k3sup is a light-weight utility to get from zero to KUBECONFIG with k3s on any local or remote VM. All you need is ssh access and the k3sup binary to get kubectl access immediately.
The tool is written in Go and is cross-compiled for Linux, Windows, MacOS and even on Raspberry Pi.
How do you say it? Ketchup, as in tomato.
This tool uses ssh to install k3s to a remote Linux host. You can also use it to join existing Linux hosts into a k3s cluster as agents. First, k3s is installed using the utility script from Rancher, along with a flag for your host's public IP so that TLS works properly. The kubeconfig file on the server is then fetched and updated so that you can connect from your laptop using kubectl.
You may wonder why a tool like this needs to exist when you can do this sort of thing with bash.
k3sup was developed to automate what can be a very manual and confusing process for many developers, who are already short on time. Once you've provisioned a VM with your favourite tooling, k3sup means you are only 60 seconds away from running kubectl get pods on your own computer. With version 0.2.0, you can even join other nodes into any existing k3s cluster.
Uses:
- Bootstrap Kubernetes with k3s onto any VM - either manually, during CI or through
cloudinit - Get from zero to
kubectlwithk3son Raspberry Pi (RPi), VMs, AWS EC2, Packet bare-metal, DigitalOcean, Civo, Scaleway, and others - Fetch a working KUBECONFIG from an existing
k3scluster - Join nodes into an existing
k3scluster withk3sup join
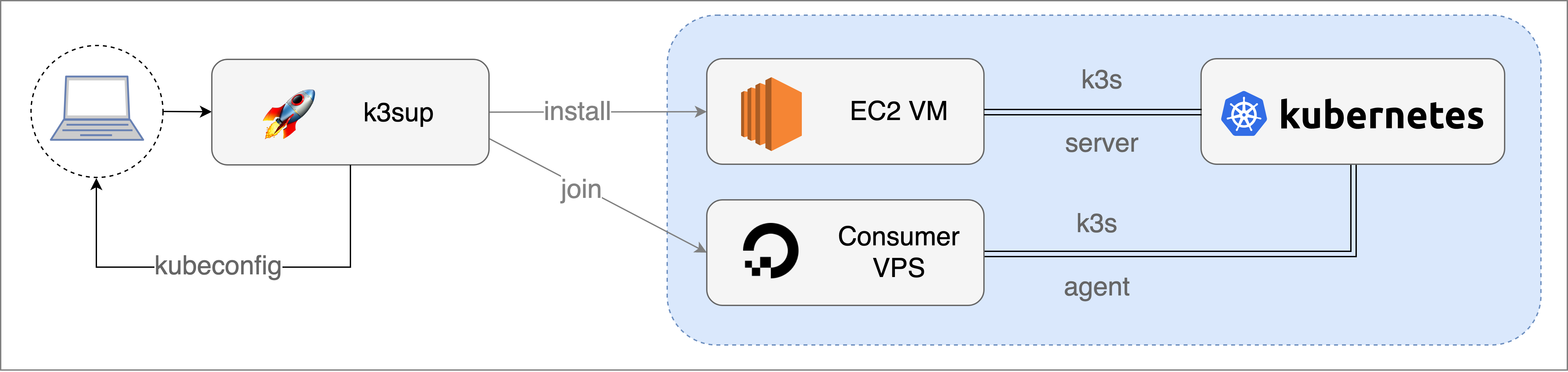 Conceptual architecture, showing
Conceptual architecture, showing k3sup running locally against any VM such as AWS EC2 or a VPS such as DigitalOcean.
k3sup is distributed as a static Go binary. You can use the installer on MacOS and Linux, or visit the Releases page to download the executable for Windows.
curl -sLS https://get.k3sup.dev | sh
sudo install k3sup /usr/local/bin/
k3sup --helpIn the demo I install Kubernetes (k3s) onto two separate machines and get my kubeconfig downloaded to my laptop each time in around one minute.
- Ubuntu 18.04 VM created on DigitalOcean with ssh key copied automatically
- Raspberry Pi 4 with my ssh key copied over via
ssh-copy-id
Watch the demo:
k3sup is Open Source Software (OSS) and was created by Alex Ellis - the Founder of OpenFaaS ® and a voluntary CNCF Ambassador.
Do you like k3sup or enjoy any of Alex's other work? 🍻
Join dozens of other developers 🏆 in supporting Alex and his work through GitHub Sponsors today. You'll get into the Insiders Track and access to regular email updates on all his work.
The k3sup tool is designed to be run on your desktop/laptop computer, but binaries are provided for MacOS, Windows, and Linux (including ARM).
You can setup a server and stop here, or go on to use the join command to add some "agents" aka nodes or workers into the cluster to expand its compute capacity.
Provision a new VM running a compatible operating system such as Ubuntu, Debian, Raspbian, or something else. Make sure that you opt-in to copy your registered SSH keys over to the new VM or host automatically.
Note: You can copy ssh keys to a remote VM with
ssh-copy-id user@IP.
Imagine the IP was 192.168.0.1 and the username was ubuntu, then you would run this:
- Run
k3sup:
export IP=192.168.0.1
k3sup install --ip $IP --user ubuntuOther options for install:
-
--skip-install- if you already have k3s installed, you can just run this command to get thekubeconfig -
--ssh-key- specify a specific path for the SSH key for remote login -
--local-path- default is./kubeconfig- set the path into which you want to save your VM'skubeconfig -
--context- default isdefault- set the name of the kubeconfig context. -
--ssh-port- default is22, but you can specify an alternative port i.e.2222 -
--k3s-extra-args- Optional extra arguments to pass to k3s installer, wrapped in quotes, i.e.--k3s-extra-args '--no-deploy traefik'or--k3s-extra-args '---docker'. -
--k3s-version- set the specific version of k3s, i.e.v0.9.1 -
Now try the access:
export KUBECONFIG=`pwd`/kubeconfig
kubectl get nodeInstall apps with k3sup >=0.4.0 directly into any Kubernetes cluster, all you need is kubectl access.
You can install openfaas for Kubernetes in a single command, it will detect whether you're using a Raspberry Pi or a regular computer.
# OpenFaaS - microservices and functions for Kubernetes
k3sup app install openfaas # PC, RPi, ARM64
# Metrics for Pods and Nodes
k3sup app install metrics-server # PC only
# Get a public IP / Service LoadBalancer via DigitalOcean
# or Packet.com
k3sup app install inlets-operator # PC only
# cert-manager - obtain free TLS certificates from LetsEncrypt
k3sup app install cert-managerFind out more:
k3sup app --help
k3sup app install --help
k3sup app install APP_NAME --helpWant to request an app? Raise an issue or let me know on Slack.
Let's say that you have a server, and have already run the following:
export SERVER_IP=192.168.0.100
export USER=root
k3sup install --ip $SERVER_IP --user $USERNext join one or more agents to the cluster:
export AGENT_IP=192.168.0.101
export SERVER_IP=192.168.0.100
export USER=root
k3sup join --ip $AGENT_IP --server-ip $SERVER_IP --user $USERThat's all, so with the above command you can have a two-node cluster up and running, whether that's using VMs on-premises, using Raspberry Pis, 64-bit ARM or even cloud VMs on EC2.
In a few moments you will have Kubernetes up and running on your Raspberry Pi 2, 3 or 4. Stand by for the fastest possible install. At the end you will have a KUBECONFIG file on your local computer that you can use to access your cluster remotely.
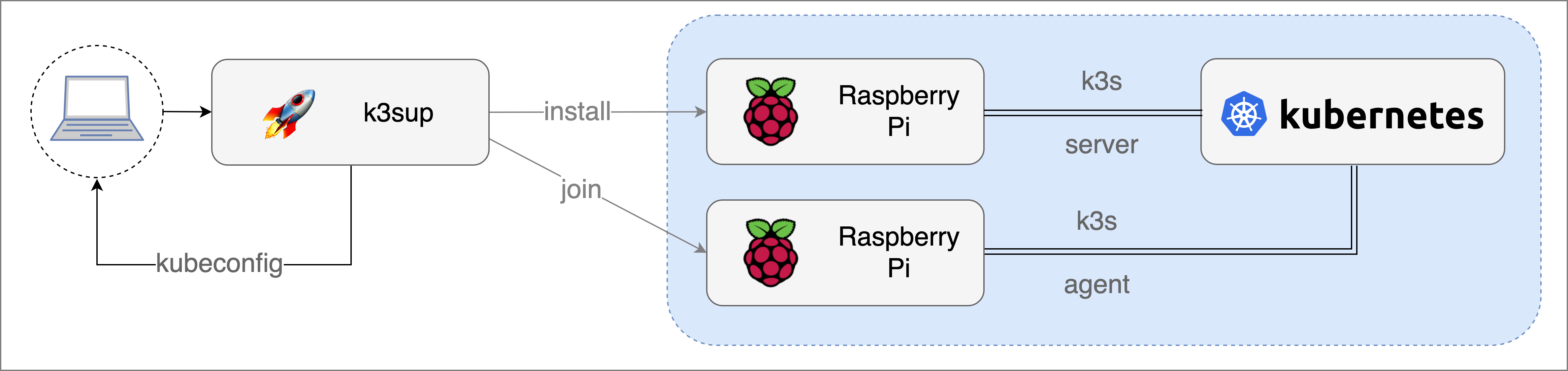 Conceptual architecture, showing
Conceptual architecture, showing k3sup running locally against bare-metal ARM devices.
-
Download etcher.io for your OS
-
Flash an SD card using Raspbian Lite
-
Enable SSH by creating an empty file named
sshin the boot partition -
Generate an ssh-key if you don't already have one with
ssh-keygen(hit enter to all questions) -
Find the RPi IP with
ping -c raspberrypi.local, then setexport SERVER_IP=""with the IP -
Copy over your ssh key with:
ssh-copy-id pi@raspberrypi.local -
Run
k3sup install --ip $SERVER_IP --user pi -
Point at the config file and get the status of the node:
export KUBECONFIG=`pwd`/kubeconfig
kubectl get node -o wideYou now have kubectl access from your laptop to your Raspberry Pi running k3s.
If you want to join some nodes, run export IP="" for each additional RPi, followed by:
k3sup join --ip $IP --server-ip $SERVER_IP --user pi
Remember all these commands are run from your computer, not the RPi.
Now where next? I would recommend my detailed tutorial where I spend time looking at how to flash the SD card, deploy k3s, deploy OpenFaaS (for some useful microservices), and then get incoming HTTP traffic.
Try it now: Will it cluster? K3s on Raspbian
If you are using public cloud, then make sure you see the notes from the Rancher team on setting up a Firewall or Security Group.
k3s docs: k3s configuration / open ports
If the ssh-key is encrypted the first step is to try to connect to the ssh-agent. If this works, it will be used to connect to the server. If the ssh-agent is not running, the user will be prompted for the password of the ssh-key.
On most Linux systems and MacOS, ssh-agent is automatically configured and executed at login. No additional actions are required to use it.
To start the ssh-agent manually and add your key run the following commands:
eval `ssh-agent`
ssh-add ~/.ssh/id_rsa
You can now just run k3sup as usual. No special parameters are necessary.
k3sup --ip $IP --user user
-
Multi-node Kubernetes on Civo in 5 minutes flat with k3sup! - Civo Learn guide
-
Zero to k3s Kubeconfig in seconds on AWS EC2 with k3sup by Saiyam Pathak
-
k3sup mentioned on Kubernetes Podcast episode 67 by Craig Box & Adam Glick
-
Blog post by Ruan Bekker:
Provision k3s to all the places with a awesome utility called "k3sup" by @alexellisuk. Definitely worth checking it out, its epic!
-
Dave Cadwallader (@geek_dave):
Alex - Thanks so much for all the effort you put into your tools and tutorials. My rpi homelab has been a valuable learning playground for CNCF tech thanks to you!
-
Checkout the Announcement tweet
Glossary:
- Kubernetes: master/slave
- k3s: server/agent
Related tools:
- k3s - Kubernetes as installed by
k3sup. k3s is a compliant, light-weight, multi-architecture distribution of Kubernetes. It can be used to run Kubernetes locally or remotely for development, or in edge locations. - k3d - this tool runs a Docker container on your local laptop with k3s inside
- kind - kind can run a Kubernetes cluster within a Docker container for local development. k3s is also suitable for this purpose through
k3d. KinD is not suitable for running a remote cluster for development. - kubeadm - a tool to create fully-loaded, production-ready Kubernetes clusters with or without high-availability (HA). Tends to be heavier-weight and slower than k3s. It is aimed at cloud VMs or bare-metal computers which means it doesn't always work well with low-powered ARM devices.
- k3v - "virtual kubernetes" - a very early PoC from the author of k3s aiming to slice up a single cluster for multiple tenants
MIT
Blogs posts, tutorials, and Tweets about k3sup (#k3sup) are appreciated. Please send a PR to the README.md file to add yours.
Show your support for k3sup through GitHub Sponsors from 5USD.
Before contributing code, please see the CONTRIBUTING guide. Note that k3sup uses the same guide as inlets.dev.
Both Issues and PRs have their own templates. Please fill out the whole template.
All commits must be signed-off as part of the Developer Certificate of Origin (DCO)

