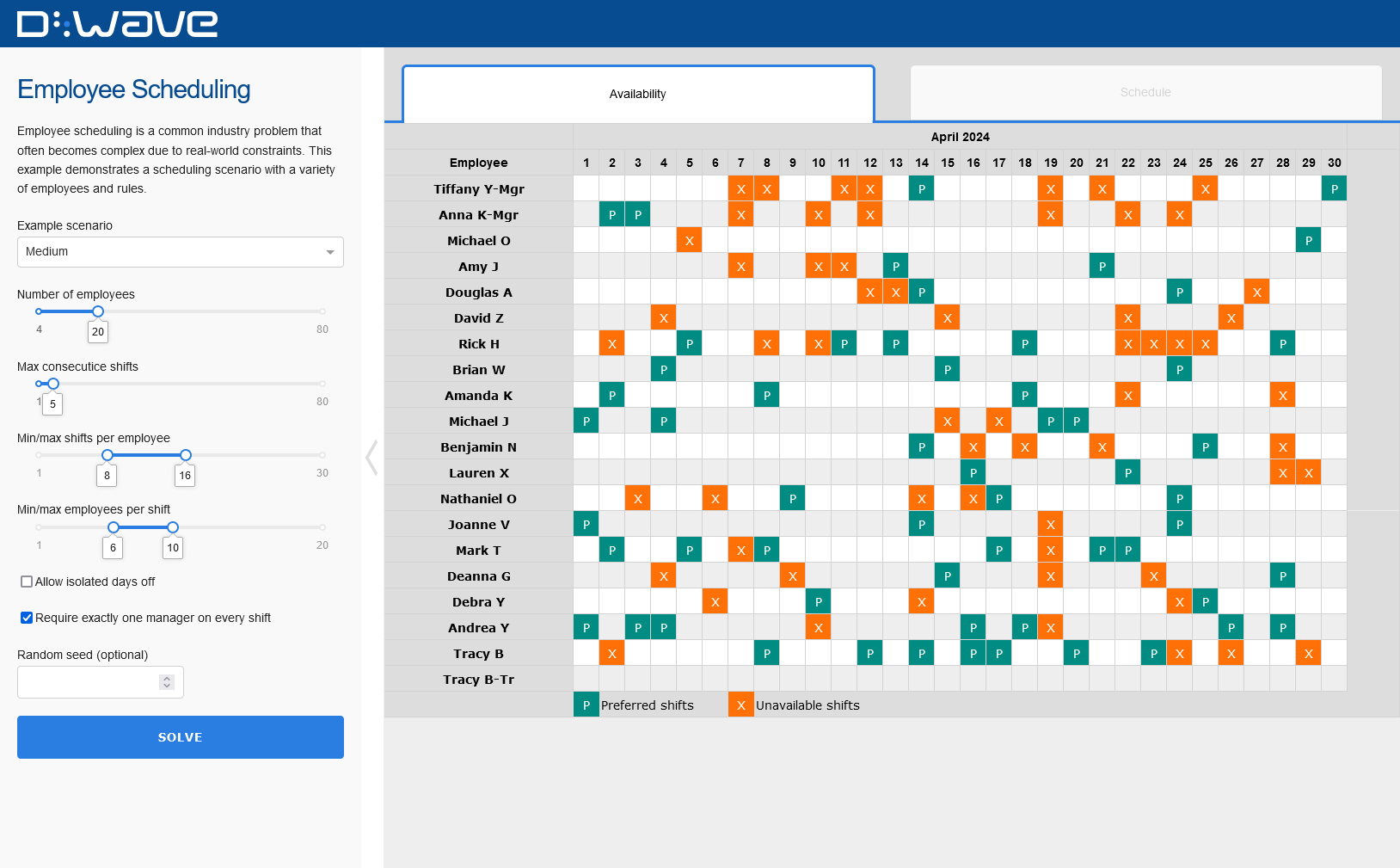
Employee scheduling is a common industry problem that often becomes complex due to real-world constraints. This example demonstrates a scheduling scenario with a variety of employees and rules.
You can run this example without installation in cloud-based IDEs that support the Development Containers specification (aka "devcontainers").
For development environments that do not support devcontainers, install
requirements:
pip install -r requirements.txt
If you are cloning the repo to your local system, working in a virtual environment is recommended.
Your development environment should be configured to access Leap’s Solvers. You can see information about supported IDEs and authorizing access to your Leap account here.
To run the demo, type the python app.py command into your terminal and then open a web browser
to the URL printed to the terminal.
Set any of the input options to configure the problem and then click the "Solve CQM" button. While the problem is being solved, you can see status updates in the browser and terminal.
The employee availability chart shows employee shift preferences and unavailable days (PTO). Preferred shifts are in teal and marked with a 'P', while unavailable shifts are in orange and marked with an 'X'.
In the chart, there are three different types of employees.
- Managers: These are employees with 'Mgr' at the end of their name.
- Employees: These are employees with no tag at the end of their name.
- Trainees: These are employees with 'Tr' at the end of their name. The trainee has the same name as their trainer. The trainee can only be scheduled to work on a shift that their trainer is also scheduled to work.
The chart displays employee preferences and availability for this month. It will always display the current month, with one column for each day in this current month.
Input options under the Basic Configuration tab are as follows:
- Number of employees: Schedules always include 2 managers and 1 trainee.
- Example scenario: Auto-populates all settings with scenarios of varying sizes that produce feasible solutions.
Additional input options under the Advanced Configuration tab are as follows:
- Allow isolated days off: Unchecked, this option means that employees are scheduled at least two consecutive days off between work days.
- Require a manager on every shift: Checked, this option means that every shift must have exactly one manager on duty to supervise.
- Min/max shifts per employee: The range you set determines the number of shifts an employee can work in the month.
- Min/max employees per shift: The range you set determines how many employees need to be assigned to each shift.
- Max consecutive shifts: The maximum number of consecutive shifts an employee can be scheduled before a day off must be scheduled.
- Random seed: Optional; use if you want consistency between subsequent runs of the example.
Once the problem has completed, the best solution returned is displayed in place of "Employee Availability". Click back to "Employee Availability" using the tabs at the top of the schedule card.
The solution returned is either the best feasible solution (if a feasible solution is found) or the best infeasible solution (if no feasible solution is found). If an infeasible solution is found, scrolling down shows the list of constraints that were violated.