Presto is a distributed SQL query engine for big data.
See the User Manual for deployment instructions and end user documentation.
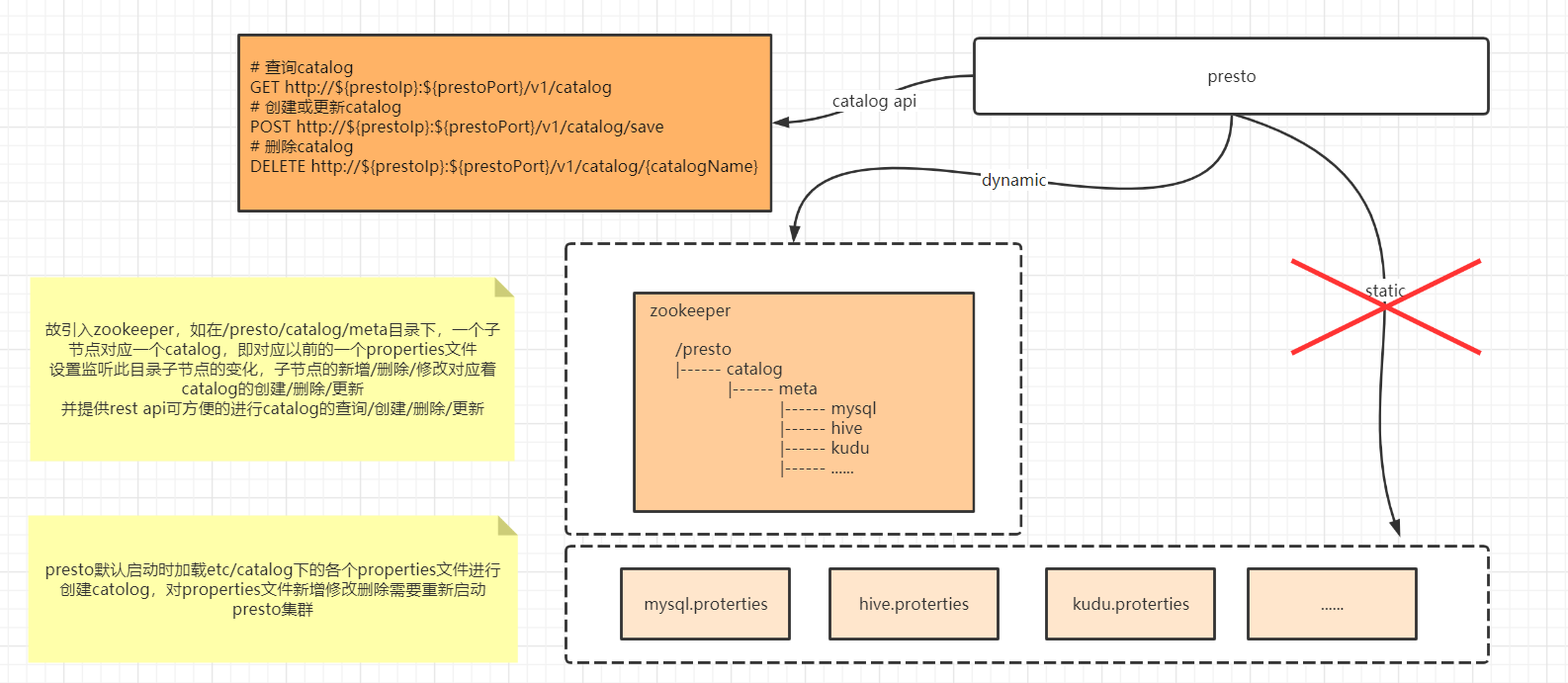
the issue about dynamic catalog on github
基于zookeeper实现presto catalog热加载,提供rest api进行catalog的curd,不需重启presto集群
Presto Dynamic Catalog, based ZooKeeper, rest api is provided for catalog curd, not need to restart.
- Presto, 345
- zookeeper, 3.4.14
详情请查看文档 Presto Dynamic Catalog
see Presto Dynamic Catalog for more information about Presto Dynamic Catalog
- Mac OS X or Linux
- Java 11, 64-bit
- Python 2.6+ (for running with the launcher script)
- Docker (for building and running tests)
Presto is a standard Maven project. Simply run the following command from the project root directory:
./mvnw clean install
On the first build, Maven will download all the dependencies from the internet and cache them in the local repository (~/.m2/repository), which can take a considerable amount of time. Subsequent builds will be faster.
Presto has a comprehensive set of unit tests that can take several minutes to run. You can disable the tests when building:
./mvnw clean install -DskipTests
After building Presto for the first time, you can load the project into your IDE and run the server. We recommend using IntelliJ IDEA. Because Presto is a standard Maven project, you can import it into your IDE using the root pom.xml file. In IntelliJ, choose Open Project from the Quick Start box or choose Open from the File menu and select the root pom.xml file.
After opening the project in IntelliJ, double check that the Java SDK is properly configured for the project:
- Open the File menu and select Project Structure
- In the SDKs section, ensure that JDK 11 is selected (create one if none exist)
- In the Project section, ensure the Project language level is set to 8 (Presto does not yet use Java 11 language features)
Presto comes with sample configuration that should work out-of-the-box for development. Use the following options to create a run configuration:
- Main Class:
io.prestosql.server.PrestoServer - VM Options:
-ea -XX:+UseG1GC -XX:G1HeapRegionSize=32M -XX:+UseGCOverheadLimit -XX:+ExplicitGCInvokesConcurrent -Xmx2G -Dconfig=etc/config.properties -Dlog.levels-file=etc/log.properties -Djdk.attach.allowAttachSelf=true - Working directory:
$MODULE_DIR$ - Use classpath of module:
presto-server-main
The working directory should be the presto-server-main subdirectory. In IntelliJ, using $MODULE_DIR$ accomplishes this automatically.
Additionally, the Hive plugin must be configured with the location of your Hive metastore Thrift service. Add the following to the list of VM options, replacing localhost:9083 with the correct host and port (or use the below value if you do not have a Hive metastore):
-Dhive.metastore.uri=thrift://localhost:9083
If your Hive metastore or HDFS cluster is not directly accessible to your local machine, you can use SSH port forwarding to access it. Setup a dynamic SOCKS proxy with SSH listening on local port 1080:
ssh -v -N -D 1080 server
Then add the following to the list of VM options:
-Dhive.metastore.thrift.client.socks-proxy=localhost:1080
-Dhive.hdfs.socks-proxy=localhost:1080
Start the CLI to connect to the server and run SQL queries:
presto-cli/target/presto-cli-*-executable.jar
Run a query to see the nodes in the cluster:
SELECT * FROM system.runtime.nodes;
In the sample configuration, the Hive connector is mounted in the hive catalog, so you can run the following queries to show the tables in the Hive database default:
SHOW TABLES FROM hive.default;
See DEVELOPMENT for information about code style, development process & guidelines.