This project provides GateKeeper and local AWS Lambda Runtime components for Java runtime
to be able to use MerLoc as live AWS Lambda development tool.
Note that, to be able to use MerLoc for Java runtime, first you need to setup MerLoc platform into your AWS account as explained at MerLoc Github page here.
Artifact versions are in X.Y.Z format
X: Major version number.- Increases only when there are big API and/or architectural changes.
- Breaks backward compatibility.
Y: Minor version number.- Increases for small API changes and big improvements.
- Breaks backward compatibility.
Z: Patch version number.- Increases for bug fixes and small improvements.
- Doesn’t break backward compatibility.
- JDK 1.8+ (for build and execution)
- Maven 3.x (for build)
To build:
$ git clone git@github.com:thundra-io/merloc-java.git
$ cd merloc-java/
$ mvn clean install
-
Add MerLoc GateKeeper layer:
arn:aws:lambda:${region}:269863060030:layer:merloc-java:${version}You can use the latest layer version (shown below) instead of the
${version}above:(badge powered by Globadge serverless)
Note that the region of the ARN is dynamic, so you need to change it accordingly to the region where you deploy your function. So let’s say that you deploy your Lambda function to the
Oregon(us-west-2) region. So the layer ARN will be:arn:aws:lambda:us-west-2:269863060030:layer:merloc-java:${version} -
You need to switch the handler so MerLoc GateKeeper will wrap your original handler.
Java 8 on Amazon Linux 1:- Set the handler to
io.thundra.merloc.aws.lambda.gatekeeper.handler.GateKeeperLambdaHandler - And then set the
MERLOC_AWS_LAMBDA_HANDLERenvironment variable value to your original handler.
Java 8 on Amazon Linux 2andJava 11 Corretto:- Set
AWS_LAMBDA_EXEC_WRAPPERenvironment variable to/opt/merloc_wrapper
- Set the handler to
-
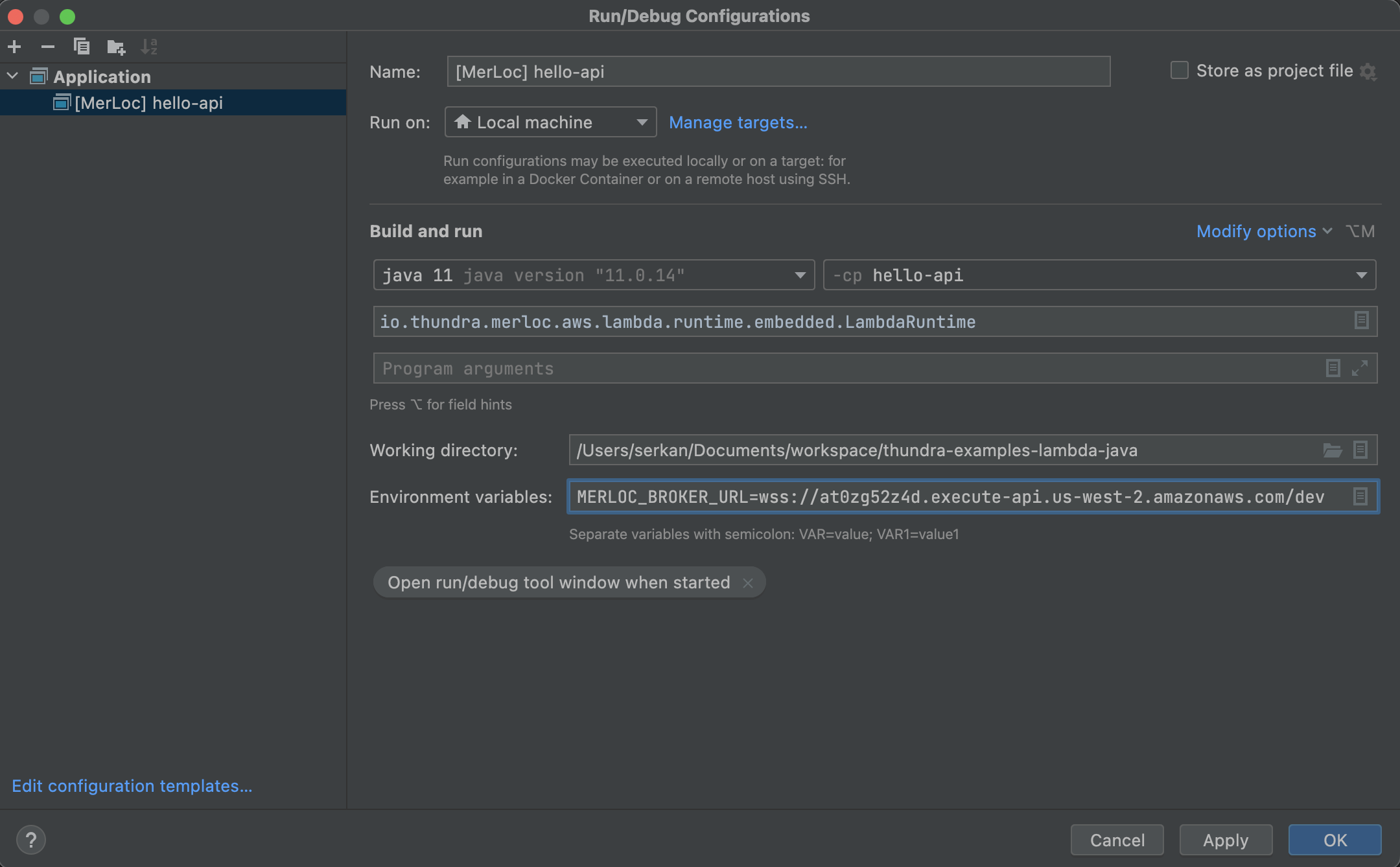
Set
MERLOC_BROKER_URLenvironment variable to the
Download MerLoc AWS Lambda embedded runtime from
https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/io/thundra/merloc/merloc-aws-lambda-runtime-embedded/${version}/merloc-aws-lambda-runtime-embedded-${version}.jar
You can use the latest version (shown below) instead of the ${version} above:
-
Click
Global Librariesand then clickJavato add a new global library.
-
Select the MerLoc AWS Lambda runtime jar from the place where you downloaded above. And then chose the modules (single or multiple modules) in which Lambda handlers are located.
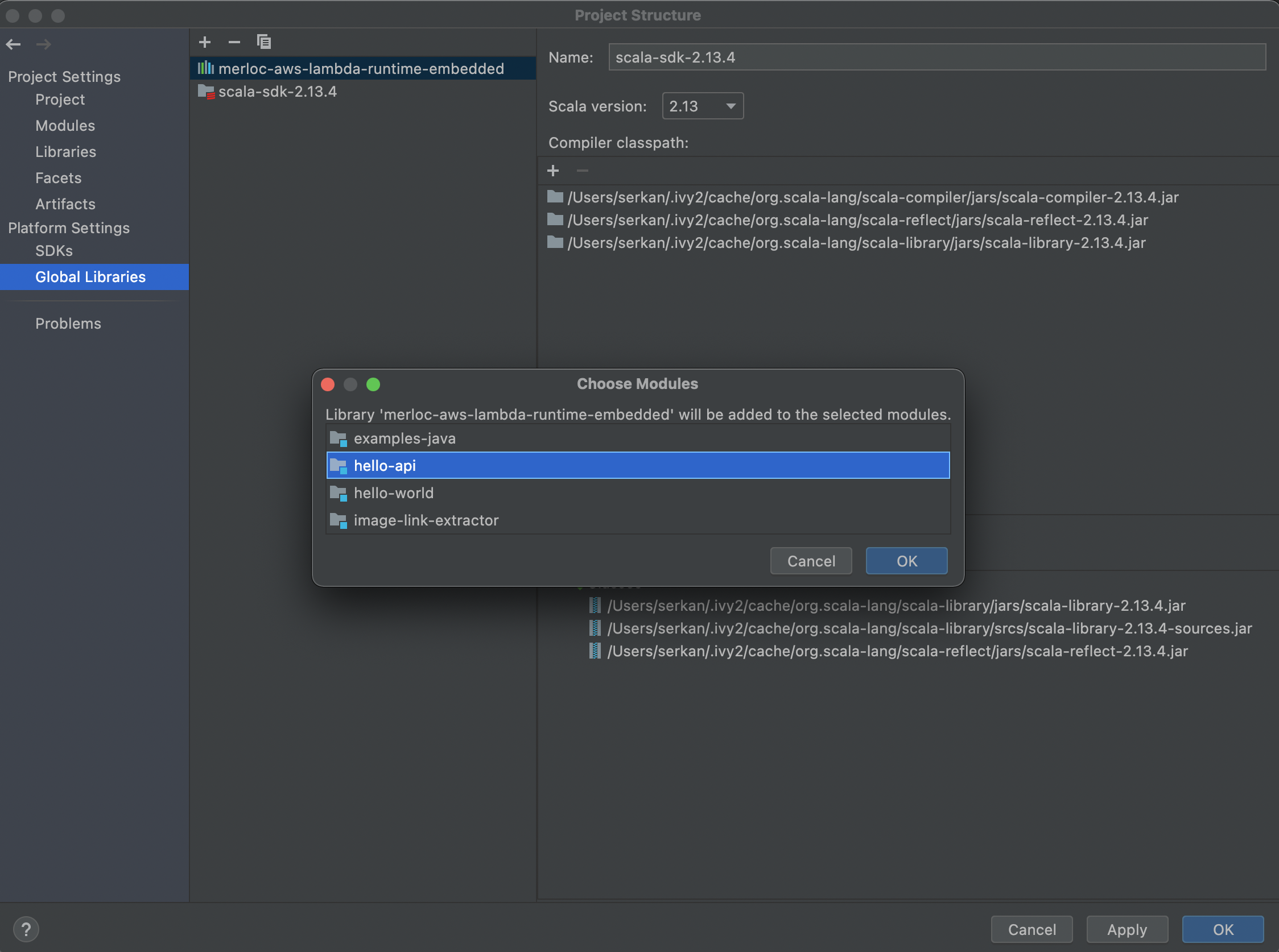
After these steps are completed, we have added MerLoc AWS Lambda runtime jar into the classpath of selected modules in which your AWS Lambda handlers exist.
-
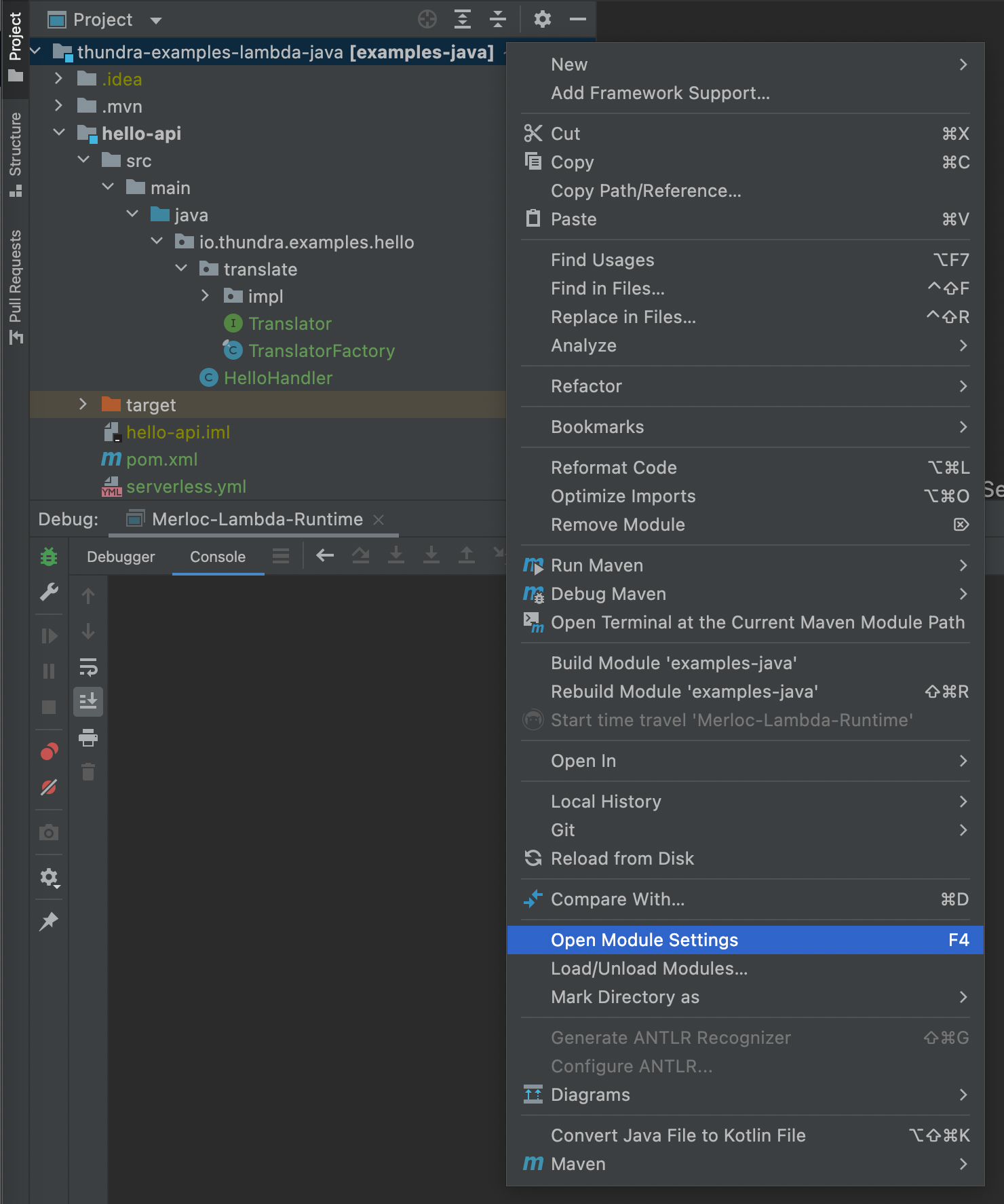
Click
Add Configurationand add a newApplicationconfiguration.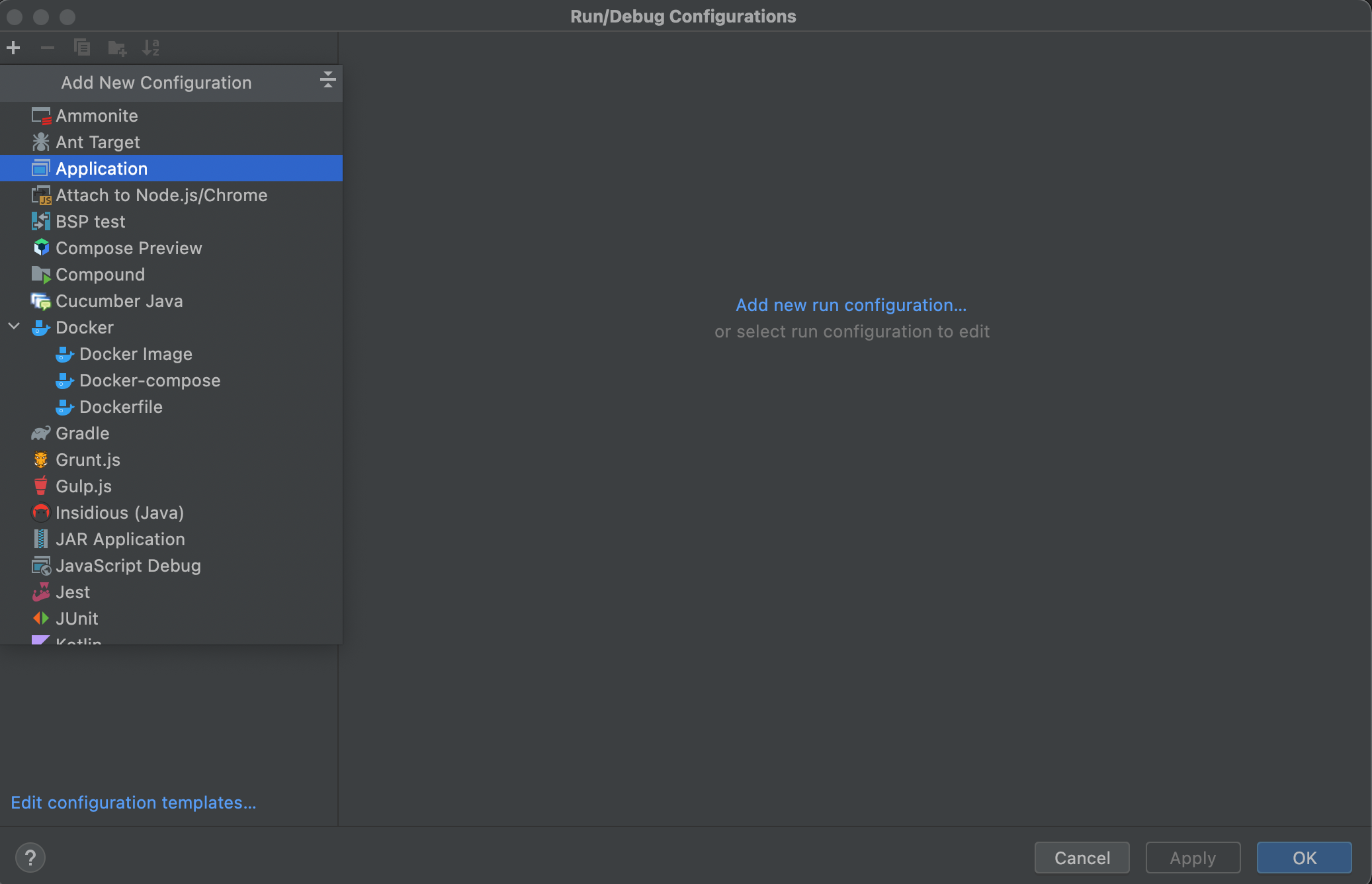
-
Select the JDK module (
java 11in the following example) and classpath module (hello-apimodule in the following example). Then setMain classtoio.thundra.merloc.aws.lambda.runtime.embedded.LambdaRuntime.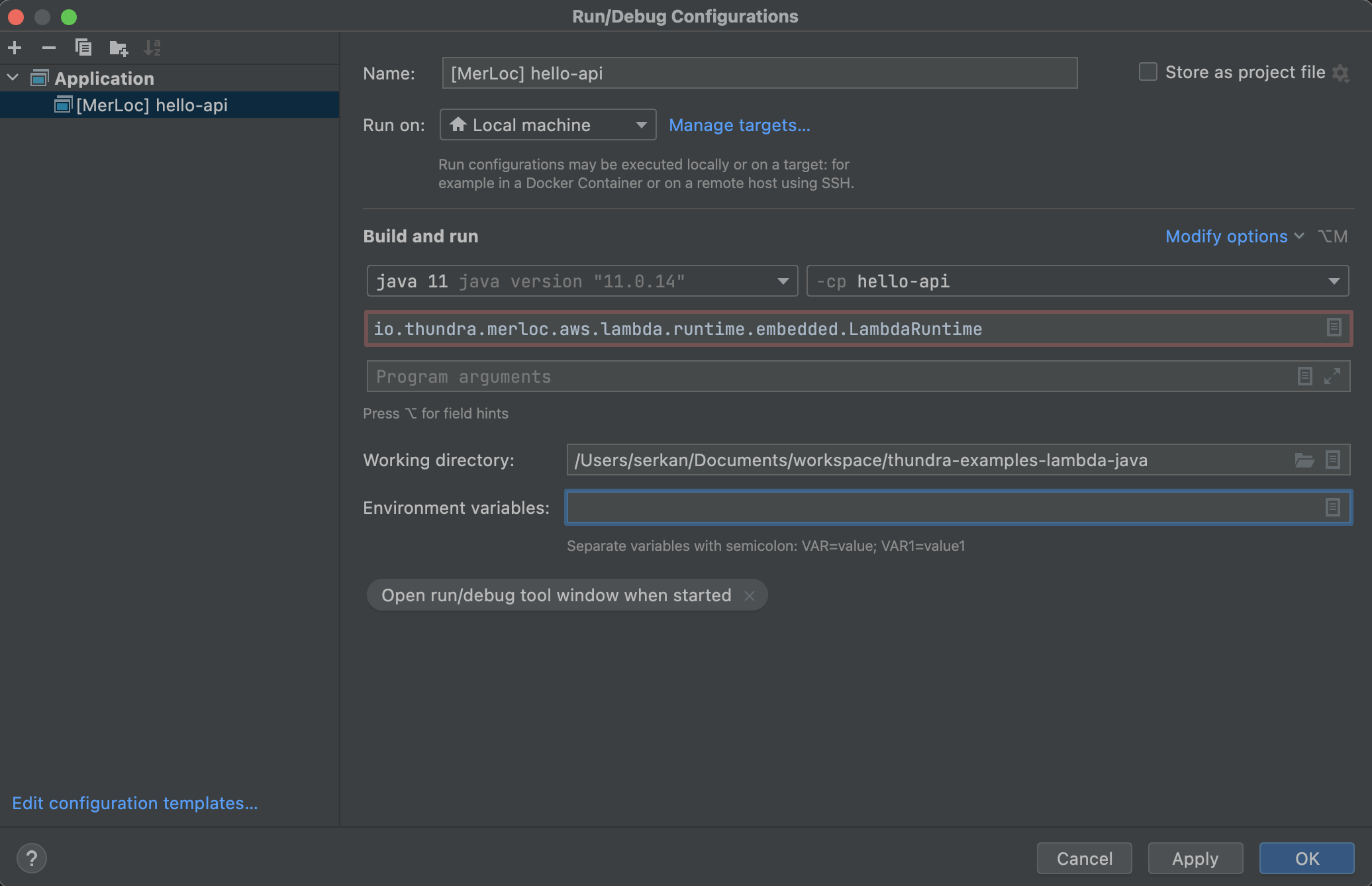
-
Set
MERLOC_BROKER_URLenvironment variable (likewise you did for GateKeeper above) to the
-
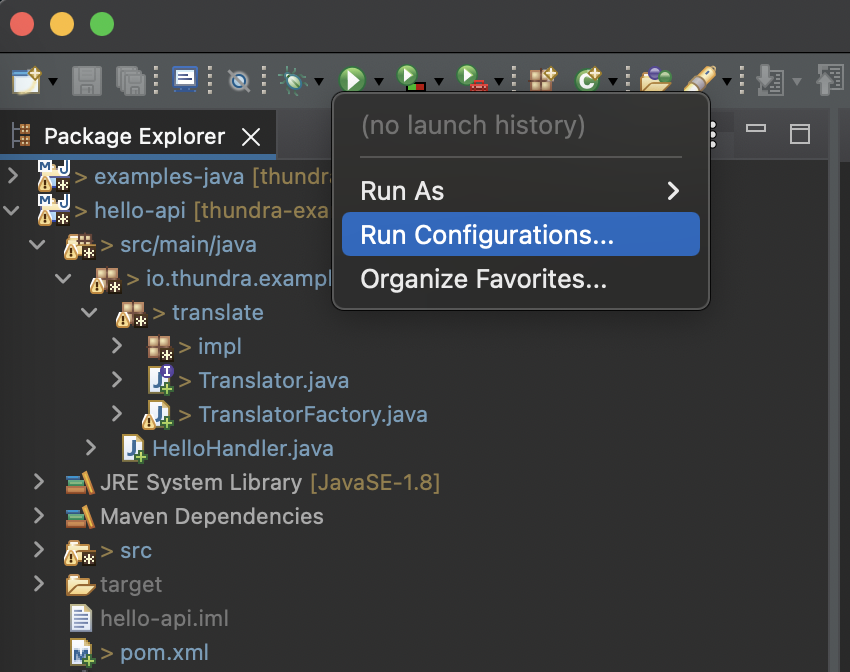
Right click on
Java Applicationand selectNew Configuration.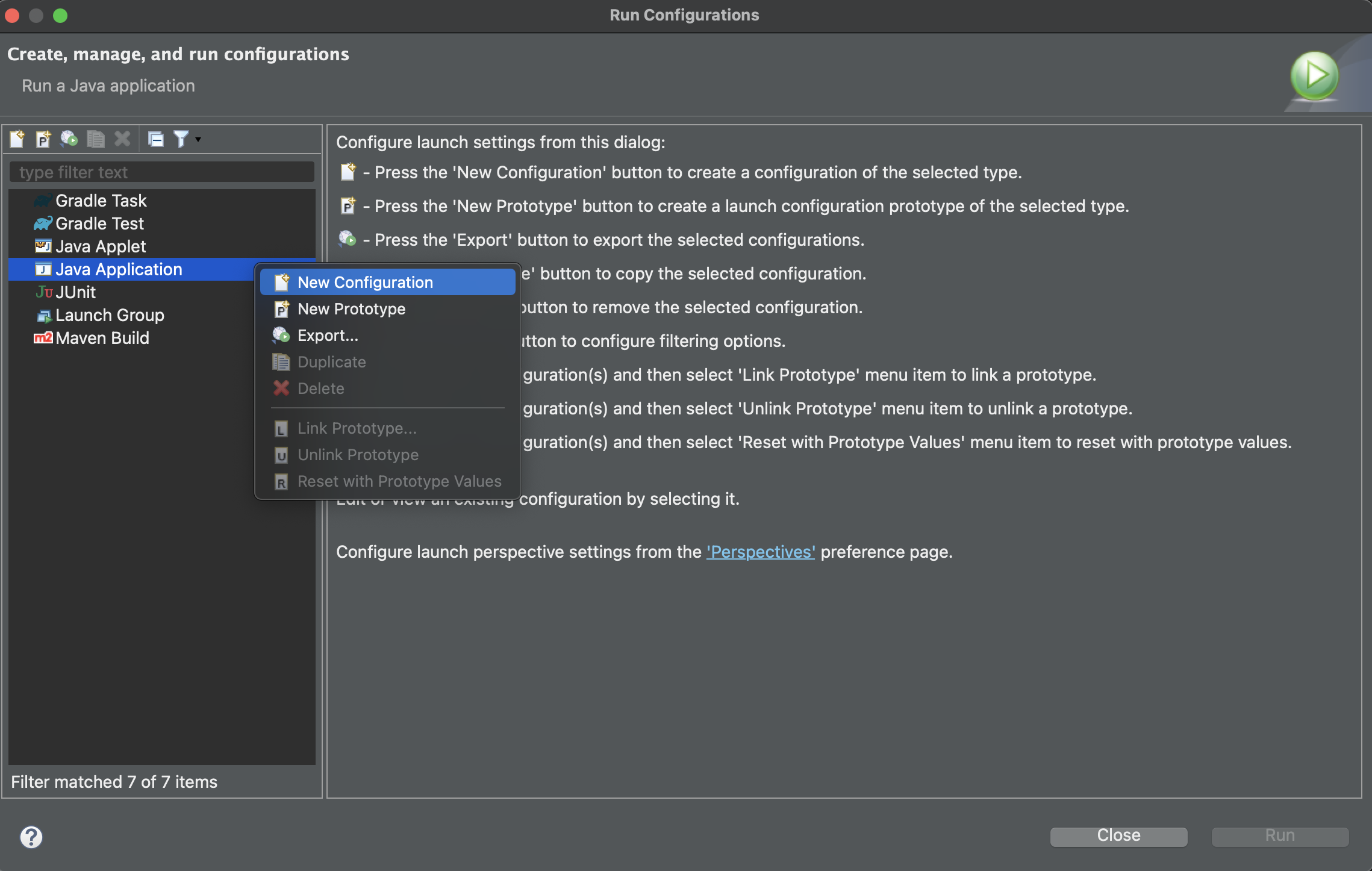
-
Select the project (
hello-apiin the following example). Then setMain classtoio.thundra.merloc.aws.lambda.runtime.embedded.LambdaRuntimeand clickApply.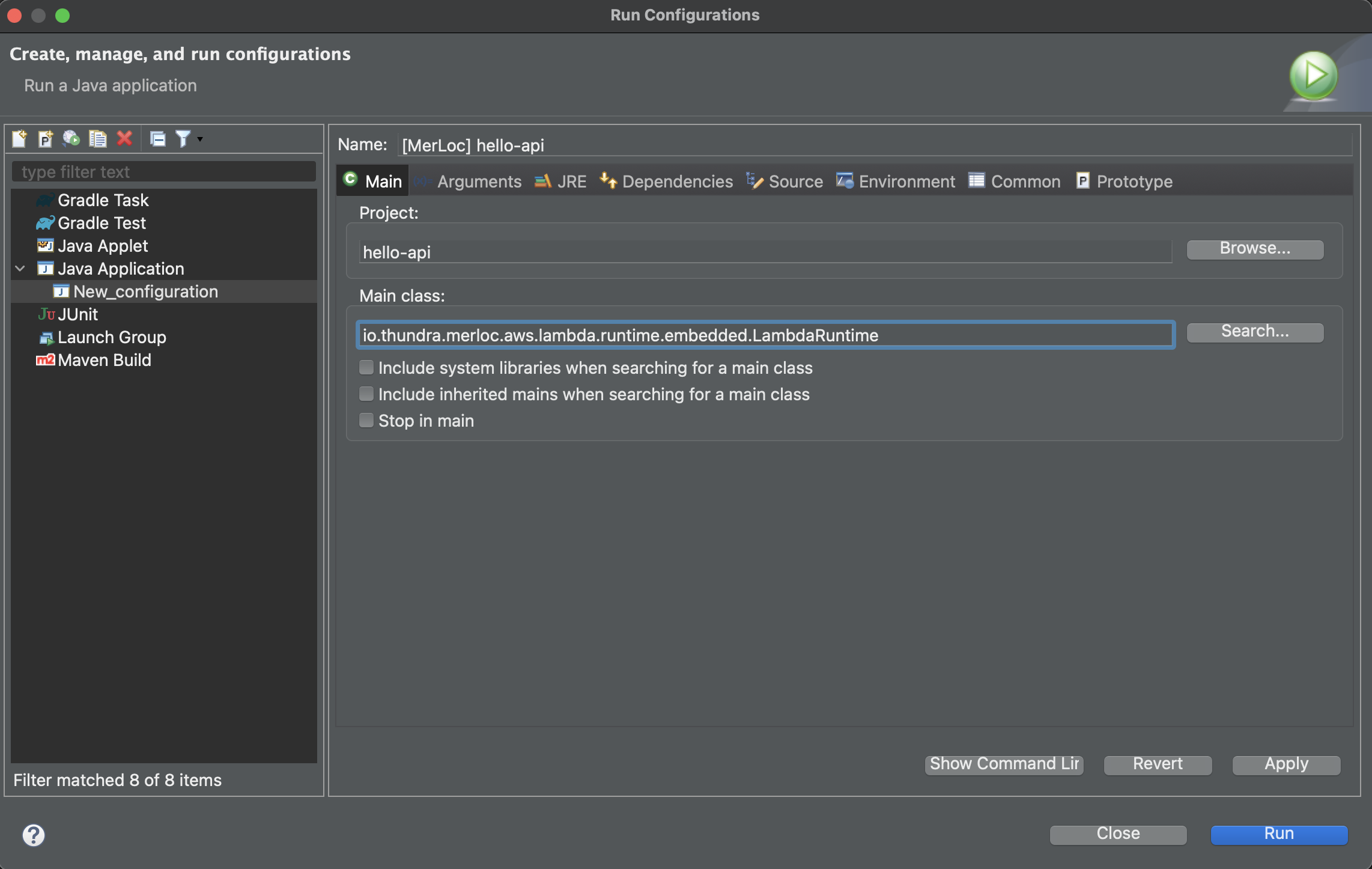
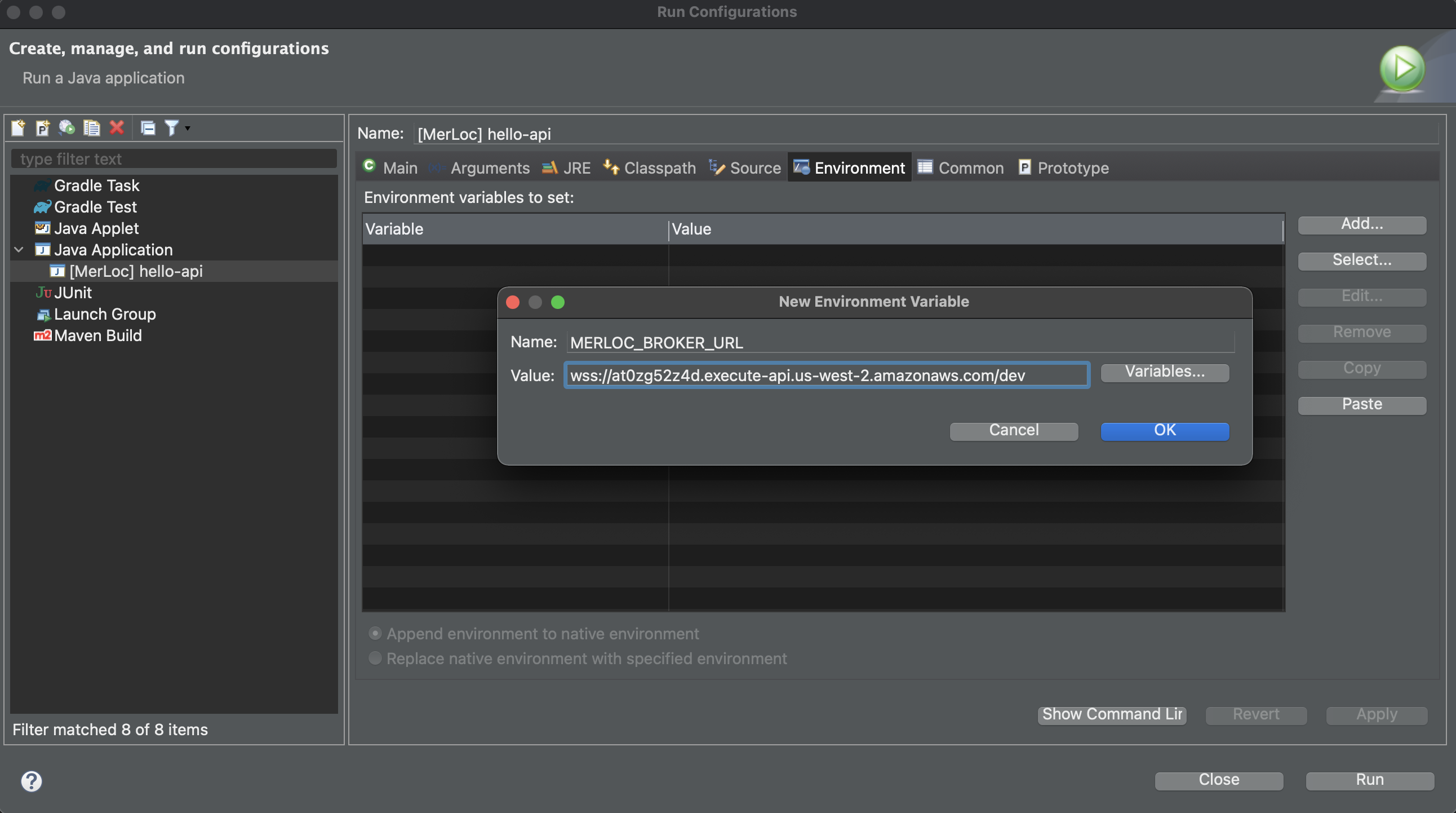
-
Click
Dependenciestab, selectClasspath Entries, clickAdd External JARsand then select the MerLoc AWS Lambda runtime jar from the place where you downloaded above.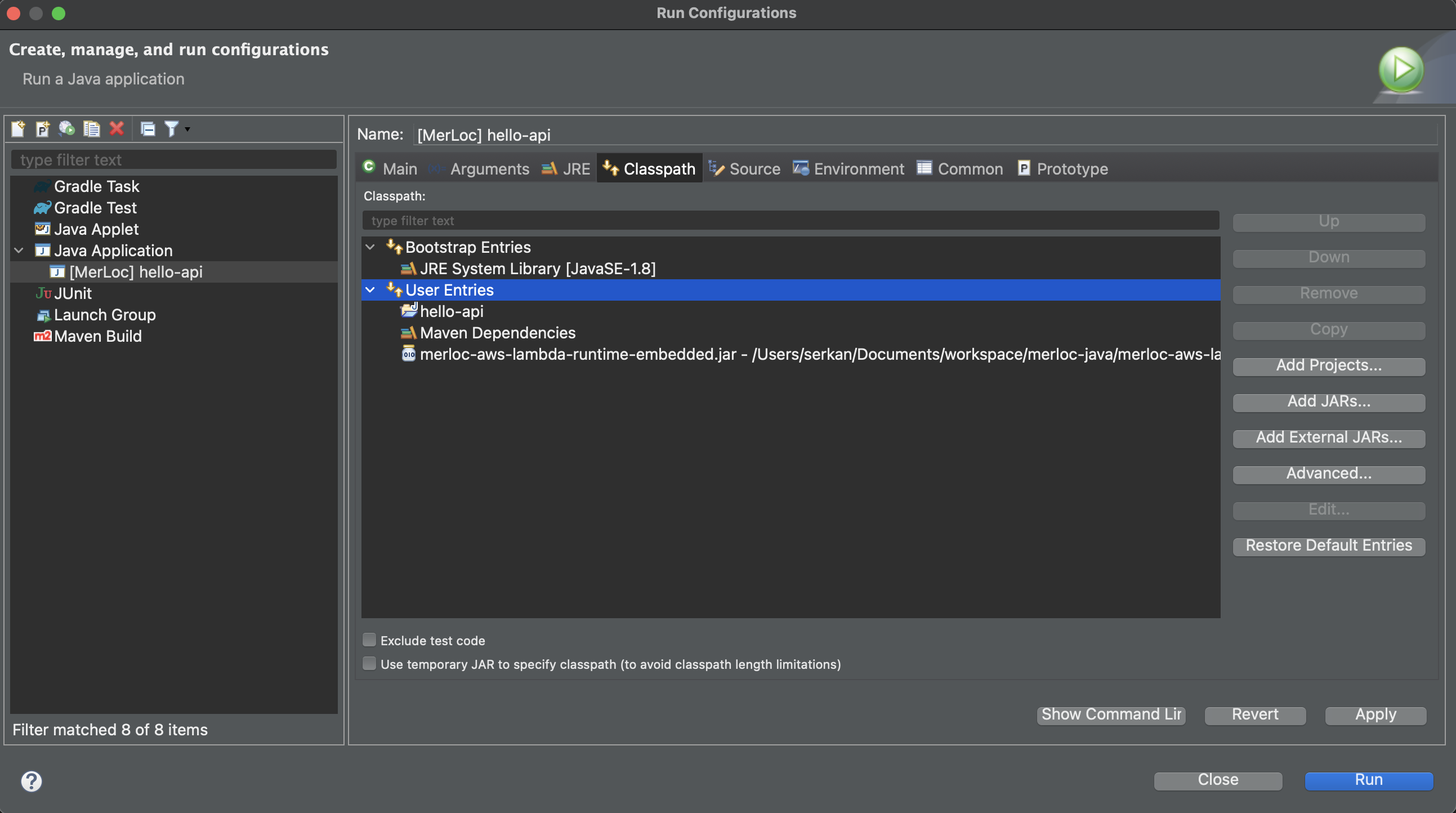
After these steps are completed, we have added MerLoc AWS Lambda runtime jar into the classpath of selected project in which your AWS Lambda handler(s) exist.
-
Set
MERLOC_BROKER_URLenvironment variable (likewise you did for GateKeeper above) to the
-
Later on, trigger the AWS Lambda function. Then, the real request will be forwarded to MerLoc AWS Lambda Runtime on your local through MerLoc GateKeeper. So it will be executed locally and response will be returned to MerLoc GateKeeper and so to AWS Lambda function caller from there.
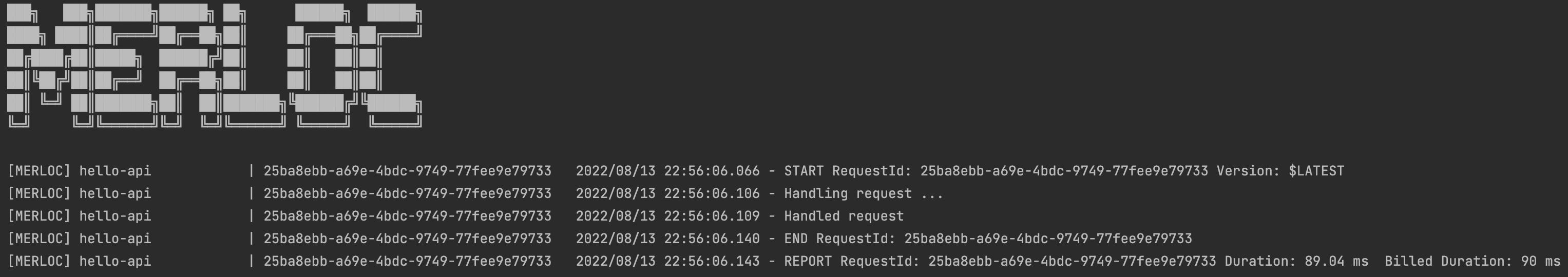
-
Click
Debugto start MerLoc AWS Lambda Runtime in debug mode.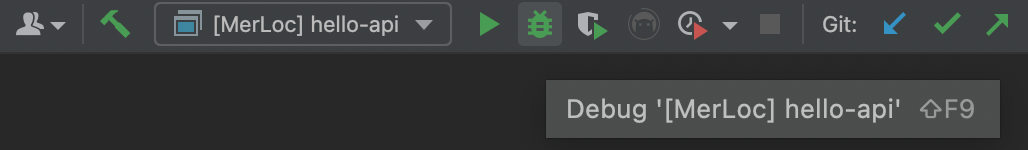
-
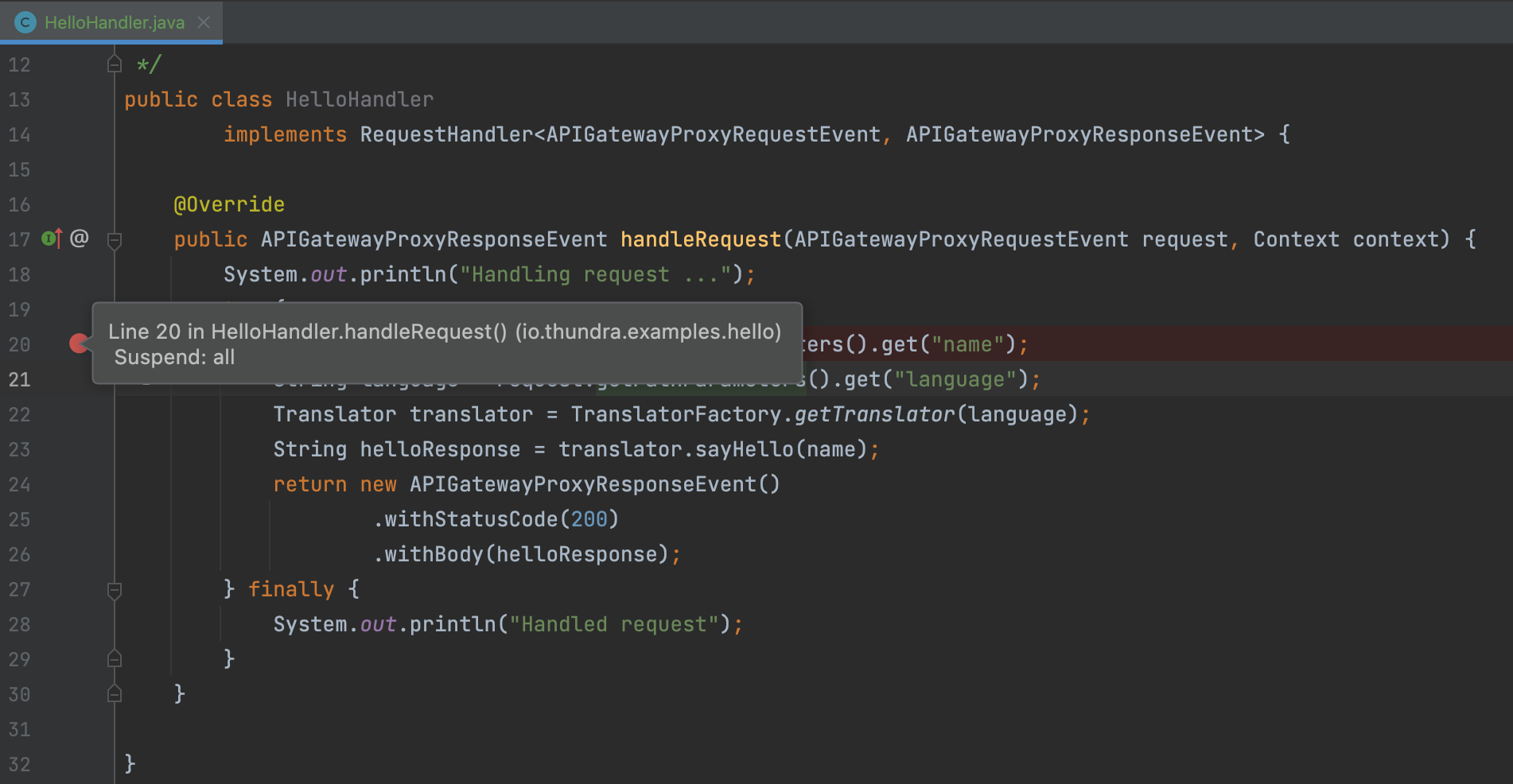
Then, trigger the AWS Lambda function. So the forwarded request will stop at the breakpoint you put on your local and you can debug AWS Lambda function locally.
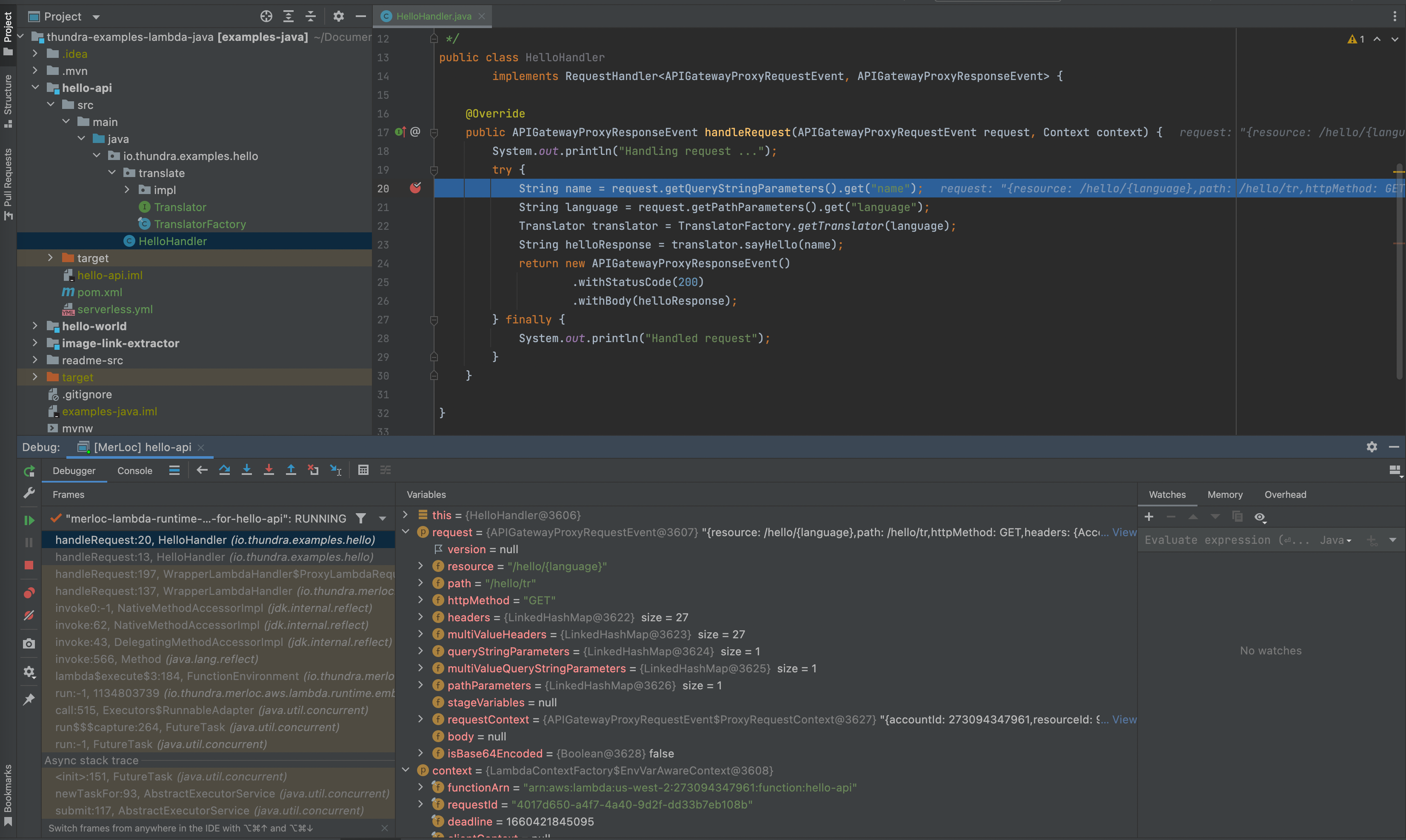
-
While running MerLoc AWS Lambda Runtime on your local, apply your changes in the source code(s). Then go to
Buildin the menu bar and clickBuild Moduleto re-build module in which you updated source code(s).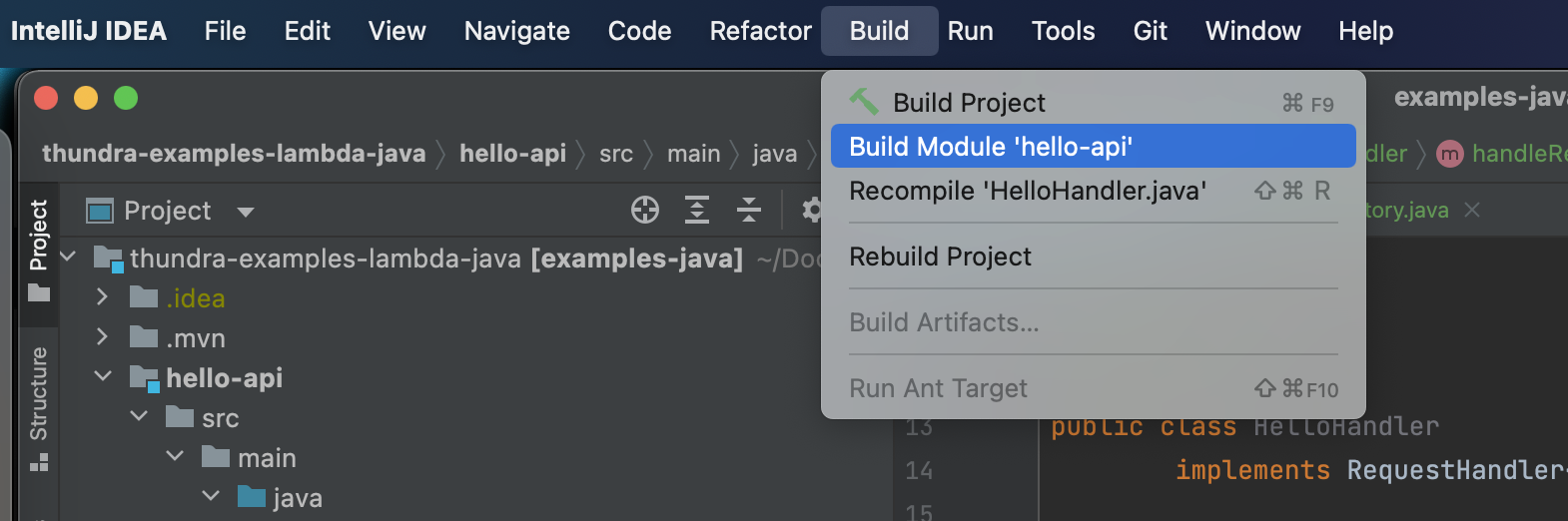
-
After that you will see MerLoc log messages in your console which says that related function environment(s) (affected by changes) have been reloaded.

-
Then, trigger your AWS Lambda function again, and you will see that your changes are live in the running function on your local.
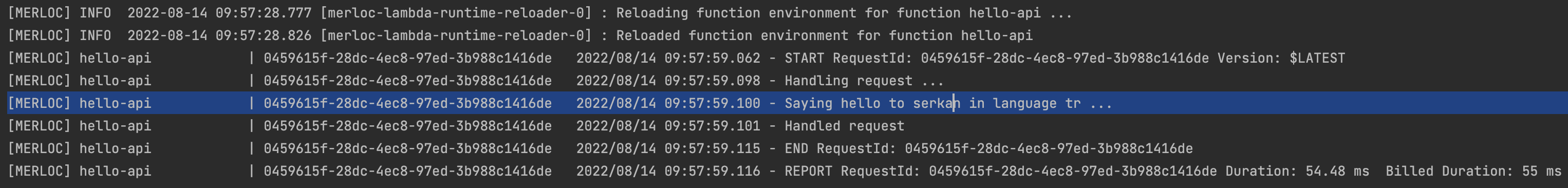
-
Open
Run Configurations. Select the configuration you created before during setup and clickRun.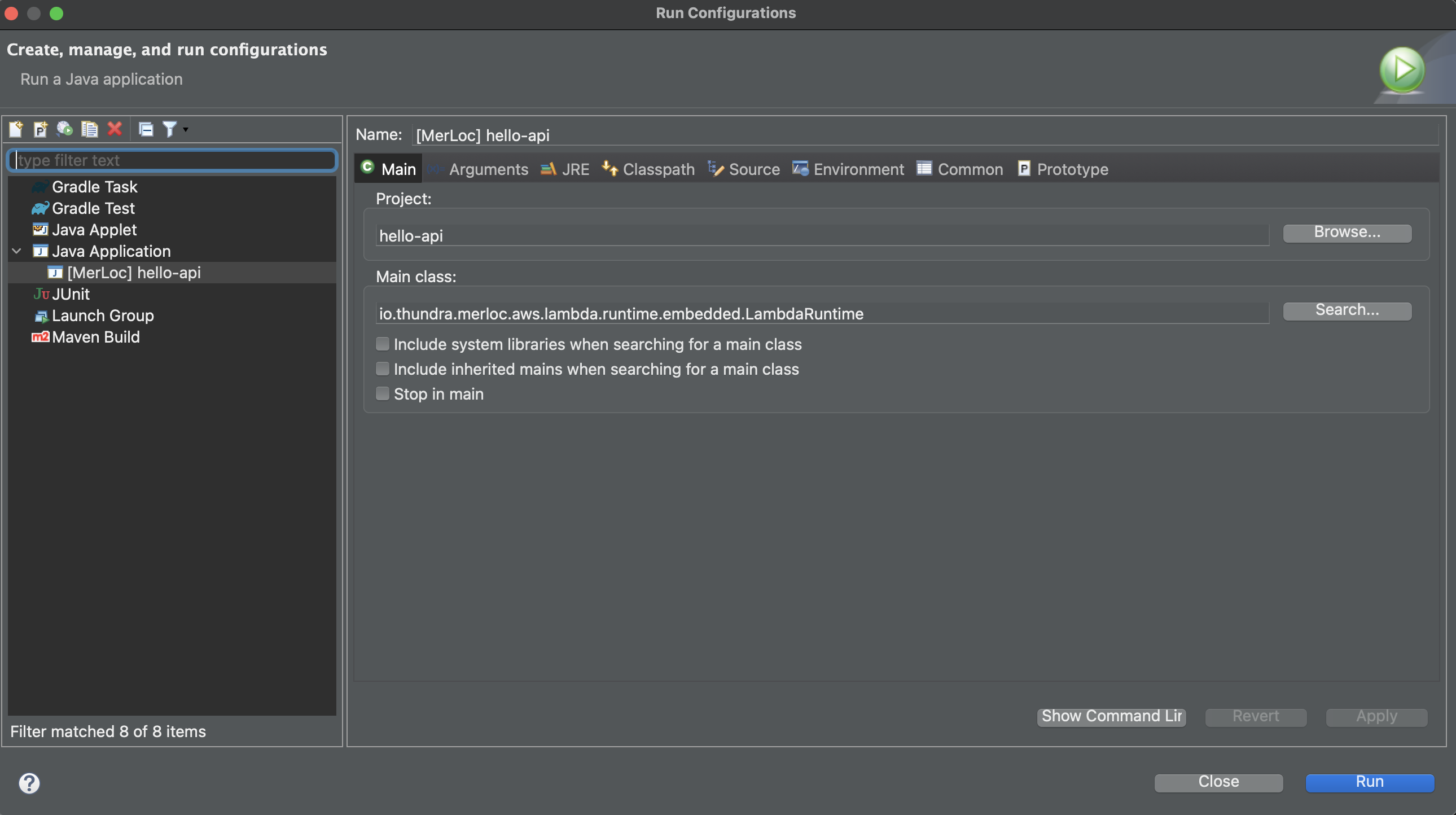
-
Later on, trigger the AWS Lambda function. Then, the real request will be forwarded to MerLoc AWS Lambda Runtime on your local through MerLoc GateKeeper. So it will be executed locally and response will be returned to MerLoc GateKeeper and so to AWS Lambda function caller from there.
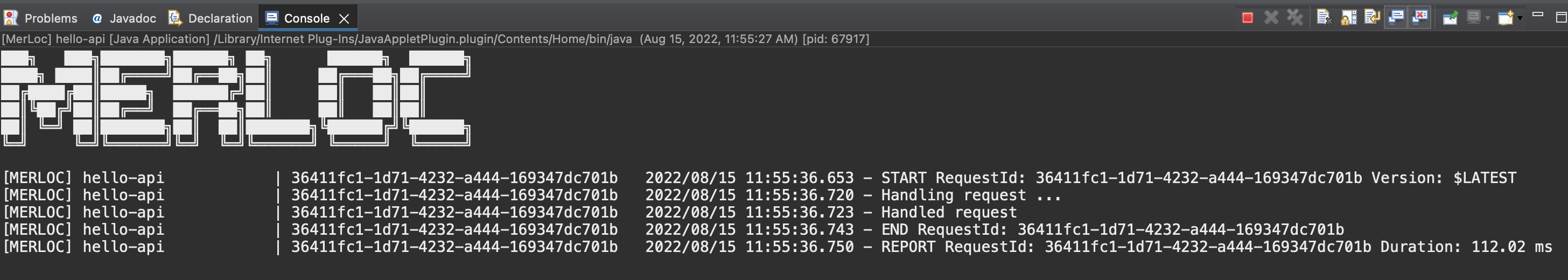
-
Open
Debug Configurations. Select the configuration you created before during setup and clickDebug.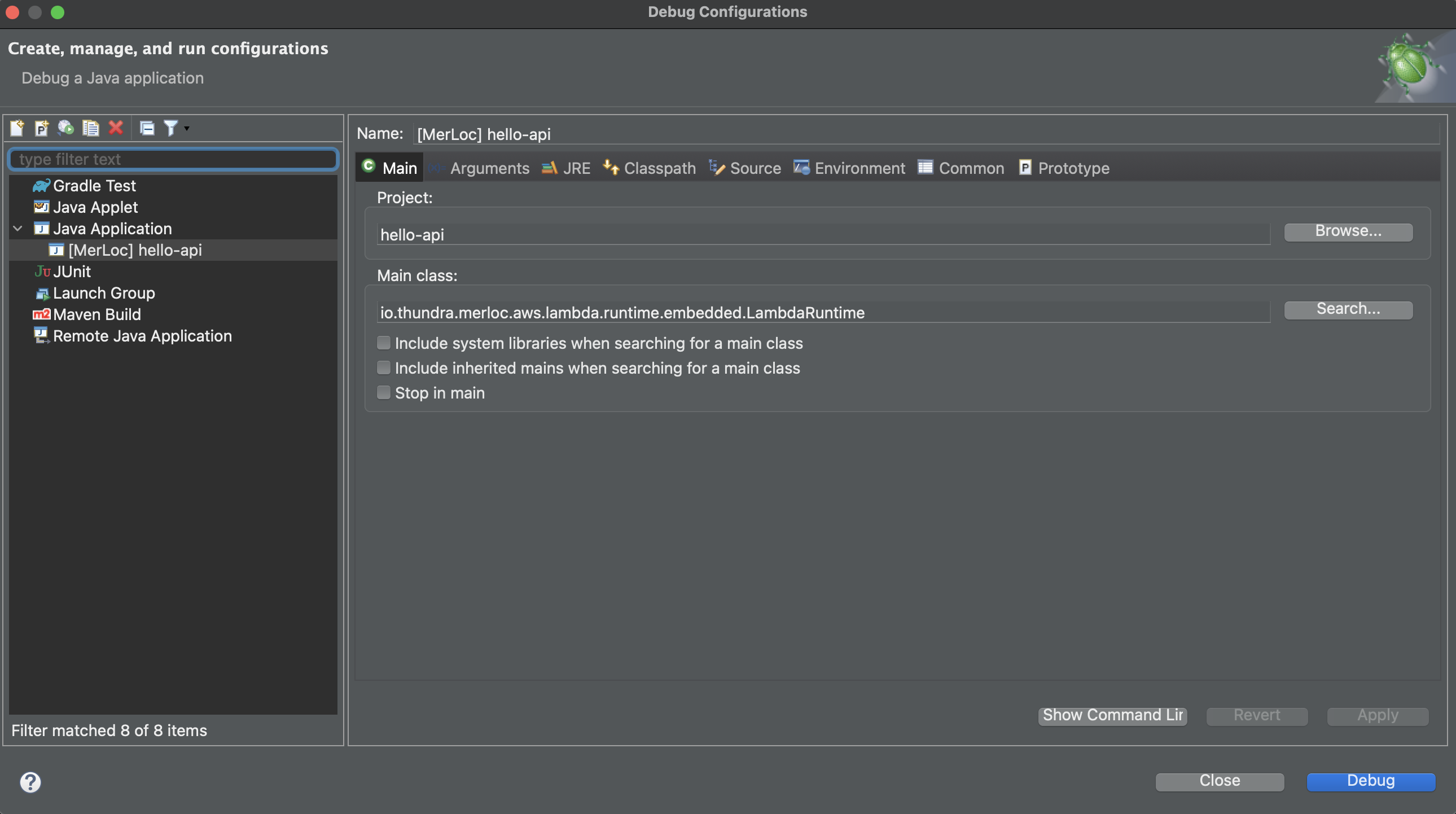
-
Then, trigger the AWS Lambda function. So the forwarded request will stop at the breakpoint you put on your local and you can debug AWS Lambda function locally.
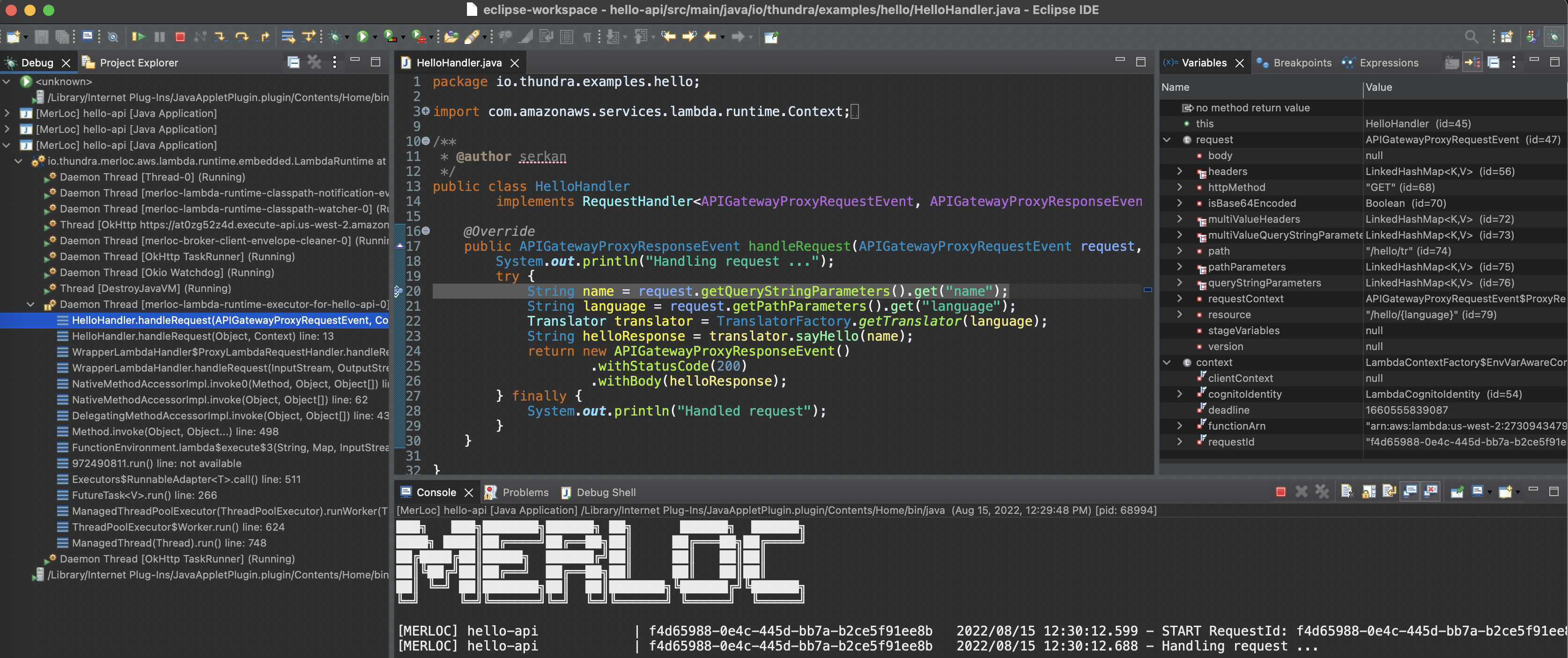
TBD
-
MERLOC_BROKER_URL: This configuration is MANDATORY. You need to set this environment variable by broker URL as mentioned in the GateKeeper Setup section. -
MERLOC_ENABLE: This configuration is OPTIONAL. Even though MerLoc GateKeeper layer is added and configured, you can disable it by setting theMERLOC_ENABLEenvironment variable tofalse. For example,MERLOC_ENABLE=false -
MERLOC_DEBUG_ENABLE: This configuration is OPTIONAL. By default, internal debug logs are disabled, but you can enable it by setting theMERLOC_DEBUG_ENABLEenvironment variable totrue. For example,MERLOC_DEBUG_ENABLE=true -
MERLOC_BROKER_CONNECTION_NAME: This configuration is OPTIONAL. By default, the name of the connection to the broker is the name of the AWS Lambda function for GateKeeper. But you can change it by setting theMERLOC_BROKER_CONNECTION_NAMEenvironment variable. For example,MERLOC_BROKER_CONNECTION_NAME=serkan-connection -
MERLOC_CLIENT_ACCESS_INTERVAL_ON_FAILURE: This configuration is OPTIONAL. By default, MerLoc GateKeeper tries to access to the client (your local AWS Lambda runtime) at every request even though the local runtime/function is not up/running or unreachable at the previous attempt. If it fails (local runtime is not up, rejected because of concurrency mode, etc ...), it bypasses MerLoc flow and forwards the request to your original handler for allowing the function to be executed as is. But such checks at every request introduce some additional little delays (up to 1 sec) if your function is configured to use MerLoc (and it is not disabled) and your local is not up. To get rid of such additional minor delay (when you are not running MerLoc on your local, and you didn't disable it), you can configureMERLOC_CLIENT_ACCESS_INTERVAL_ON_FAILUREenvironment variable to specify the client (your local AWS Lambda runtime) access check interval in seconds instead of at every request. So if a client (your local AWS Lambda runtime) access check fails, MerLoc GateKeeper will not check until the configured seconds have passed since the last failed check. For example (check every 5 minutes instead of at every request in case of failure),MERLOC_CLIENT_ACCESS_INTERVAL_ON_FAILURE=300
-
MERLOC_BROKER_URL: This configuration is MANDATORY. You need to set this environment variable by broker URL as mentioned in the AWS Lambda Runtime Setup section. -
MERLOC_AWS_LAMBDA_RUNTIME_CONCURRENCY_MODE: This configuration is OPTIONAL. Configures concurrency level at runtime level globally. Valid values are:REJECT: Rejects any invocation from any function if local runtime is busy executing other invocation. In this case, GateKeeper is informed by local runtime with the rejection and then GateKeeper forwards the request to the original user handler.WAIT: Waits any invocation from any function until runtime is available if local runtime is busy executing another invocation.PER_FUNCTION: Disables global lock between functions and runtime lock is handled at per function basis according toMERLOC_AWS_LAMBDA_RUNTIME_FUNCTION_CONCURRENCY_MODEconfiguration mentioned below. The default value isREJECT. For example,
MERLOC_AWS_LAMBDA_RUNTIME_CONCURRENCY_MODE=PER_FUNCTION -
MERLOC_AWS_LAMBDA_RUNTIME_FUNCTION_CONCURRENCY_MODE: This configuration is OPTIONAL. Configures concurrency level at function level so executing a function doesn't block executing another function. Valid values are:REJECT: Rejects an invocation from a function if local runtime is busy executing other invocation of that function. In this case, GateKeeper is informed by local runtime with the rejection and then GateKeeper forwards the request to the original user handler.WAIT: Waits an invocation from a function until runtime is available if local runtime is busy executing another invocation of that function. The default value isREJECT. For example,
MERLOC_AWS_LAMBDA_RUNTIME_FUNCTION_CONCURRENCY_MODE=WAIT -
MERLOC_DEBUG_ENABLE: This configuration is OPTIONAL. By default, internal debug logs are disabled, but you can enable it by setting theMERLOC_DEBUG_ENABLEenvironment variable totrue. For example,MERLOC_DEBUG_ENABLE=true -
MERLOC_BROKER_CONNECTION_NAME: This configuration is OPTIONAL. By default, the name of the connection to the broker isdefaultfor local AWS Lambda runtime. Local AWS Lambda runtime connection with namedefaultmatches with all GateKeeper connections if there is no another local AWS Lambda runtime connection with the function name (or connection name set byMERLOC_BROKER_CONNECTION_NAMEat GateKeeper) specifically. But you can change it by setting theMERLOC_BROKER_CONNECTION_NAMEenvironment variable. For example,MERLOC_BROKER_CONNECTION_NAME=serkan-connection
-
If the resources (AWS RDS, AWS OpenSearch/Elasticsearch, AWS ElastiCache, etc ...) you are accessing inside the function are deployed inside a VPC, your local needs to have access to resources in the VPC. So you need to setup a VPN connection from your local machine to the VPC network. You can check this AWS blog post to learn how to do that.
-
Currently, AWS Lambda layers are not supported. So if you use layers, they will not be available on your local while running function locally as MerLoc doesn't download and extract layers onto your local environment.
Please use GitHub Issues for any bug report, feature request and support.
If you would like to contribute, please
- Fork the repository on GitHub and clone your fork.
- Create a branch for your changes and make your changes on it.
- Send a pull request by explaining clearly what is your contribution.
Tip: Please check the existing pull requests for similar contributions and consider submit an issue to discuss the proposed feature before writing code.
Licensed under Apache License 2.0.