This example showcases Next.js's Static Generation feature using WordPress as the data source.
Once you have access to the environment variables you'll need, deploy the example using Vercel:
- DatoCMS
- Sanity
- TakeShape
- Prismic
- Contentful
- Strapi
- Agility CMS
- Cosmic
- ButterCMS
- Storyblok
- GraphCMS
- Kontent
- Ghost
- Blog Starter
- Builder.io
Execute create-next-app with npm, Yarn, or pnpm to bootstrap the example:
npx create-next-app --example cms-wordpress cms-wordpress-app
# or
yarn create next-app --example cms-wordpress cms-wordpress-app
# or
pnpm create next-app --example cms-wordpress cms-wordpress-appFirst, you need a WordPress site. There are many solutions for WordPress hosting, such as WP Engine and WordPress.com.
Once the site is ready, you'll need to install the WPGraphQL plugin. It will add GraphQL API to your WordPress site, which we'll use to query the posts. Follow these steps to install it:
- Download the WPGraphQL repo as a ZIP archive.
- Inside your WordPress admin, go to Plugins and then click Add New.
- Click the Upload Plugin button at the top of the page and upload the WPGraphQL plugin.
- Once the plugin has been added, activate it from either the Activate Plugin button displayed after uploading or from the Plugins page.
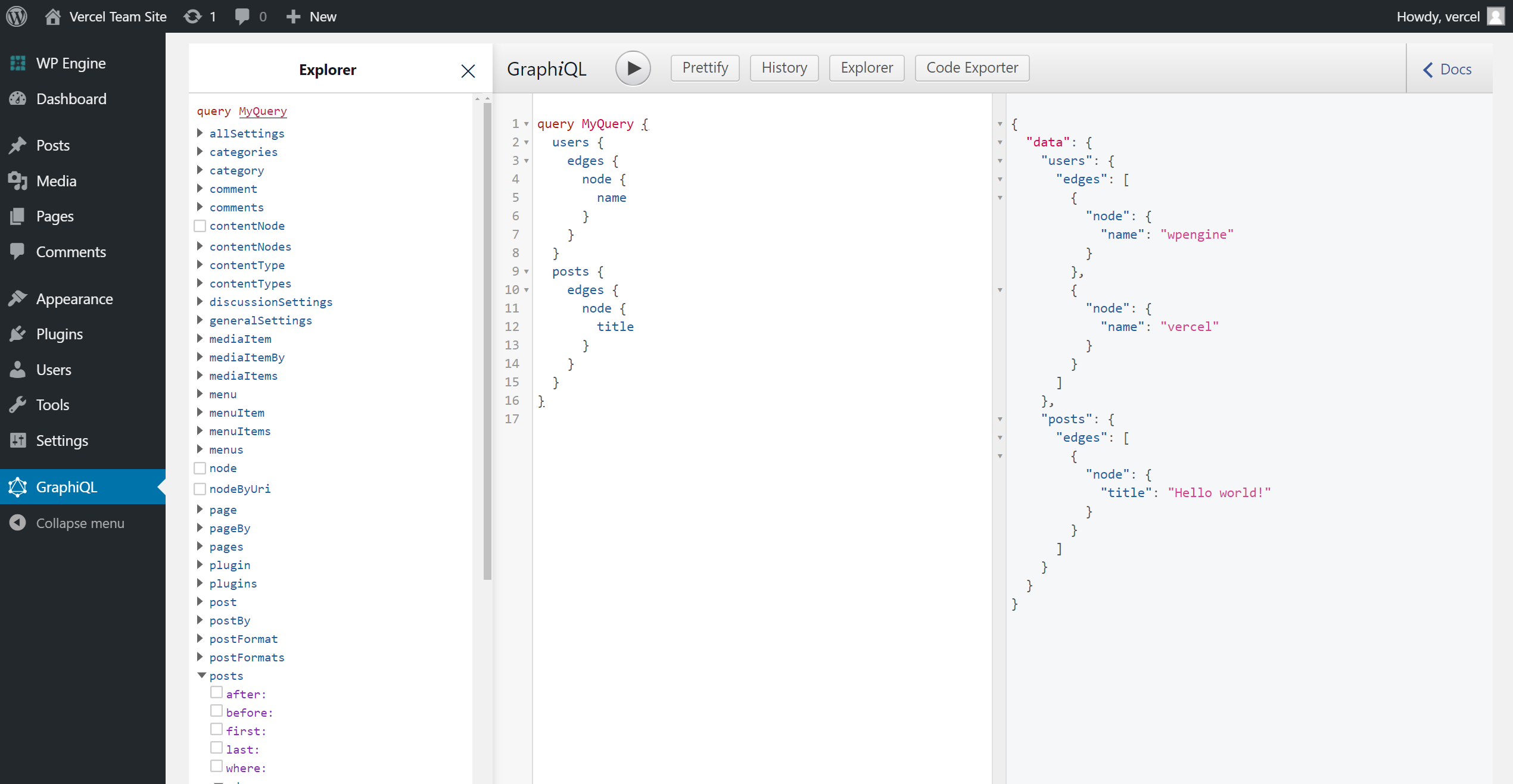
The WPGraphQL plugin also gives you access to a GraphQL IDE directly from your WordPress Admin, allowing you to inspect and play around with the GraphQL API.
Inside your WordPress admin, go to Posts and start adding new posts:
- We recommend creating at least 2 posts
- Use dummy data for the content
- Pick an author from your WordPress users
- Add a Featured Image. You can download one from Unsplash
- Fill the Excerpt field
When you’re done, make sure to Publish the posts.
Note: Only published posts and public fields will be rendered by the app unless Preview Mode is enabled.
Copy the .env.local.example file in this directory to .env.local (which will be ignored by Git):
cp .env.local.example .env.localThen open .env.local and set WORDPRESS_API_URL to be the URL to your GraphQL endpoint in WordPress. For example: https://myapp.wpengine.com/graphql.
Your .env.local file should look like this:
WORDPRESS_API_URL=...
# Only required if you want to enable preview mode
# WORDPRESS_AUTH_REFRESH_TOKEN=
# WORDPRESS_PREVIEW_SECRET=npm install
npm run dev
# or
yarn install
yarn devYour blog should be up and running on http://localhost:3000! If it doesn't work, post on GitHub discussions.
This step is optional. By default, the blog will work with public posts from your WordPress site. Private content such as unpublished posts and private fields cannot be retrieved. To have access to unpublished posts you'll need to set up authentication.
To add authentication to WPGraphQL, first you need to add the WPGraphQL JWT plugin to your WordPress Admin following the same process you used to add the WPGraphQL plugin.
Adding the WPGraphQL JWT plugin will disable your GraphQL API until you add a JWT secret (GitHub issue).
Once that's done, you'll need to access the WordPress filesystem to add the secret required to validate JWT tokens. We recommend using SFTP — the instructions vary depending on your hosting provider. For example:
Once you have SFTP access, open wp-config.php and add a secret for your JWT:
define( 'GRAPHQL_JWT_AUTH_SECRET_KEY', 'YOUR_STRONG_SECRET' );You can read more about this in the documentation for WPGraphQL JWT Authentication.
Now, you need to get a refresh token to make authenticated requests with GraphQL. Make the following GraphQL mutation to your WordPress site from the GraphQL IDE (See notes about WPGraphiQL from earlier). Replace your_username with the username of a user with the Administrator role, and your_password with the user's password.
mutation Login {
login(
input: {
clientMutationId: "uniqueId"
password: "your_password"
username: "your_username"
}
) {
refreshToken
}
}Copy the refreshToken returned by the mutation, then open .env.local, and make the following changes:
- Uncomment
WORDPRESS_AUTH_REFRESH_TOKENand set it to be therefreshTokenyou just received. - Uncomment
WORDPRESS_PREVIEW_SECRETand set it to be any random string (ideally URL friendly).
Your .env.local file should look like this:
WORDPRESS_API_URL=...
# Only required if you want to enable preview mode
WORDPRESS_AUTH_REFRESH_TOKEN=...
WORDPRESS_PREVIEW_SECRET=...Important: Restart your Next.js server to update the environment variables.
On your WordPress admin, create a new post like before, but do not publish it.
Now, if you go to http://localhost:3000, you won’t see the post. However, if you enable Preview Mode, you'll be able to see the change (Documentation).
To enable Preview Mode, go to this URL:
http://localhost:3000/api/preview?secret=<secret>&id=<id>
<secret>should be the string you entered forWORDPRESS_PREVIEW_SECRET.<id>should be the post'sdatabaseIdfield, which is the integer that you usually see in the URL (?post=18→ 18).- Alternatively, you can use
<slug>instead of<id>.<slug>is generated based on the title.
You should now be able to see this post. To exit Preview Mode, you can click on Click here to exit preview mode at the top.
You can deploy this app to the cloud with Vercel (Documentation).
To deploy your local project to Vercel, push it to GitHub/GitLab/Bitbucket and import to Vercel.
Important: When you import your project on Vercel, make sure to click on Environment Variables and set them to match your .env.local file.
Alternatively, you can deploy using our template by clicking on the Deploy button below.