Constructing a UNet requires you to keep track of every signal size that flow through the UNet. This can lead to size mismatches when constructing the
neutral network. To remedy this issue, I created a small PyTorch UNet module
that calculates the sizes for you. You can even customize the building blocks
used to construct the UNet.
Install PyTorch following instructions on their website. Then install this package:
pip install git+https://github.com/thomasjpfan/pytorch_unet.git
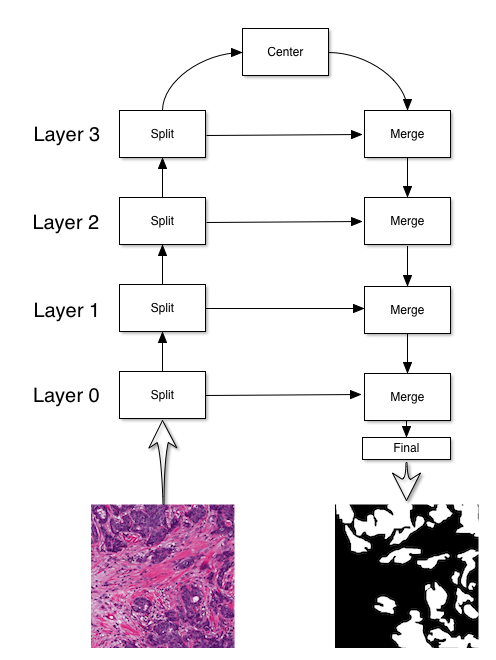
The UNet architecture, introduced in this paper, has the following structure:
The primary use for a UNet is to perform segmentation. In the above case, the
UNet is used to detect cancerous regions in the input image. There are four
blocks to constructing a UNet: split, center, merge, and final blocks. My implementation of UNet has the following initialization method:
class UNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, *,
input_shape,
num_classes,
layers=4,
features_root=16,
split_block=SplitBlock,
merge_block=MergeBlock,
center_block=CenterBlock,
final_block=FinalBlock,
double_center_features=True):
...You can alter any of the four blocks used to generate the UNet. The layers parameter determines how tall the UNet is. For example, the image above has four layers. Each split layer upscales the signal to 2**layer*features_root where layer is the zero-indexed layer number.
I will use the short hand, (features, size), in my diagrams to denote the shape features x size x size of my signals. For example, (112, 32), means the signal has the shape 112x32x32.
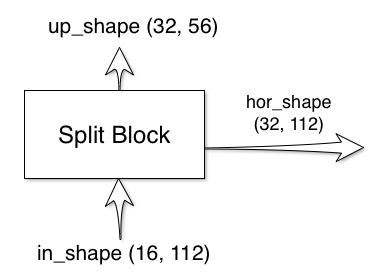
The split block has two outputs and one input:
The shapes of the outputs are calculated for you, all you have to do is
provide your custom implementation of the split block. For reference, here is
the default split_block implementation:
class SplitBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_shape, up_shape, hor_shape, layer):
...
def forward(self, x):
...
return self.max_pool(hor), horThe extra layer index is passed in, just in case you want to adjust the block for different layers. To create your custom implementation, just copy the SplitBlock implementation and change the bodies of __init__ and forward. Make sure that the forward call returns two values, the first being the up signal and second being the hor signal. The parameters {}_shape uses the convention (features, size). You can use these parameters to perform assertions on the signal shapes during
initialization.
The center block has one input and one output:
This block does not change the size of the signal, only the number of features change. Thus the default center_block implementation just needs the feature number:
class CenterBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_feats, out_feats):
...
def forward(self, x):
return self.layers(x)If double_center_features from UNet initialization is True, out_feats is two times in_feats, otherwise they are the same.
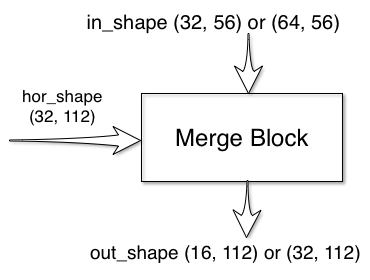
The merge block has two inputs and one output:
The default implementation of this block is:
class MergeBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_shape, out_shape, hor_shape, layer):
...
def forward(self, x, hor):
return outThe in_shape and out_shape parameters depends on the double_center_features. If the features were doubled at the center block, the features going down the merge block will also be doubled. forward takes in
two inputs and outputs one signal.
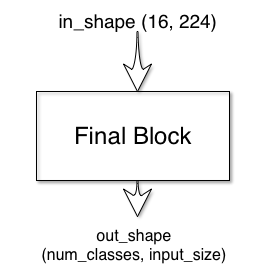
The final block has one input and one output:
The default final block just has a single convolution layer:
class FinalBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_feats, out_feats):
self.layer = nn.Conv2d(in_feats, out_feats, kernel_size=1)
def forward(self, x):
return self.layer(x)The final block outputs a signal of size (num_classes, input_size), which
which was passed into UNet initialization. Each pixel is given a logit value
for each class. This can transform to a probability by using a sigmoid layer.