The purpose of this project is to use the expressive power of the Python language to declaratively implement finite state machines.
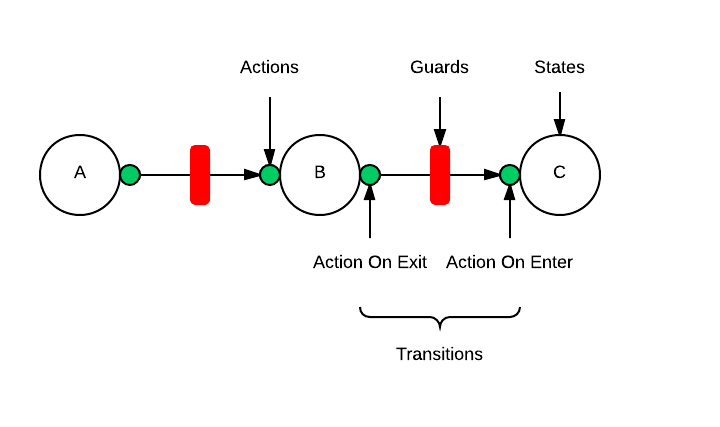
A few concepts are important to understand in order to properly use this project. As an aid, an image has been provided below to help convey the ideas covered in this section.
Actions
An action is executed upon entering or exiting a state. Actions are the mechanism by which a finite state machine (FSM) gets work done.
Guards
A guard constrains transitions by allowing transitions to occur only under specific circumstances. A good example of how guards are useful can be found in the security domain. In this domain a guard can be implemented that only allows a transition to occur if the user has previously authenticated with the system.
States
A state is considered to be the value of all the variables in an FSM at some point in time. All the states of interest as well as the initial state must be declared while initializing the FSM in order for it to build it's internal transition table.
Transitions
A transition is the action of moving an FSM from an initial state to a desired state. All the possible transitions must be declared while initializing the FSM in order to constrain how states are traversed.
class LightSwitch(FiniteStateMachine):
# Initial state.
initial_state = 'off'
# Possible transitions.
transitions = [
('off', 'on'),
('on', 'off'),
('off', 'broken'),
('on', 'broken')
]
# Initialize the FSM.
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super(LightSwitch, self).__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.electricity = True
# Handle incoming events.
def on_message(self, message):
if message == 'turn on':
self.transition(to = 'on', event = message)
elif message == 'turn off':
self.transition(to = 'off', event = message)
elif message == 'break':
self.transition(to = 'broken', event = message)
# Attach a guard to the FSM that protects transitions into
# the on state. The guard is a predicate that returns True
# or False based on the availability of electricity to the
# socket.
@Guard(state = 'on')
def check_electricity(self):
return self.electricity
# Attach an action to the FSM that will execute anytime
# the off state is entered.
@Action(state = 'off')
def turn_off(self, message):
self.indicator = 'dim'
# Attach an action to the FSM that will execute anytime
# the on state is entered.
@Action(state = 'on')
def turn_on(self, message):
self.indicator = 'lit'
# Attach an action to the FSM that will execute anytime
# the broken state is entered.
@Action(state = 'broken')
def smash(self, message):
self.indicator = 'broken'
# Instantiate an FSM and send it events to process.
light_switch = LightSwitch()
light_switch.on_message('turn on')
light_switch.on_message('turn off')
light_switch.on_message('break')