nginx | Apache HTTPD | Lighttpd | express.js | koa.js | Customization
Simple HTTP Error Page Generator. Create a bunch of custom error pages - suitable to use with Lighttpd, Nginx, expressjs, koajs ,Apache-Httpd or any other Webserver.
- Static pages (for webservers)
- Multi-Language (i18n) support
- Generator script to customize pages
- Native express.js middleware
- Native koa.js middleware
Just clone/download the git repository or use the prebuild packages (only the generated html files are included)
Direct Download
Shell/Bash
# TAR Archive
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/AndiDittrich/HttpErrorPages/master/dist/pages.tarNGINX supports custom error-pages using multiple error_page directives.
File: default.conf
Example - assumes HttpErrorPages are located into /var/ErrorPages/.
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
root /var/www;
index index.html;
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ =404;
# add one directive for each http status code
error_page 400 /ErrorPages/HTTP400.html;
error_page 401 /ErrorPages/HTTP401.html;
error_page 402 /ErrorPages/HTTP402.html;
error_page 403 /ErrorPages/HTTP403.html;
error_page 404 /ErrorPages/HTTP404.html;
error_page 500 /ErrorPages/HTTP500.html;
error_page 501 /ErrorPages/HTTP501.html;
error_page 502 /ErrorPages/HTTP502.html;
error_page 503 /ErrorPages/HTTP503.html;
}
# redirect the virtual ErrorPages path the real path
location /ErrorPages/ {
alias /var/ErrorPages/;
internal;
}Apache Httpd 2.x supports custom error-pages using multiple ErrorDocument directives.
File: httpd.conf or .htaccess
Example - assumes HttpErrorPages are located into your document root /var/www/...docroot../ErrorPages.
ErrorDocument 400 /ErrorPages/HTTP400.html
ErrorDocument 401 /ErrorPages/HTTP401.html
ErrorDocument 403 /ErrorPages/HTTP403.html
ErrorDocument 404 /ErrorPages/HTTP404.html
ErrorDocument 500 /ErrorPages/HTTP500.html
ErrorDocument 501 /ErrorPages/HTTP501.html
ErrorDocument 502 /ErrorPages/HTTP502.html
ErrorDocument 503 /ErrorPages/HTTP503.htmlLighttpd supports custom error-pages using the server.errorfile-prefix directive.
File: lighttpd.conf
Example - assumes HttpErrorPages are located into /var/www/ErrorPages/.
server.errorfile-prefix = "/var/www/ErrorPages/HTTP"HttpErrorPages are available as NPM-Package - just install http-error-pages via npm/yarn
Installation
yarn add http-error-pages
Example
A ready-to-use example can be found in examples/express.js
const _express = require('express');
const _webapp = _express();
const _httpErrorPages = require('http-error-pages');
async function bootstrap(){
// demo handler
_webapp.get('/', function(req, res){
res.type('.txt').send('HttpErrorPages Demo');
});
// throw an 403 error
_webapp.get('/my403error', function(req, res, next){
const myError = new Error();
myError.status = 403;
next(myError);
});
// throw an internal error
_webapp.get('/500', function(req, res){
throw new Error('Server Error');
});
// use http error pages handler (final statement!)
// because of the asynchronous file-loaders, wait until it has been executed
await _httpErrorPages.express(_webapp, {
lang: 'en_US',
footer: 'Hello <strong>World</strong>'
});
// start service
_webapp.listen(8888);
}
// invoke bootstrap operation
bootstrap()
.then(function(){
console.log('Running Demo on Port 8888');
})
.catch(function(e){
console.error(e);
});Options
Syntax: Promise _httpErrorPages.express(expressWebapp [, options:Object])
template- the path to a custom EJS template used to generate the pages. default assets/template.ejscss- the path to a precompiled CSS file injected into the page. default assets/layout.cssfooter- optional page footer content (html allowed). default nulllang- language definition which should be used (available in thei18n/directory). default en_US
HttpErrorPages are available as NPM-Package - just install http-error-pages via npm/yarn
Installation
yarn add http-error-pages
Example
A ready-to-use example can be found in examples/koa.js. Keep in mind that the following example has to be executed within an async context!
const _koa = require('koa');
const _webapp = new _koa();
const _httpErrorPages = require('http-error-pages');
// use http error pages handler (INITIAL statement!)
// because of the asynchronous file-loaders, wait until it has been executed - it returns an async handler
_webapp.use(await _httpErrorPages.koa({
lang: 'en_US',
footer: 'Hello <strong>World</strong>'
}));
// add other middleware handlers
_webapp.use(async (ctx, next) => {
if (ctx.path == '/'){
ctx.type = 'text';
ctx.body = 'HttpErrorPages Demo';
}else{
return next();
}
});
// start service
_webapp.listen(8888);Options
Syntax: Promise _httpErrorPages.koa([options:Object])
template- the path to a custom EJS template used to generate the pages. default assets/template.ejscss- the path to a precompiled CSS file injected into the page. default assets/layout.cssfooter- optional page footer content (html allowed). default nulllang- language definition which should be used (available in thei18n/directory). default en_US
First of all, clone or download the http-error-pages repository.
You have to install the node dev dependencies to build the pages:
# run the yarn command within the cloned repository
yarn install
# or if you more familiar with npm..
npm installTo customize the pages, you can edit any of the template files and finally run the generator-script.
All generated html files are located into the dist/ directory by default.
If you wan't to add custom pages/additional error-codes, just put a new entry into the i18n/pages-en_US.json file (its recommended to copy the file).
The generator-script will process each entry and generates an own page.
- config.json - basic configuration options
- assets/layout.scss - the SCSS based styles
- assets/template.ejs - the EJS based page template
- i18n/pages-.json - the page definitions (multilanguage)
- dist/*.html - generator output directory
To modify the page styles, just edit the SCSS based layout assets/layout.scss and finally run gulp to generate the css code. The new layout file is stored in assets/layout.css - run the page generator to create the pages.
Example
# start gulp sccs via npm
$ npm run gulp
> http-error-pages@0.6.0 gulp HttpErrorPages
> gulp
[08:40:33] Using gulpfile HttpErrorPages/gulpfile.js
[08:40:33] Starting 'sass'...
[08:40:34] Finished 'sass' after 108 ms
[08:40:34] Starting 'default'...
[08:40:34] Finished 'default' after 40 μs
# generate http-error-pages using modified stylesheet
$ npm run static
> http-error-pages@0.6.0 static HttpErrorPages
> node bin/generator.js static
Paths
|- Config: HttpErrorPages/config.json
|- Template: HttpErrorPages/assets/template.ejs
|- Styles: HttpErrorPages/assets/layout.css
|- Pages: HttpErrorPages/i18n/pages-en_US.json
Generating static pages
|- Page <HTTP404.html>
|- Page <HTTP403.html>
|- Page <HTTP400.html>
|- Page <HTTP500.html>
|- Page <HTTP501.html>
|- Page <HTTP502.html>
|- Page <HTTP520.html>
|- Page <HTTP503.html>
|- Page <HTTP521.html>
|- Page <HTTP533.html>
|- Page <HTTP401.html>
Static files generatedTo use a different language just provide a custom page definition - in case the file is located in i18n you can use the --lang option
Example
$ npm run static -- --lang pt_BR
> http-error-pages@0.6.0 static HttpErrorPages
> node bin/generator.js static "--lang" "pt_BR"
Paths
|- Config: HttpErrorPages/config.json
|- Template: HttpErrorPages/assets/template.ejs
|- Styles: HttpErrorPages/assets/layout.css
|- Pages: HttpErrorPages/i18n/pages-pt_BR.json
Generating static pages
|- Page <HTTP404.html>
|- Page <HTTP400.html>
|- Page <HTTP401.html>
|- Page <HTTP403.html>
|- Page <HTTP500.html>
|- Page <HTTP501.html>
|- Page <HTTP502.html>
|- Page <HTTP520.html>
|- Page <HTTP503.html>
|- Page <HTTP521.html>
|- Page <HTTP533.html>
Static files generated
Create custom error codes/pages used by e.g. CloudFlare
Example
// webserver origin error
"520": {
"title": "Origin Error - Unknown Host",
"message": "The requested hostname is not routed. Use only hostnames to access resources."
},
// webserver down error
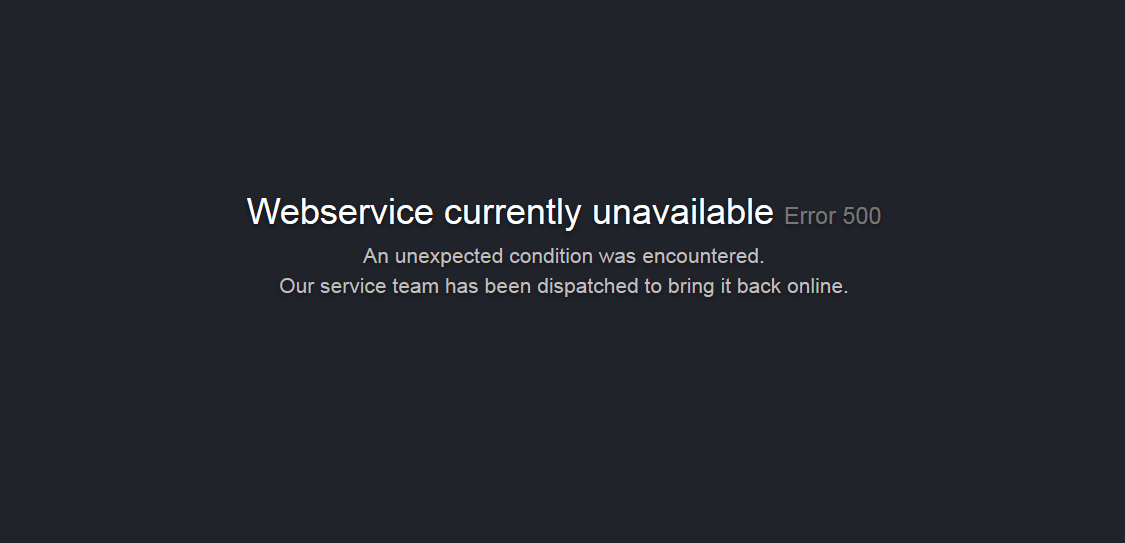
"521": {
"title": "Webservice currently unavailable",
"message": "We've got some trouble with our backend upstream cluster.\nOur service team has been dispatched to bring it back online."
},The footer message can easily be changed/removed by editing config.json.
Example - customm footer
{
// Output Filename Scheme - eg. HTTP500.html
"scheme": "HTTP%d.html",
// Footer content (HTML Allowed)
"footer": "Contact <a href=\"mailto:info@example.org\">info@example.org</a>"
}Example - no footer
{
// Output Filename Scheme - eg. HTTP500.html
"scheme": "HTTP%d.html"
}The HTML template is based on ejs and located in assets/template.ejs - you can apply any kind of changes.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>HTTP<%= code %> - <%= title %></title>
</head><body>
<h2>Hello World</h2>
<div class="cover"><h1><%= title %> <small>Error <%= code %></small></h1><p class="lead"><%= message %></p></div>
</body></html>The http-error-pages generator allows you to use custom template/config files directly. This is the recommended method to create full-customized pages.
$ npm run static -- --help
> http-error-pages@0.6.0 static HttpErrorPages
> node bin/generator.js static "--help"
Usage: static [options] [config]
run http-error-pages generator
Options:
-t, --template <path> path to your custom EJS template file
-s, --styles <path> path to your custom stylesheet (precompiled as CSS!)
-p, --pages <path> path to your custom page definition
-l, --lang <lang> the language of the default page definition
-o, --out <path> output directory
-h, --help output usage information
Example - use custom files
We assume you've created a folder named example_org which contains all relevant template files
# via npm run-script (cross platform)
$ npm run static -- -t example_org/template.ejs -s example_org/styles.css -p example_org/pages.json -o example_org/output
# .. or directly (linux only)
$ http-error-pages -t example_org/template.ejs -s example_org/styles.css -p example_org/pages.json -o example_org/outputHttpErrorsPages is OpenSource and licensed under the Terms of The MIT License (X11) - your're welcome to contribute