A collection of common utilities and functions for maths, geometry generation & processing in SideFX Houdini VEX (incl. some OpenCL). Most of these were created when I started using Houdini in earnest in early 2016, but have proven themselves useful ever since and extend the built-in VEX arsenal. Some operations (e.g. Marching squares, Parallel Transport Frames, Disjoint Set etc.) were ported from some of my Clojure libraries.
You can either download a ZIP file of this library or clone the repo via Git:
git clone https://github.com/thi-ng/vexed-generation.gitAdd the following variables to your houdini.env file (replacing
<absulute-path-to-vexed-generation> with the location of where you
cloned this repo on your drive), then start Houdini:
HOUDINI_VEX_PATH = <absulute-path-to-vexed-generation>/vex;&;
HOUDINI_OCL_PATH = <absulute-path-to-vexed-generation>/opencl;&;
See here for more details about the houdini.env file.
Vexed generation functions can be used in any suitable VEX context (SOP,
SHOP etc.). Simply include vgen.h into your VEX source code / wrangle
snippet. See /vex for available functions.
All functions, types/structs in this library are prefixed with vg_.
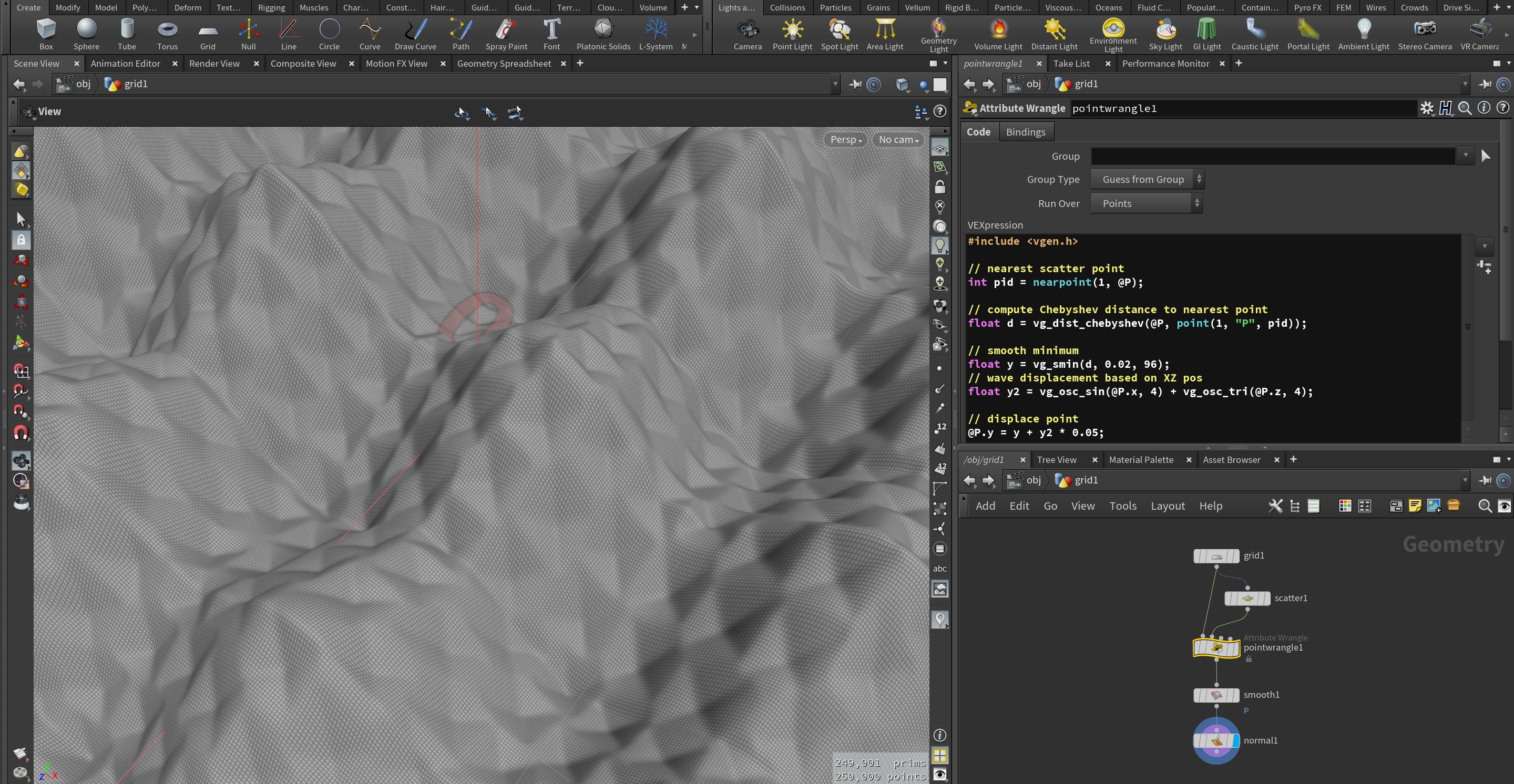
- Create a new "Grid" and configure it to:
- ZX plane
- size 1x1
- rows / cols 500 x 500
- Attach a "Scatter" node, set point count to 500, relax iterations to 20
- Attach a "Point Wrangle" using the "Grid" as first input and "Scatter" as 2nd input:
#include <vgen.h>
// version check
vg_min_version("1.4.0");
// nearest scatter point
int pid = nearpoint(1, @P);
// compute Chebyshev distance to nearest point
float d = vg_dist_chebyshev(@P, point(1, "P", pid));
// smooth minimum
float y = vg_smin(d, 0.02, 96);
// wave displacement based on XZ pos
float y2 = vg_osc_sin(@P.x, 4) + vg_osc_tri(@P.z, 4);
// displace point
@P.y = y + y2 * 0.05;TYPE here refers to one of possible types (float, vector2, vector, vector4 etc).
TYPE[] vg_into(TYPE a[]; const TYPE b[])int vg_indexof(TYPE a[]; const TYPE b)
TYPE[] vg_point_attribs_TYPE(int geo; string attr; const int pts[])vector[] vg_point_positions(int geo; const int pts[])vector[] vg_point_positions(int geo, prim)
vector2 vg_centroid(const vector2 pts[])vector vg_centroid(const vector pts[])vector vg_centroid(int geo; const int pts[])vector vg_prim_centroid(int geo, prim)int[] vg_add_edge_centroids(int geo; const int pts[])int[] vg_add_edge_centroids_uv(int geo; const int pts[])
A Disjoint Set is a data structure for undirected graphs:
vgDisjointSet ds;
// init w/ max ID
ds->init(10);
// connect IDs
ds->union(0, 3);
ds->union(2, 3);
// check if IDs are connected
ds->unified(0, 2);
// 1vector vg_closest_point_line(const vector a; const vector b; const vector p)int vg_closest_point_id(int geo; const int pts[]; const vector p)vector vg_closest_point_edges(int geo; const int edges[]; const vector p)float vg_dist_manhattan(TYPE a, b)float vg_dist_chebyshev(TYPE a, b)
Implementation based on thi.ng/ndarray
float data[];
resize(data, cols * rows);
for(int i = @numpt; --i >= 0;) {
data[i] = vector(point(0,"P", i)).y;
}
vgMSQ msq;
msq->init(data, cols, rows);
// set border values
msq->set_border(0);
// extract contours for isovalue 0.1
msq->find_contours(0, 0.1, ident());float vg_absmin(float a, b)float vg_absmax(float a, b)TYPE vg_ceil(TYPE x, prec)TYPE vg_clamp(TYPE x, a, b)int vg_eqdelta(TYPE a, b; float eps)TYPE vg_fract(TYPE x)TYPE vg_floor(TYPE x, prec)TYPE vg_mix(const TYPE a, b, t)TYPE vg_mix_bilinear(const TYPE a, b, c, d; float u, v)TYPE vg_mix_bilinear(const TYPE a, b, c, d; const vector2 uv)TYPE vg_mod(TYPE x, y)TYPE vg_round(TYPE x, prec)TYPE vg_sclamp(TYPE x, a, b; float k)TYPE vg_smin_exp(TYPE a, b; float k)TYPE vg_smin_poly(TYPE a, b; float k)TYPE vg_smin_pow(TYPE a, b; float k)TYPE vg_smin(TYPE a, b; float k)TYPE vg_smax(TYPE a, b; float k)TYPE vg_smoothstep(const TYPE e, e2, t)TYPE vg_smootherstep(const TYPE e, e2, t)TYPE vg_step(const TYPE e, t)float vg_signedArea2_xy(vector a,b,c)float vg_signedArea2_xz(vector a,b,c)float vg_signedArea2_yz(vector a,b,c)int vg_sign(float x, eps)int vg_in_range(TYPE x, min, max)int vg_minid(float a, b, c?, d?)int vg_maxid(float a, b, c?, d?)
float vg_osc_cos(float phase, freq, amp, dc)float vg_osc_saw(float phase, freq, amp, dc)float vg_osc_sin(float phase, freq, amp, dc)float vg_osc_square(float phase, freq, amp, dc)float vg_osc_sin(float phase, freq, amp, dc)float vg_osc_tri(float phase, freq, amp, dc)float vg_osc_tri_concave(float phase, freq, amp, dc)float vg_osc_sinsaw(float phase,freq, amp, dc, t)float vg_osc_sinsquare(float phase,freq, amp, dc, t)float vg_osc_sintri(float phase,freq, amp, dc, t)float vg_osc_sawsquare(float phase,freq, amp, dc, t)float vg_osc_sawtri(float phase,freq, amp, dc, t)float vg_osc_squaretri(float phase,freq, amp, dc, t)float[] vg_sample_ramp(string op_path; int n)float vg_osc_wavetable(float table[]; float phase, freq, amp, dc)float vg_osc_by_id(string id; float phase, freq, amp, dc)
Implementation based on thi.ng/geom
int[] vg_tessellate_first(int geo; const int pts[])int[] vg_tessellate_first(int geo, prim)int[] vg_tessellate_trifan(int geo; const int pts[])int[] vg_tessellate_trifan(int geo, prim)int[] vg_tessellate_quadfan(int geo; const int pts[])int[] vg_tessellate_quadfan(int geo, prim)int[] vg_tessellate_quadfan_uv(int geo; const int pts[])int[] vg_tessellate_quadfan_uv(int geo, prim)int[] vg_tessellate_mid(int geo; const int pts[])int[] vg_tessellate_mid(int geo, prim)int vg_add_triangle(int geo, a, b, c)int[] vg_quad_strip(int geo; const int row1[]; const int row2[]; int num, closed)
vector2 vg_vec2(float x, y)vector2 vg_vec2(vector3 v)vector2 vg_vec2(vector4 v)vector vg_vec3(vector2 v)vector vg_vec3(vector2 xy; float z)vector vg_vec3(vector4 v)vector4 vg_vec4(vector2 xy, zw)vector4 vg_vec4(vector xyz; float w)
Here TYPE is one of vector2, vector, vector4:
TYPE vg_swizzle(TYPE v; int x, y, z?, w?)
This project is licensed under the Apache Software License 2.0
© 2016 - 2020 Karsten Schmidt