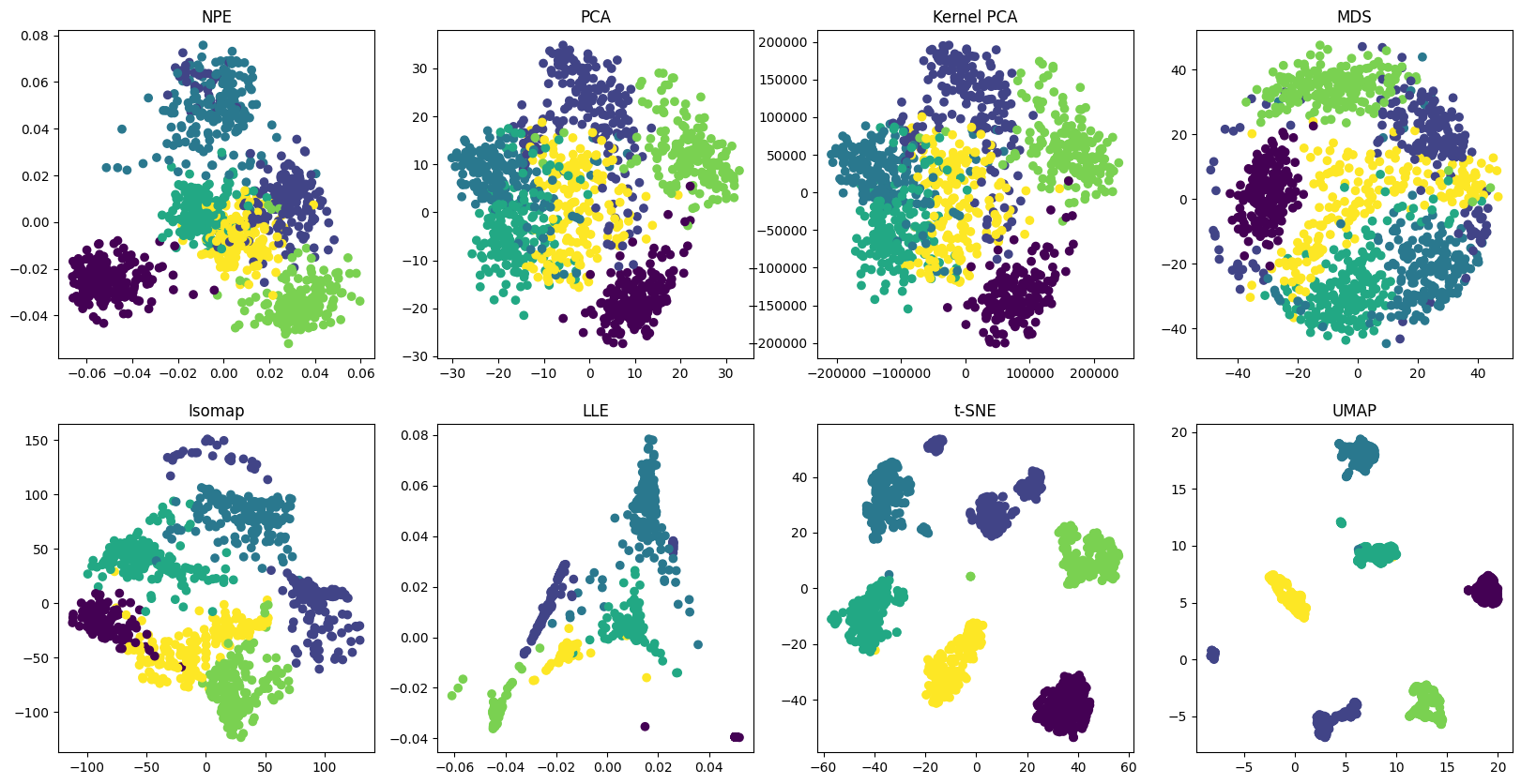
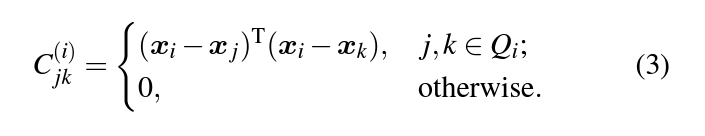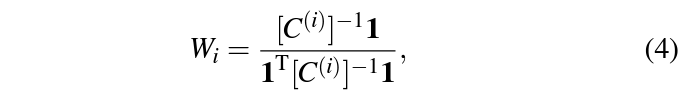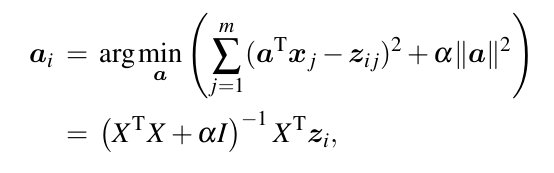Recently there has been a lot of interest in geometrically motivated approaches to data analysis in high dimensional spaces. We consider the case where data is drawn from sampling a probability distribution that has support on or near a submanifold of Euclidean space. In this paper, we propose a novel subspace learning algorithm called Neighborhood Preserving Embedding (NPE). Different from Principal Component Analysis (PCA) which aims at preserving the global Euclidean structure, NPE aims at preserving the local neighborhood structure on the data manifold. Therefore, NPE is less sensitive to outliers than PCA. Also, comparing to the recently proposed manifold learning algorithms such as Isomap and Locally Linear Embedding, NPE is defined everywhere, rather than only on the training data points. Furthermore, NPE may be conducted in the original space or in the reproducing kernel Hilbert space into which data points are mapped. This gives rise to kernel NPE. Several experiments on face database demonstrate the effectiveness of our algorithm
To construct the weight matrix
with contraints
Let
Then, let
In this step, we compute the linear projections. Solve the following generalized eigenvector problem:
The eigenvalue problem can be solved by two steps.
First step: solve the following eigenvalue problem to get the bottom non-zero eigenvectors
where