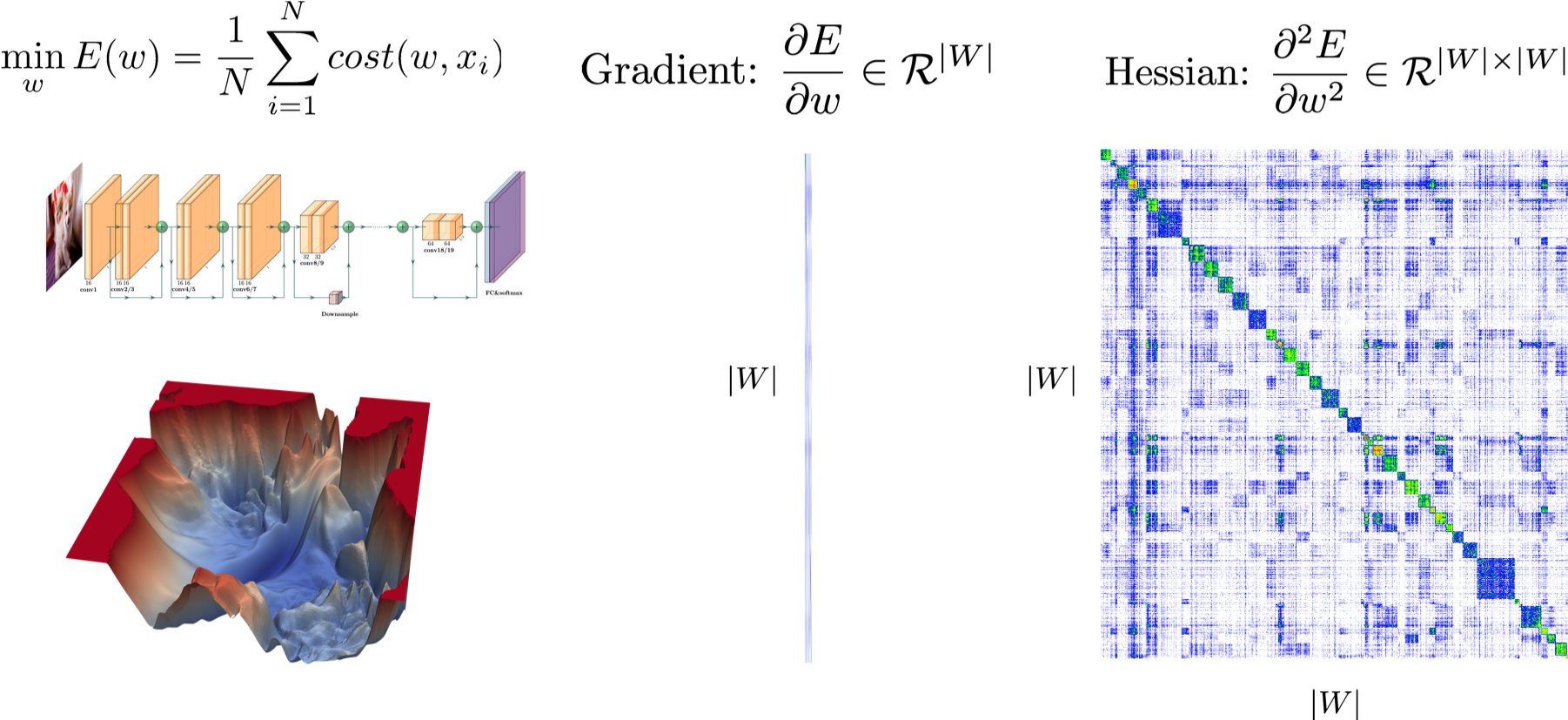PyHessian is a pytorch library for Hessian based analysis of neural network models. The library enables computing the following metrics:
- Top Hessian eigenvalues
- The trace of the Hessian matrix
- The full Hessian Eigenvalues Spectral Density (ESD)
For more details please see:
This project was supported through NSF funding and we are interested in documenting related publications written on or with the help of PyHessian. This will allows us to continue developing the library, and will also be a good summary for related and on going work on second order methods. You can see the current list here. Please contact us if you have a related paper and we would be glad to add it to the list.
You can install the library from pip
pip install pyhessian
You can also compile the library from source
git clone https://github.com/amirgholami/PyHessian.git
python setup.py install
Before running the Hessian code, we need a (pre-trained) NN model. Here, we provide a training file to train ResNet20 model on Cifar-10 dataset:
export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0; python training.py [--batch-size] [--test-batch-size] [--epochs] [--lr] [--lr-decay] [--lr-decay-epoch] [--seed] [--weight-decay] [--batch-norm] [--residual] [--cuda] [--saving-folder]
optional arguments:
--batch-size training batch size (default: 128)
--test-batch-size testing batch size (default:256)
--epochs total number of training epochs (default: 180)
--lr initial learning rate (default: 0.1)
--lr-decay learning rate decay ratio (default: 0.1)
--lr-decay-epoch epoch for the learning rate decaying (default: 80, 120)
--seed used to reproduce the results (default: 1)
--weight-decay weight decay value (default: 5e-4)
--batch-norm do we need batch norm in ResNet or not (default: True)
--residual do we need residual connection or not (default: True)
--cuda do we use gpu or not (default: True)
--saving-folder saving path of the final checkpoint (default: checkpoints/)
After the model checkpoint is saved, we can run the following code to get the top eigenvalue, trace, and the Eigenvalue Spectral Density of Hessian:
export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0; python example_pyhessian_analysis.py [--mini-hessian-batch-size] [--hessian-batch-size] [--seed] [--batch-norm] [--residual] [--cuda] [--resume]
optional arguments:
--mini-hessian-batch-size mini hessian batch size (default: 200)
--hessian-batch-size hessian batch size (default:200)
--seed used to reproduce the results (default: 1)
--batch-norm do we need batch norm in ResNet or not (default: True)
--residual do we need residual connection or not (default: True)
--cuda do we use gpu or not (default: True)
--resume resume path of the checkpoint (default: none, must be filled by user)
The output density plot is saved as example.pdf
PyHessian has been developed as part of the following paper. We appreciate it if you would please cite the following paper if you found the library useful for your work:
- Z. Yao, A. Gholami, K Keutzer, M. Mahoney. PyHessian: Neural Networks Through the Lens of the Hessian, Spotlight at ICML workshop on Beyond First-Order Optimization Methods in Machine Learning, 2020, PDF.