True,
presto_glue_catalog=True,
bootstraps_paths=None,
debugging=True,
applications=["Hadoop", "Spark", "Ganglia", "Hive"],
visible_to_all_users=True,
key_pair_name=None,
spark_jars_path=[f"s3://...jar"],
maximize_resource_allocation=True,
keep_cluster_alive_when_no_steps=True,
termination_protected=False,
spark_pyarrow=True,
tags={
"foo": "boo"
}
)
print(cluster_id)wrangler = awswrangler.Session()
for row in wrangler.athena.query(query="...", database="..."):
print(row)AWS Data Wrangler tries to parallelize everything that is possible (I/O and CPU bound task). You can control the parallelism level using the parameters:
- procs_cpu_bound: number of processes that can be used in single node applications for CPU bound case (Default: os.cpu_count())
- procs_io_bound: number of processes that can be used in single node applications for I/O bound cases (Default: os.cpu_count() * PROCS_IO_BOUND_FACTOR)
Both can be defined on Session level or directly in the functions.
Some special cases will not work with parallelism:
- GeoPandas
- Columns with non-picklable objects
To handle that use procs_cpu_bound=1 and avoid the distribution of the dataframe.
Pandas has a too generic "data type" named object. Pandas object columns can be string, dates, etc, etc, etc. We can handle this object column fine inferring the types of theses objects inside the values, Pyarrow does that like a charm. So the real problem starts when we have a completely null object column because we don't have anything to infer.
To work with null object columns you can explicitly set the expected Athena data type for the target table doing:
import awswrangler
import pandas as pd
dataframe = pd.DataFrame({
"col": [1, 2],
"col_string_null": [None, None],
"col_date_null": [None, None],
})
session = awswrangler.Session()
session.pandas.to_parquet(
dataframe=dataframe,
database="DATABASE",
path=f"s3://...",
cast_columns={
"col_string_null": "string",
"col_date_null": "date"
})-
AWS Data Wrangler practically only makes integrations. So we prefer to dedicate our energy / time writing integration tests instead of unit tests. We really like an end-to-end approach for all features.
-
All integration tests are between a local Docker container and a remote/real AWS service.
-
We have a Docker recipe to set up the local end (testing/Dockerfile).
-
We have a Cloudformation to set up the AWS end (testing/template.yaml).
DISCLAIMER: Make sure to know what you are doing. This steps will charge some services on your AWS account. And requires a minimum security skills to keep your environment safe.
-
Pick up a Linux or MacOS.
-
Install Python 3.6+
-
Install Docker and configure at least 4 cores and 8 GB of memory
-
Fork the AWS Data Wrangler repository and clone that into your development environment
-
Go to the project's directory create a Python's virtual environment for the project (python -m venv venv && source venv/bin/activate)
-
Run ./setup-dev-env.sh
-
Go to the testing directory
-
Configure the parameters.json file with your AWS environment infos (Make sure that your Redshift will not be open for the World! Configure your security group to only give access for your IP.)
-
Deploy the Cloudformation stack ./deploy-cloudformation.sh
-
Open the docker image ./open-image.sh
-
Inside the image you finally can run ./run-tests.sh