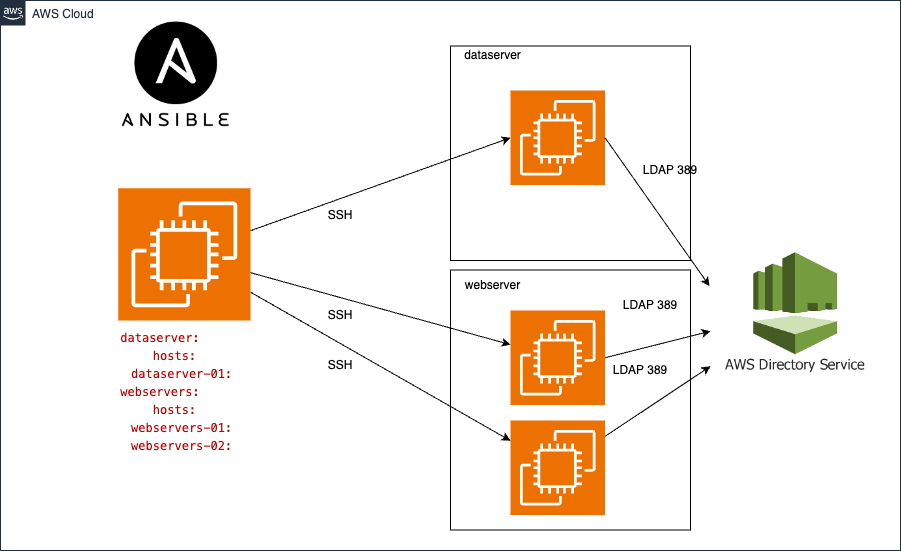
Description: Automating the Process of Joining Linux Systems to an Active Directory Domain using Ansible and SSSD
.
├── ansible.cfg # contains important Ansible settings that control how Ansible operates
├── ansible-navigator.log # output of ansible-navigator
├── CHANGELOG.md # Changelogs keep track of project versioning
├── inventory
│ ├── groups # the groups file is used to define and organize host groups
│ ├── group_vars
│ │ ├── dataseserver.yml
│ │ └── department
│ │ ├── department.yml
│ │ └── vault.yaml # contains AD credatilas
│ └── hosts.yml
├── output # output of ansible-playbook
├── playbooks
│ └── ad_join.yaml # AD playbook
├── README.md
└── roles # this hierarchy represents a "role"
└── ad_join # ad_join role contains the steps to join the domain using the SSSD
├── CHANGELOG.md
├── defaults # define default variable values for the role.
│ └── main.yml
├── files
├── handlers # The handlers directory is used to define handlers,
│ └── main.yml
├── meta # defines metadata about an Ansible role
│ └── main.yml
├── README.md
├── tasks
│ ├── ad_join.yml # Import all tasks to join the AD
│ ├── check.yml # Check if the instance joined correctly the domaine.
│ ├── discover.yml # Discover the defined AD: /usr/sbin/realm discover { domain }}
│ ├── install.yml # Install the required Red Hat packages
│ ├── join.yml # defines step to join the doamin and check: realm join -v -U admin corp.example.com --install=/
│ ├── leave.yml # realm leave example.com
│ ├── main.yml # entry point for the role.
│ ├── permit.yml # To allow all user access
│ ├── sshd_config.yml # sshd_config config update
│ └── sssd_config.yml # sssd_config config update
├── templates
├── tests
│ ├── inventory
│ └── test.yml
└── vars
└── main.yml # Variables defined in this file are added to the role's variables and take precedence over the defaults/main.yml file.To automate the process of joining Linux systems to an Active Directory (AD) domain using SSSD, follow these steps:
on Ubuntu
sudo apt install ansibleon Centos 7
yum -y install ansibleon Centos 8
pip3 install ansible --userOn RHEL 7
sudo subscription-manager repos --enable rhel-7-server-ansible-2.9-rpms
yum -y install ansibleOn RHEL 8
subscription-manager repos --enable ansible-2.9-for-rhel-8-x86_64-rpms
yum install ansibleOr you can use ansible-navigator
sudo subscription-manager repos --enable ansible-automation-platform-2.0-early-access-for-rhel-8-x86_64-rpms
# Isntall ansible-navigator
dnf install ansible-navigatorOn RHEL 9:
sudo subscription-manager repos --enable ansible-automation-platform-2.2-for-rhel-9-x86_64-rpms
sudo dnf -y update
# Isntall ansible-navigator
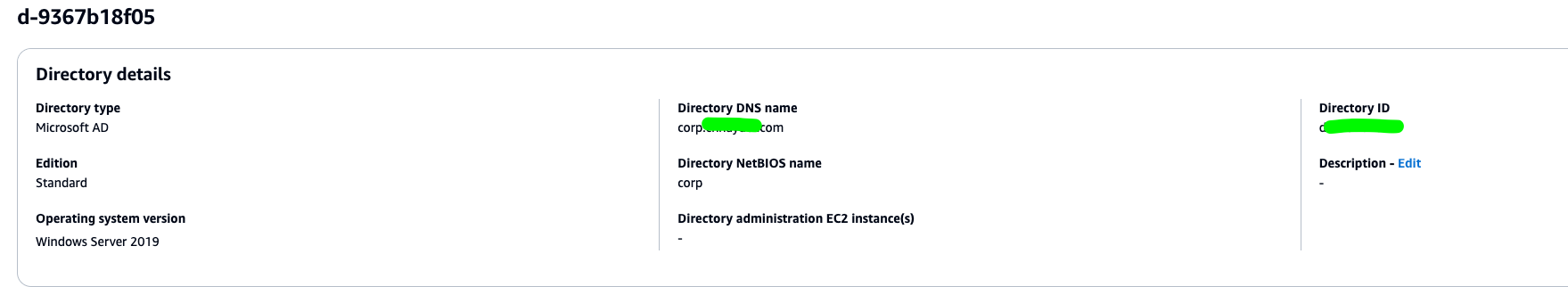
sudo dnf -y install ansible-navigatorConfigure AWS Managed Microsoft AD Active Directory
Directory services options in AWS
Ensure that your servers can resolve the domain name. You can use 'dig corp.example.com' to check.
Ensure that you can reach the domain name via LDAP port (389) and DNS port (53). You need to whitelist your outbound traffic to your AD server.
You can use the cloud key-pair to connect to your instance or generate new ssh key as below :
ssh-keygenCopy ssh-key to managed node
ssh-copy-id user@ipCreate config file
vim ~/.ssh/configAdd the following configuration to conig
Host dataserver-01
Hostname 10.x.x.x
User ec2-user
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_rsa
Host webserver-01
Hostname 10.x.x.x
User ec2-user
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_rsaThe 'ad_join' role has default variables. To use this role, you need to override the existing variables with your AD credentials. You need to provide the details to join Linux into the domain, like the domain user who has the right to add clients into the domain, DNS server, and user password. The default role variables are specified:
ad_server:
user: admin # Admin user
pass: 'test' # Pass user
domain: corp.exmple.com # domain name
admin_group: "AWS Delegated Administrators" # Admin AD group
ou_membership: OU=Computers,DC=example,DC=com # ou_membership
admin_sudo: 'AWS\ Delegated\ Administrators' The inventory is designed to be more generic for all IT organizations. You can create your customized inventory or override the existing one.
[department]
[department:children]
dataseserver
webservers
[dataseserver]
[webservers]
The databaseservers and webservers groups are part of the department group. Let's assume that you have two EC2 instances, one for the database server and the other for the web server. You would like to join both instances to the AD. So, we can add the AD configuration in the department group to override the role variables.
Under 'inventory/group_vars/department/department.yml':
ad_server:
user: "admin"
domain: "corp.chhayder.com"
admin_group: "AWS Delegated Administrators"
admin_sudo: 'AWS\ Delegated\ Administrators'Here, the last variable you need to override is pass. However, it is not a best practice to define a plain-text password. We need to provide the admin user password in a secure way to the inventory. Ansible Vault provides a way to encrypt and manage sensitive data such as passwords. For more information about Ansible Vault, please refer to:
A brief introduction to Ansible Vault
TThe inventory includes inventory/group_vars/department/vault.yaml which contains the ad_server.pass definition. You simply need to edit this file and provide your AD password as follows:
ansible-vault edit inventory/group_vars/department/vault.yamlUpdate the pass value key.
ad_server:
pass: 'exmple'For ansible-playbook: You need to provide the password to decrypt vault.yaml:
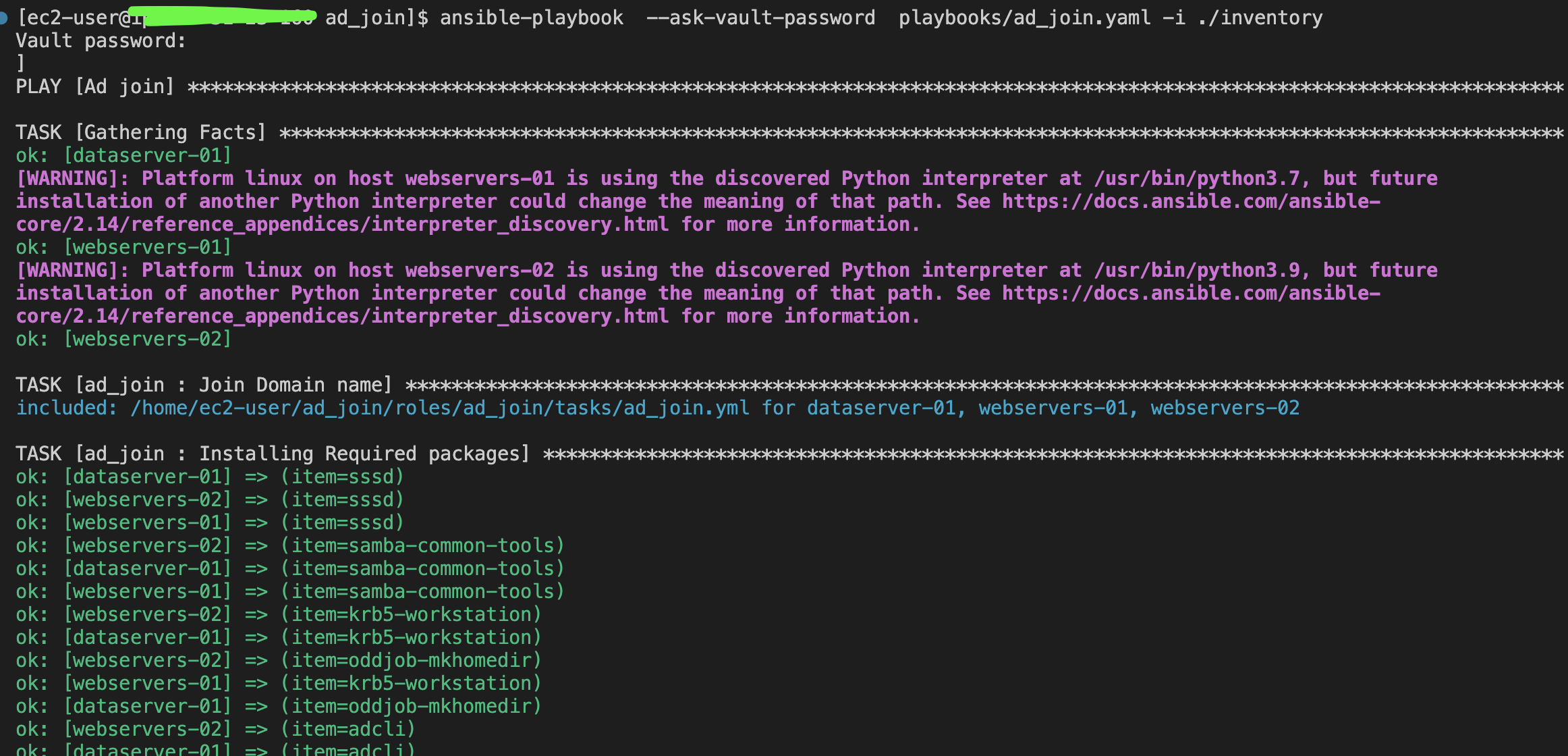
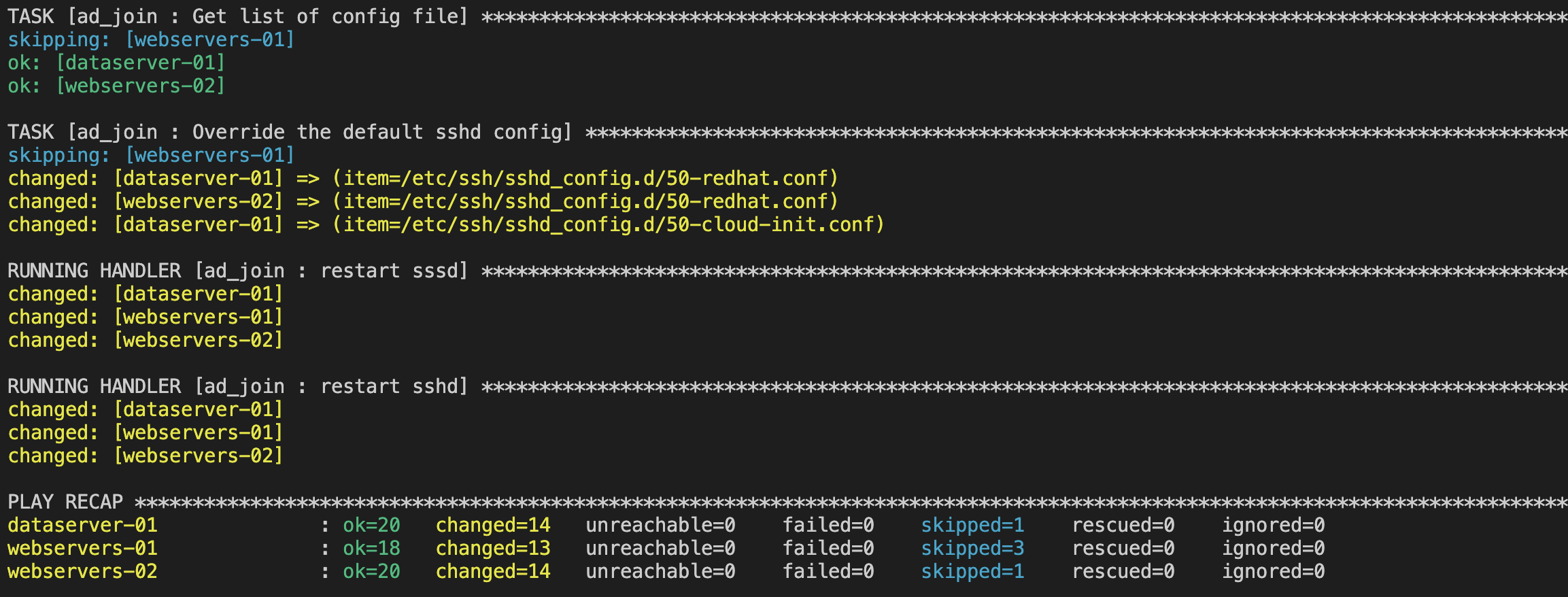
ansible-playbook --ask-vault-password playbooks/ad_join.yaml -i ./inventoryFor ansible-navigator:
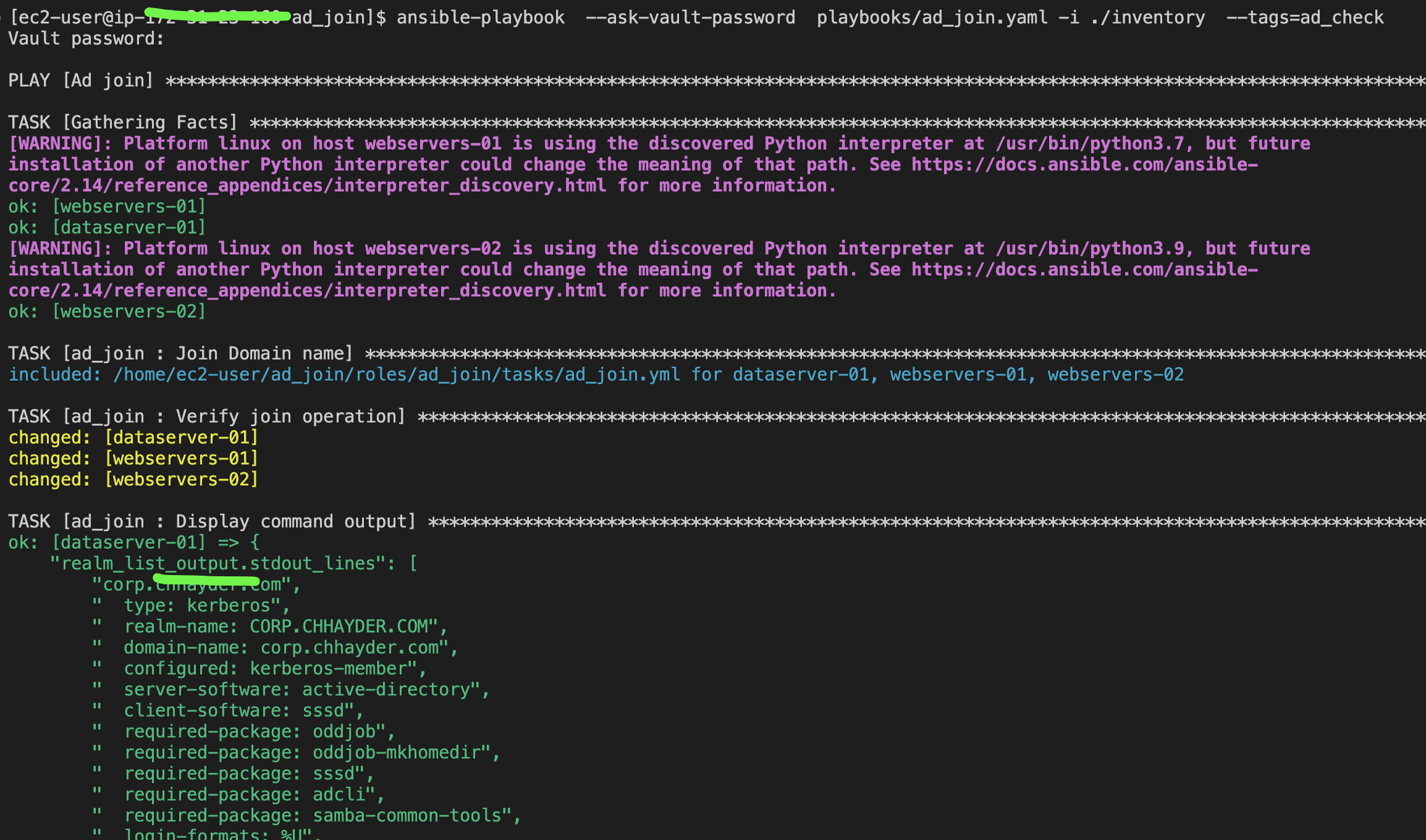
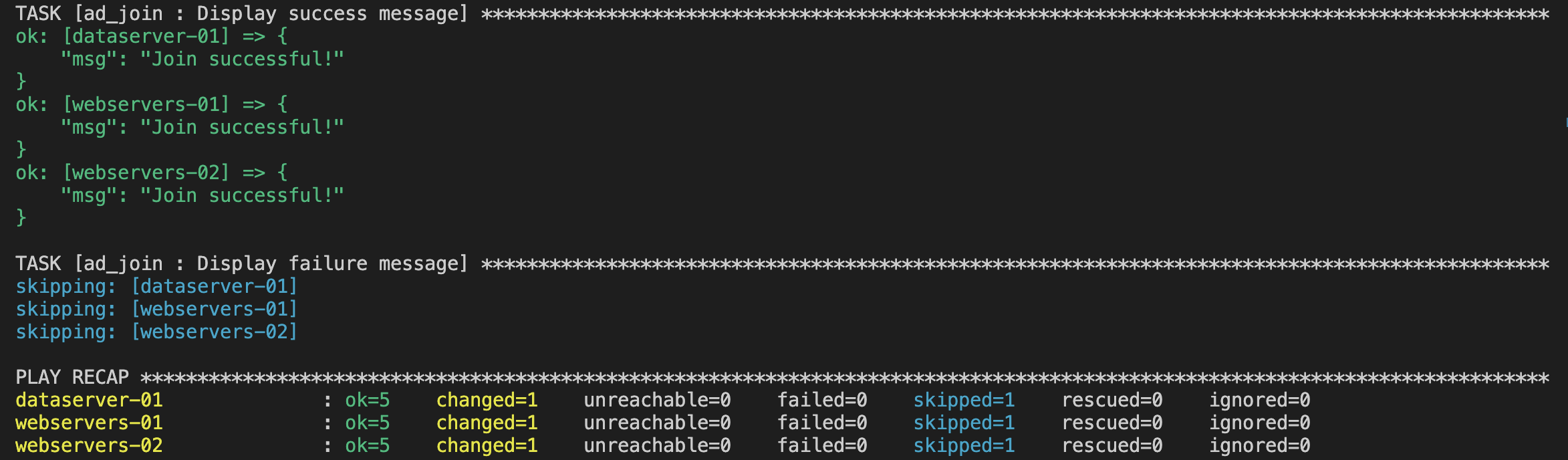
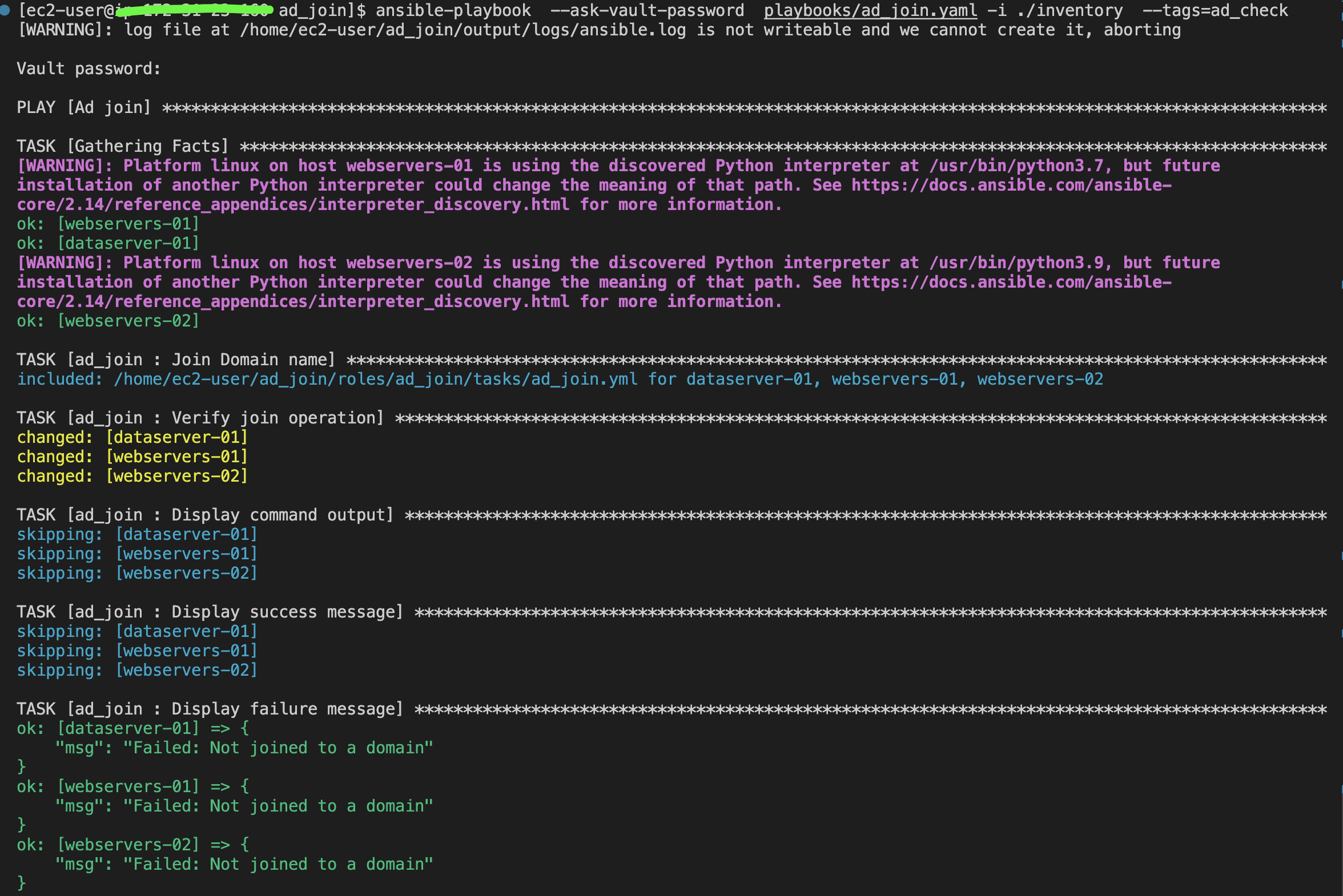
ansible-navigator run -m stdout playbooks/ad_join.yaml --playbook-artifact-enable false --vault-id one@promptTo verify if your instance has already joined the domain, you can run the same playbook using the ad_check tag:
ansible-playbook --ask-vault-password playbooks/ad_join.yaml -i ./inventory --tags=ad_checkFor ansible-navigator:
ansible-navigator run -m stdout playbooks/ad_join.yaml --playbook-artifact-enable false --vault-id one@prompt --tags=ad_checkOr You can connect to the instance and run the follwoinfg commands.
sudo realm listid __user_name__ssh -l user@corp.exmple.com IPxxxxxxxxxxThe user can enter the username in either the username@example.com or EXAMPLE\username format. Then, you should be able to connect to the server with the specified user. Furthermore, if your user is part of the AWS Delegated Administrators group in the AD, it allows you to run programs with the security privileges.
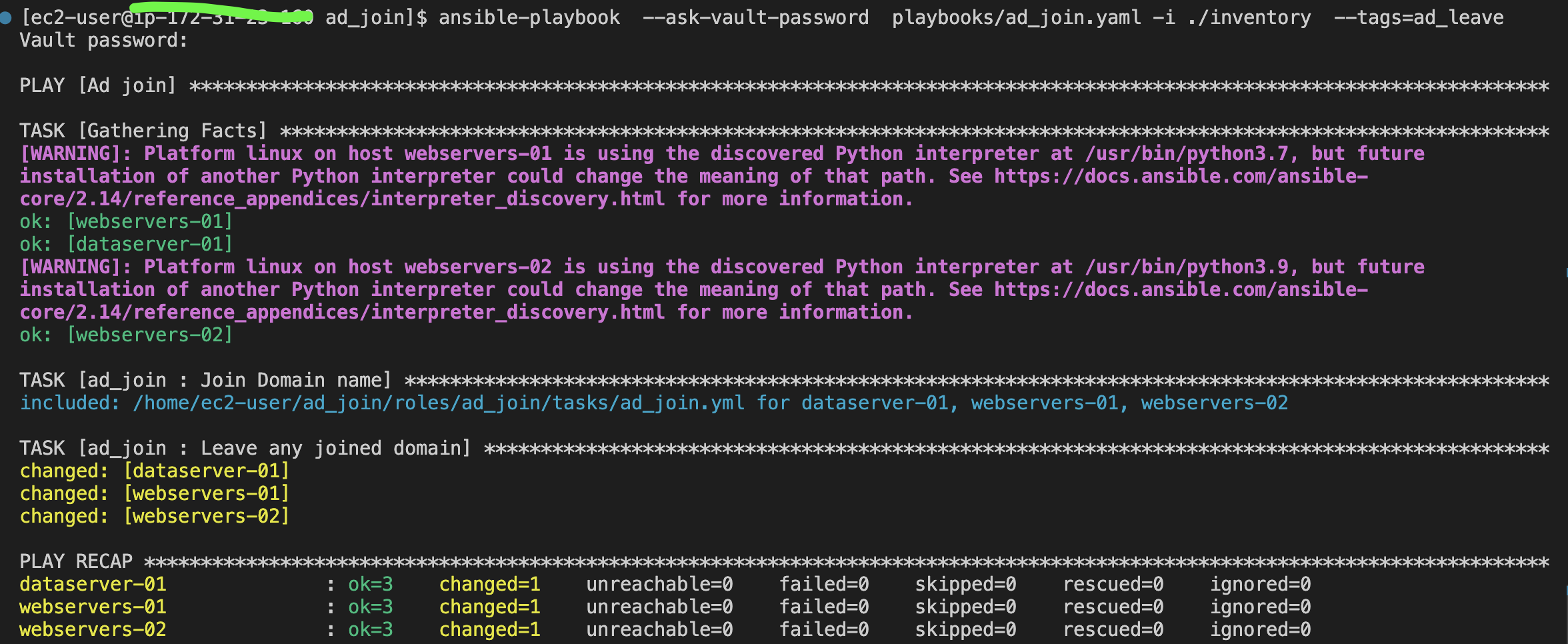
If you want to reverse the process and remove yourself from the domain, You can run the same playbook using the ad_leave tag:
ansible-playbook --ask-vault-password playbooks/ad_join.yaml -i ./inventory --tags=ad_leaveFor ansible-navigator:
ansible-navigator run -m stdout playbooks/ad_join.yaml --playbook-artifact-enable false --vault-id one@prompt --tags=ad_leaveOr you can simply run the ‘realm leave’ command followed by the domain name, as shown below.
realm leave example.com3 EC2 instance:
- RHEL 9.4 instance dataserver-01
- Amazon 2023 instance webservers-01
- Amazon 2 webservers-02
SSH Configuration
cat ~/.ssh/config
Host dataserver-01
HostName IPxx.xxx.xxx.xx
User ec2-user
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/xxx.pem
Host webservers-01
HostName IPxx.xxx.xxx.xx
User ec2-user
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/xxx.pem
Host webservers-02
Hostname IPxx.xxx.xxx.xx
User ec2-user
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/xxx.pemAWS AD Directory