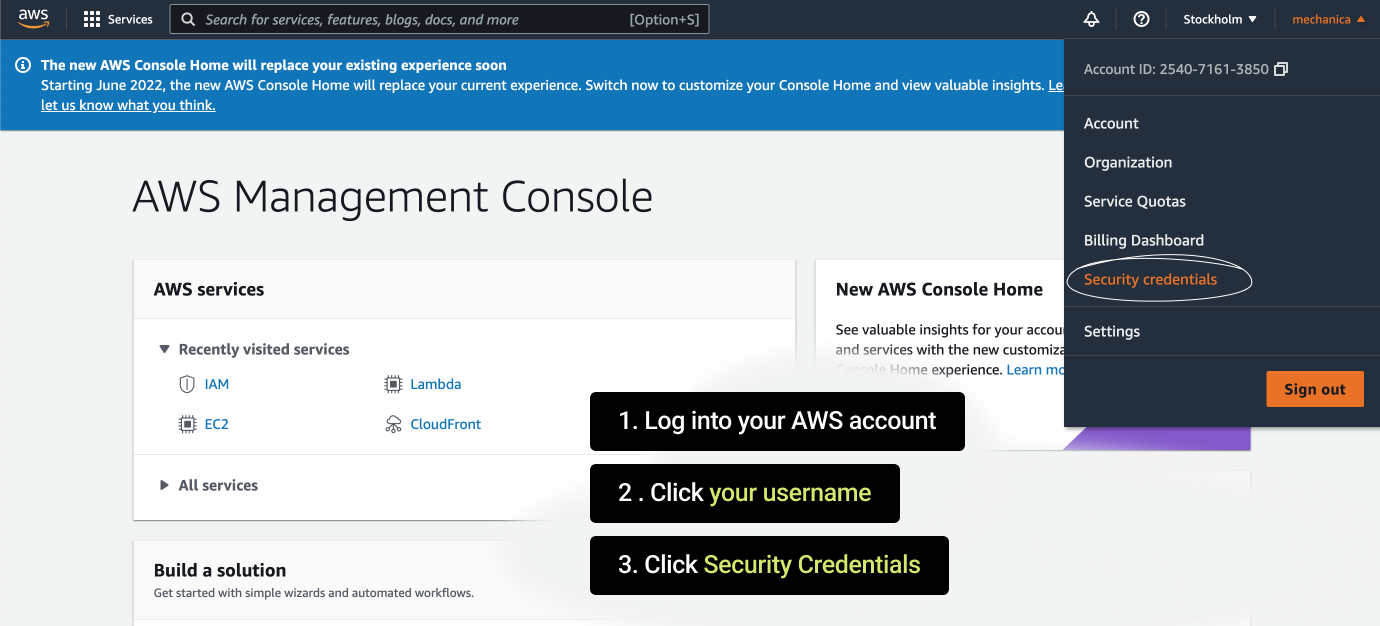
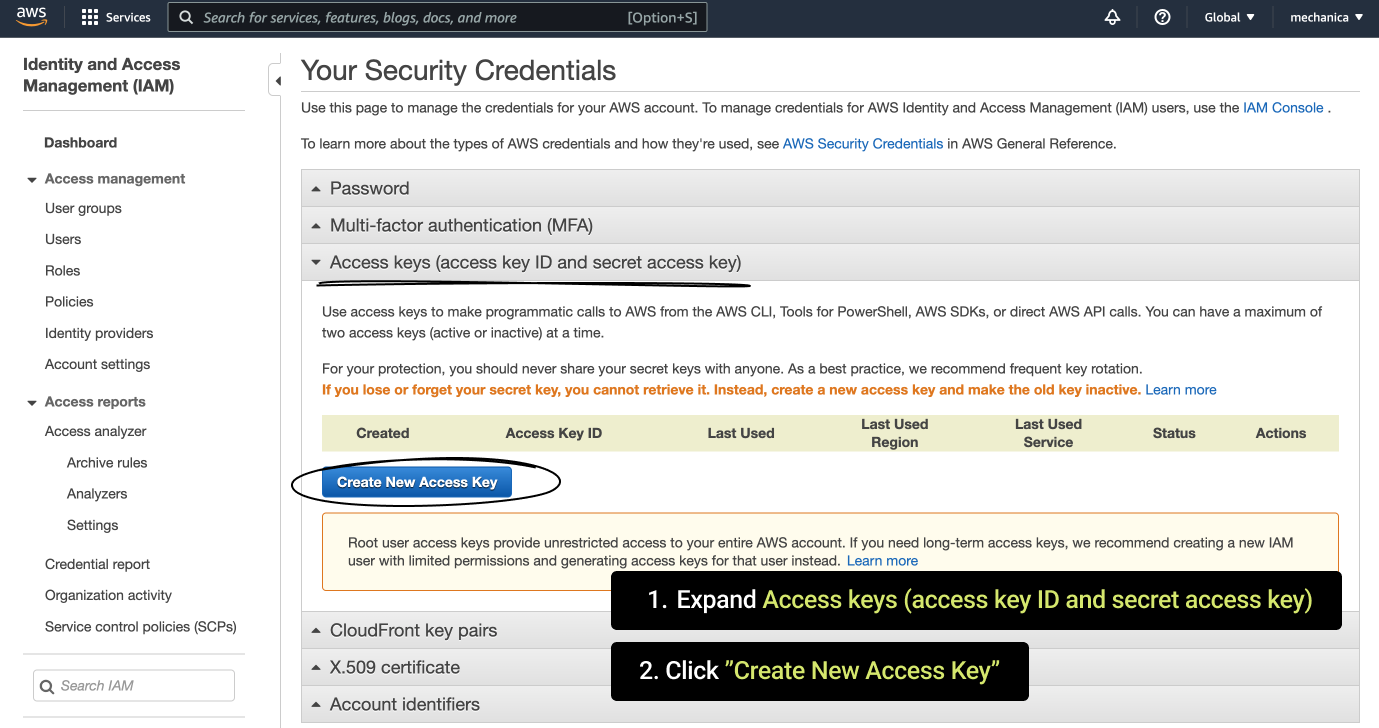
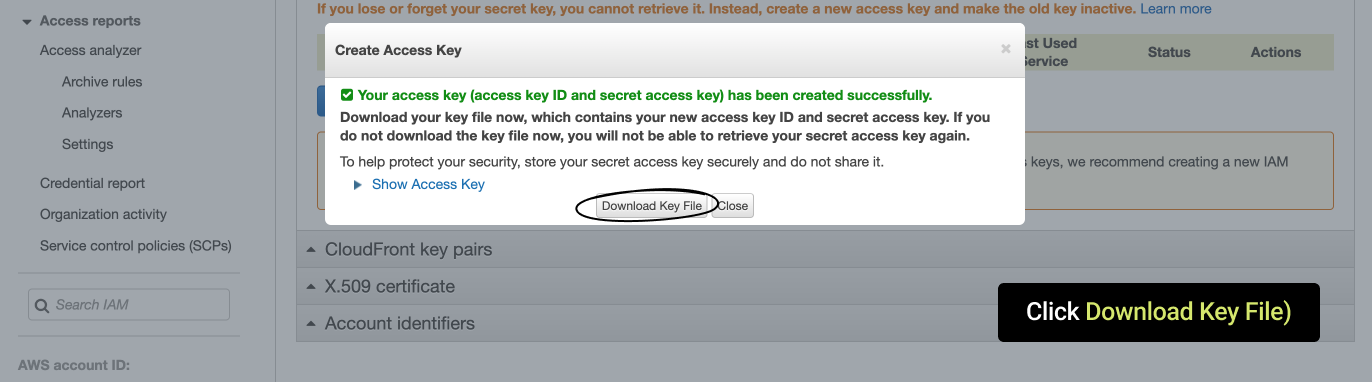
- Then in
~for Mac/Linux or inC:\Users<USER_NAME>for Windows
Create a folder.awsand a filecredentials(with no extension) in it.
Write your credentials in the file this way:[default] aws_access_key_id = YOUR_ACCESS_KEY_ID aws_secret_access_key = YOUR_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY
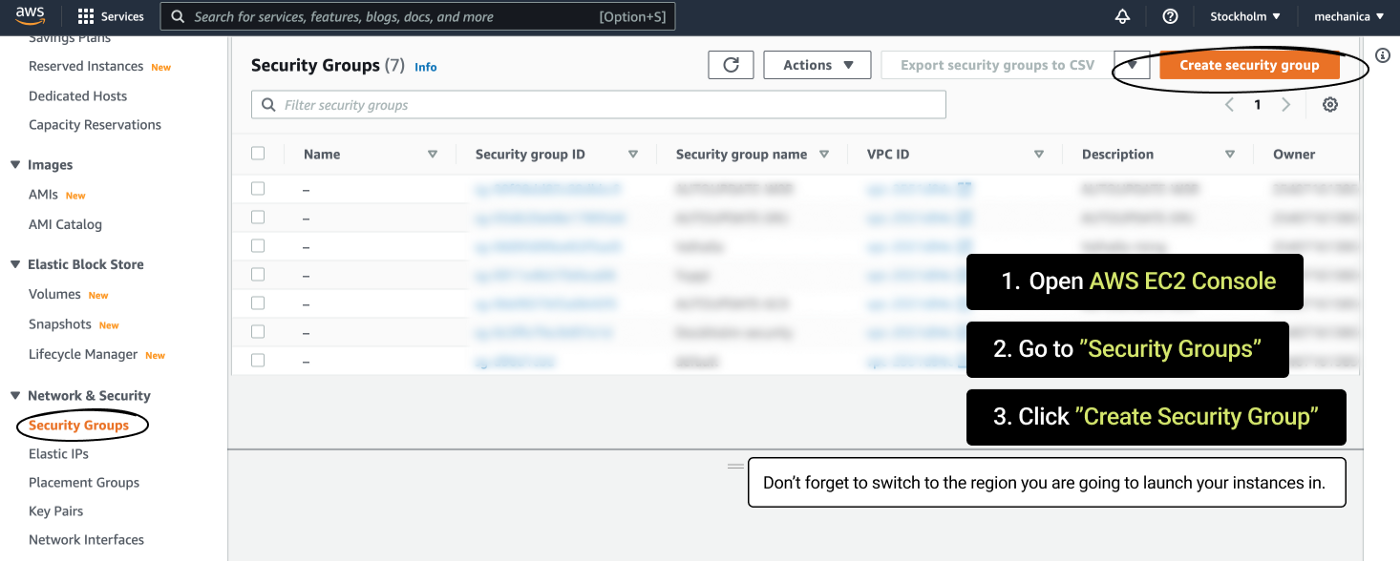
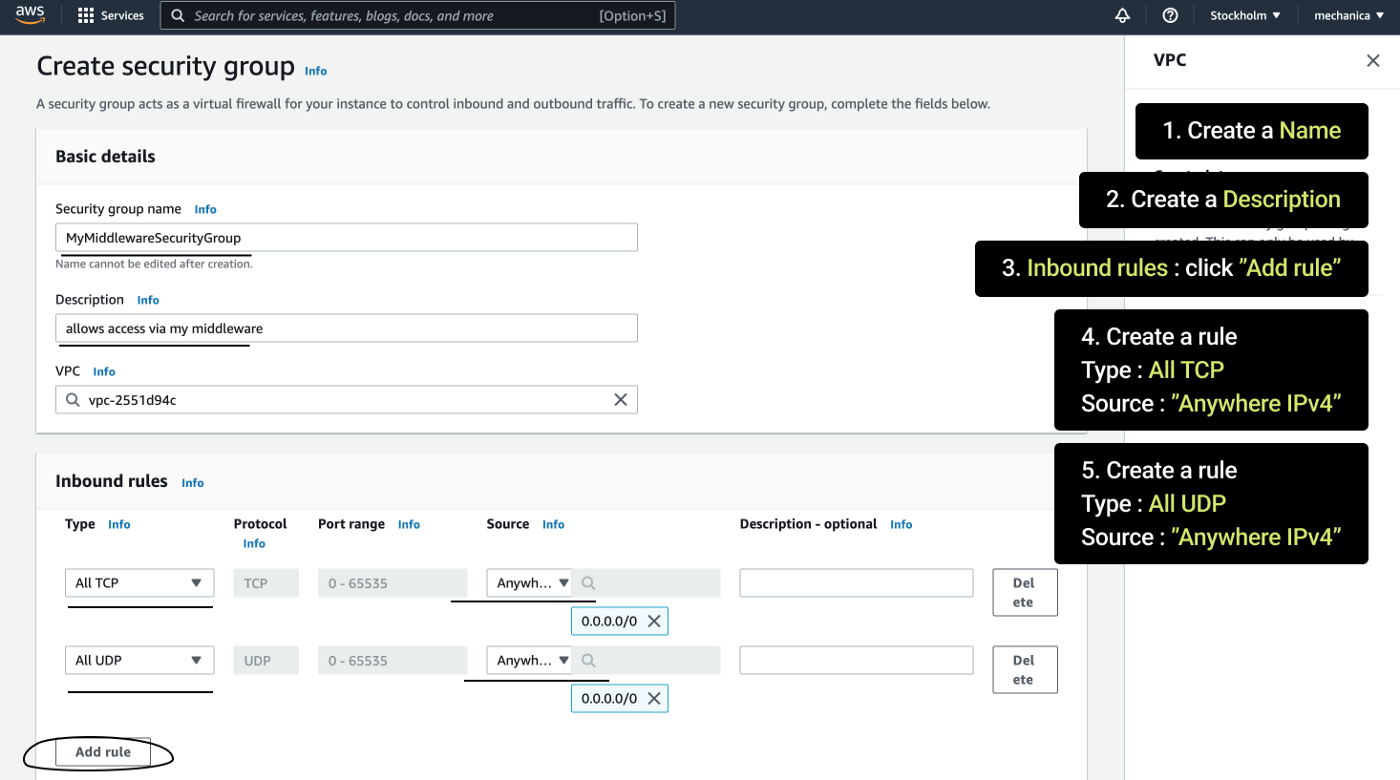
1) Log into AWS Console 2) Change your region to the desired one 3) Go to Security Groups 4) Click “Create security group” 5) Then create a Security Group in AWS Console with those parameters:
- Name
- Description
- Inbound Rules:
- Type — All TCP, Source — Anywhere IPv4
- Type — All UDP, Source — Anywhere IPv4
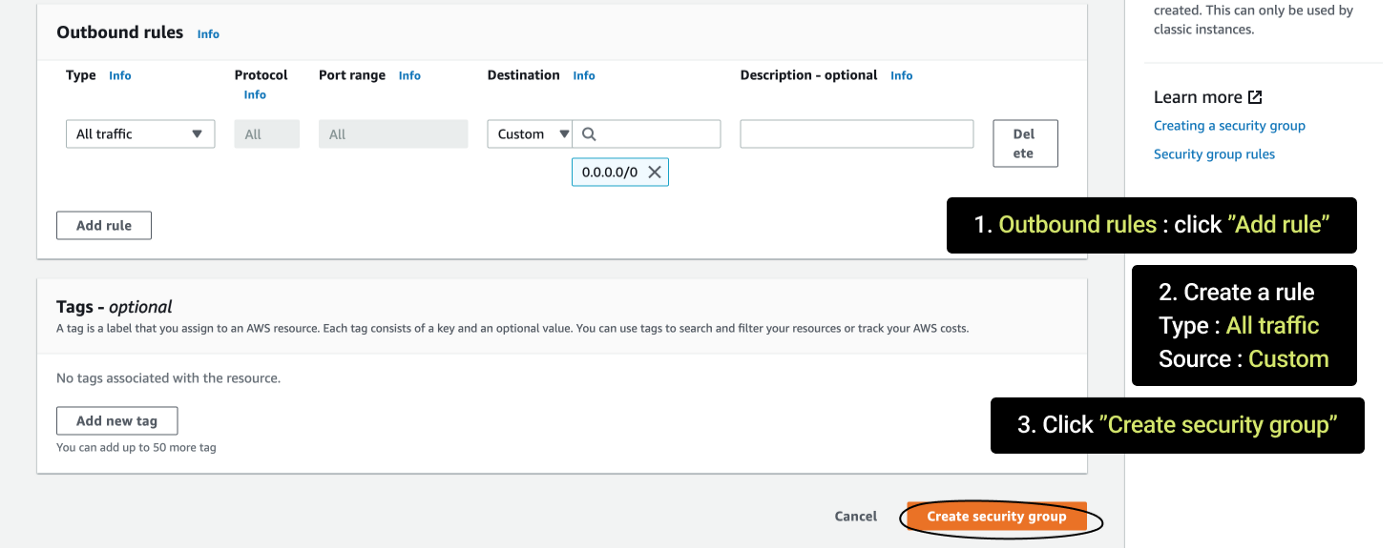
- Outbound rules
- Type — All Traffic, Source — Custom
server/index.js file like this
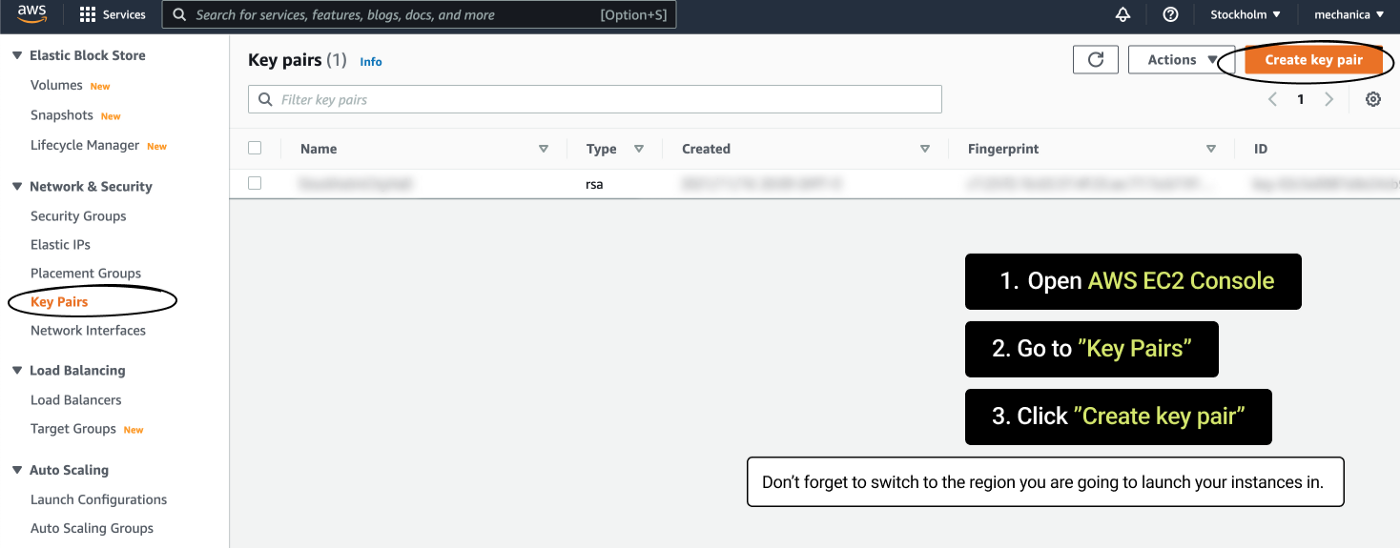
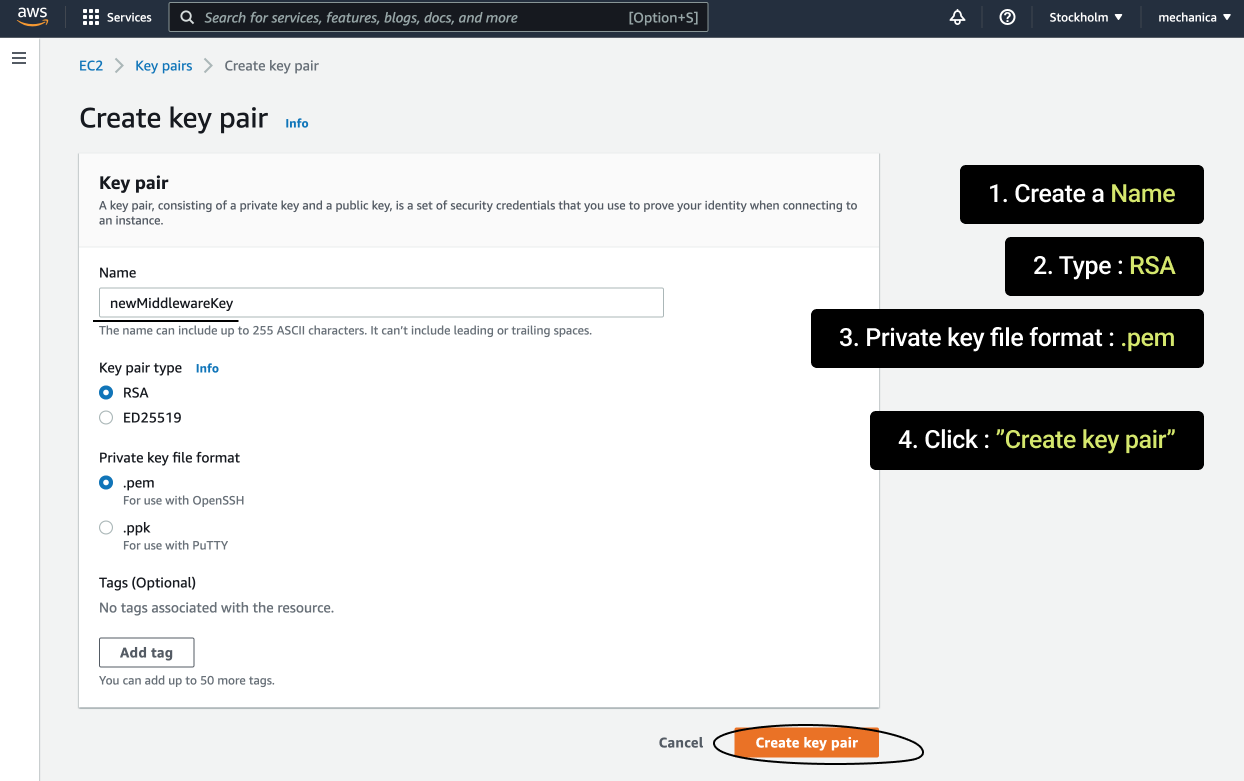
const SECURITY_GROUP = "sg-0d17b51c3a3f8fab7"; // REPLACE WITH YOUR SECURITY GROUP IDAttention! Create a key pair in the region you plan to launch your instances in. 1) Log into AWS Console 2) Change your region to the desired one 3) Go to Key Pairs 4) Click “Create key pair” 5) Save the key pair name and paste it in the
server/index.js under the security group id like this
const KEY_PAIR_NAME = "us-test"; // REPLACE WITH YOUR KEY PAIR NAMEIn the same
server/index.js file under the key pair paste the region that is active in your AWS Console so it looks like this
const REGION = "us-east-1"; // REPLACE WITH YOUR REGIONYou need Node.js to be installed on your computer. Open
server folder in terminal and run
npm i
node index.js
You will get something like this as a response
Your AMI creation date is - 5/3/2022 Server listening on 3001In the second terminal window open
client folder and run
npm i
npm start
The web page will be automatically opened in your browser
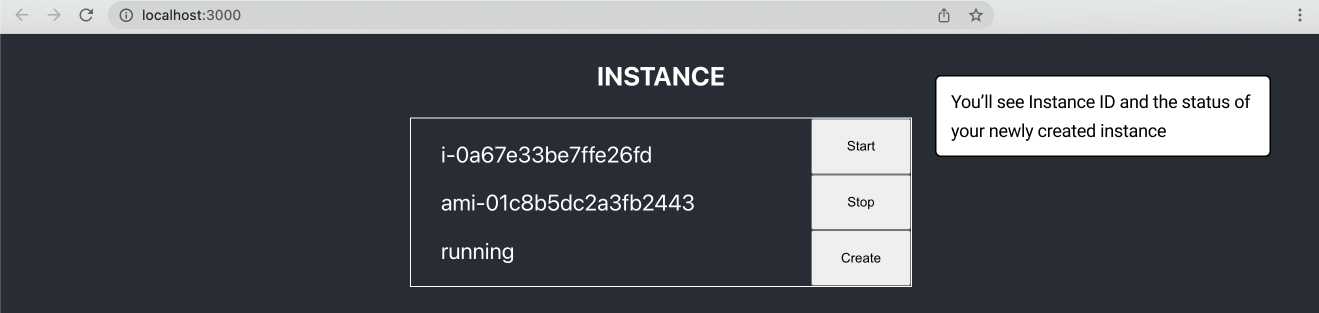
Create a new instance.
 You’ll see your instance launching.
You’ll see your instance launching.
 Please wait for 2–3 minutes for your instance to complete launching.
Please wait for 2–3 minutes for your instance to complete launching.
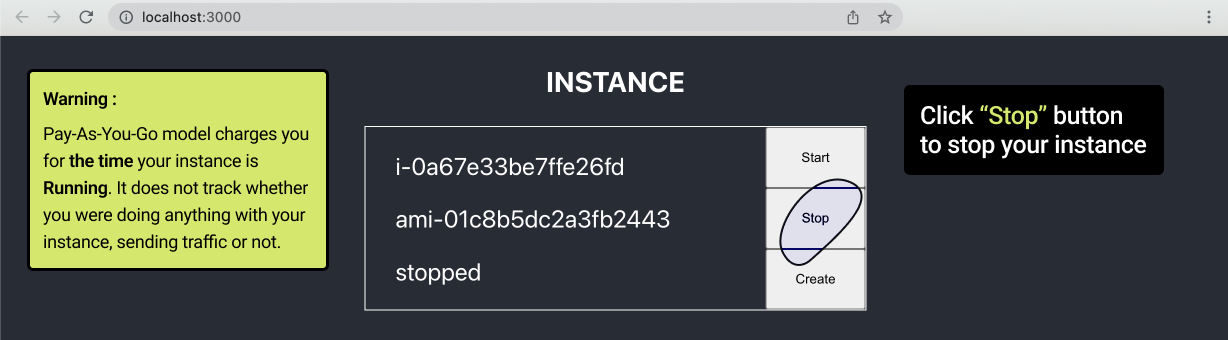
AWS Pay-As-You-Go model charges for the time you are using the resources. The system does not consider whether you are doing anything with the instance or not, whether you are sending any traffic or not.
This means that you need to Stop or Terminate you instance upon completion of your tasks to avoid unnecessary charges.
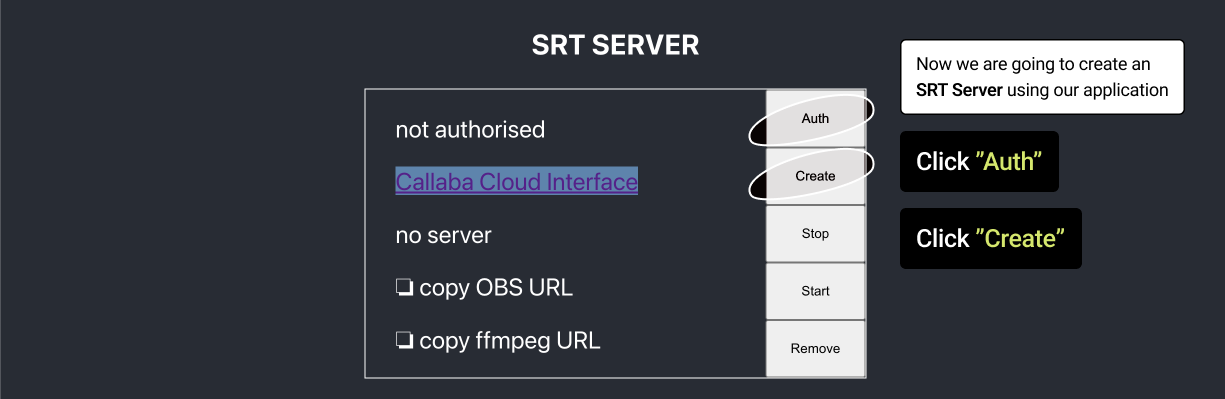
Now we are going to create SRT Server to send our stream to. -authenticate(){
fetch('http://' + this.state.ipAddress + '/api/auth/login',
{
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
},
body: JSON.stringify(
{
email: "admin",
password: this.state.instanceData.Reservations[this.state.instanceIndex].Instances[0].InstanceId
})
})
.then(response => response.json())
.then(data => {
this.setState({callabaToken: data.token});
console.log(data);
})
}
The function requests Callaba authentication token and saves it to state to sign requests with it.
-
createStream(){ fetch('http://' + this.state.ipAddress + '/api/srt-servers/create', { method: 'POST', headers: { 'x-access-token': this.state.callabaToken, 'Content-Type': 'application/json', }, body: JSON.stringify( { server_name: "Test SRT server", // CHANGE WITH ANY SERVER NAME YOU WANT server_type: "SERVER_TYPE_SRT", server_port: 1935, server_latency: 200, server_maxbw: -1, server_timeout: 60, server_rcvbuf: 48234496, server_active: true }) }) .then(response => response.json()) .then(data => { this.setState({serverId: data._id, serverState: "server running"}); }) }In the request's body you can specify such settings asserver_name,server_portAfter executing the request the received server id will be saved to state.
createPlayer(){
fetch('http://' + this.state.instanceData.Reservations[this.state.instanceIndex].Instances[0].PublicIpAddress + '/api/vod/create',
{
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'accept': 'application/json',
'x-access-token': this.state.callabaToken,
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
body: JSON.stringify(
{
active: true,
dash_fragment_length: 60,
dash_fragment_size: 3,
hls_fragment_length: 60,
hls_fragment_size: 3,
initial_live_manifest_size: 3,
input: {
input_module_id: this.state.serverId,
input_stream_id: "",
input_type: "INPUT_TYPE_SRT_SOFTWARE"
},
live_sync_duration_count: 3,
transcoding: {
audio_transcoding: "Disabled",
output_audio_bitrate: 320,
output_video_bitrate: 8000,
video_transcoding: "Disabled"
},
vod_name: "Test SRT player",
vod_port: 10001
})
})
.then(response => response.json())
.then(data => this.setState({playerId: data._id, playerState: "running"}))
}
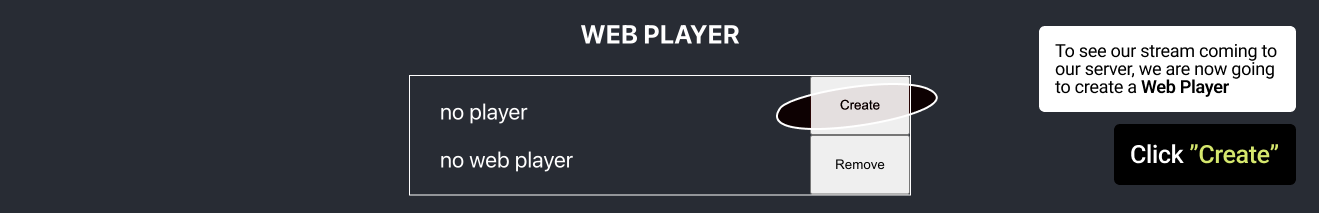
It uses the server id to specify the server it gets the stream from.After receiving data as a response the function saves the player's id to state. It is used by app to generate a link to the created player:
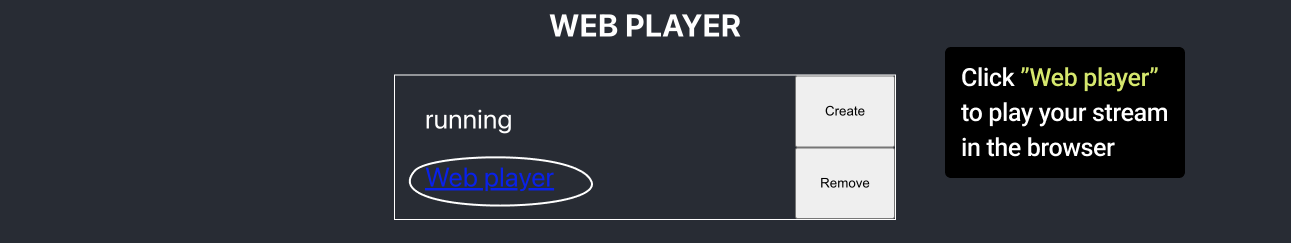
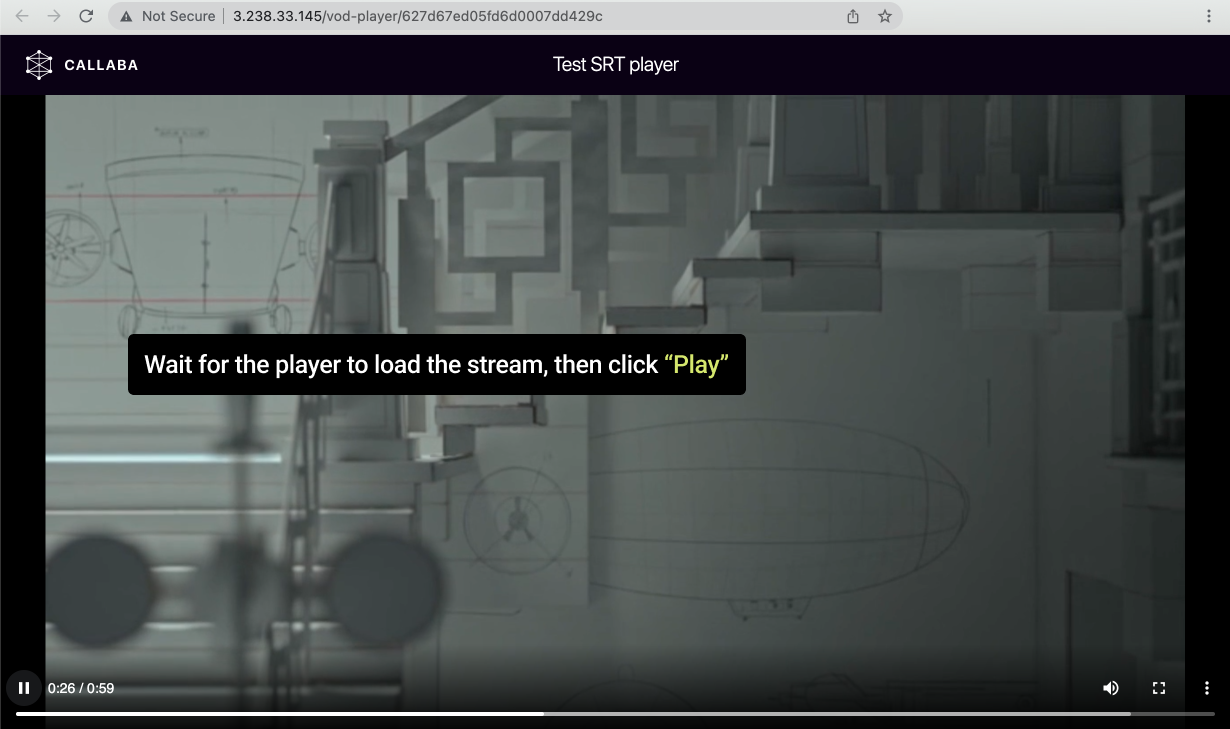
http:// + instanceIpAdress + /vod-player/ + playerId- Once your player is ready, click Web Player link to view your stream in the browser. - Wait for the player to load your stream, then click play. It is important to Stop or Terminate your instances upon completion of your stream or your task, as AWS Pay-As-You-Go model charges for the time you are using the resources.
Click “Stop” to stop your instance.
stopStream(){
fetch('http://' + this.state.ipAddress + '/api/srt-servers/stop',
{
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'accept': 'application/json',
'x-access-token': this.state.callabaToken,
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
body: JSON.stringify({id: this.state.serverId})
})
.then(response => response.json())
.then(data => {
if(data.ok) this.setState({serverState: "server stopped"});
})
}
startStream(){
fetch('http://' + this.state.ipAddress + '/api/srt-servers/start',
{
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'accept': 'application/json',
'x-access-token': this.state.callabaToken,
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
body: JSON.stringify({id: this.state.serverId})
})
.then(response => response.json())
.then(data => {
if(data.ok) this.setState({serverState: "server running"});
})
}
removeStream(){
fetch('http://' + this.state.ipAddress + '/api/srt-servers/remove',
{
method: 'DELETE',
headers: {
'accept': 'application/json',
'x-access-token': this.state.callabaToken,
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
body: JSON.stringify({id: this.state.serverId})
})
.then(response => response.json())
.then(data => {
if(data.ok) this.setState({serverState: "no server", serverId: "no server id"});
})
}
removePlayer(){
fetch('http://' + this.state.ipAddress + '/api/vod/remove',
{
method: 'DELETE',
headers: {
'accept': 'application/json',
'x-access-token': this.state.callabaToken,
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
body: JSON.stringify({id: this.state.playerId})
})
.then(response => response.json())
.then(() => this.setState({playerState: "no player"}))
}
createRestream(){
fetch('http://'+ this.state.ipAddress +'/api/restream/create',
{
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'accept': 'application/json',
'x-access-token': this.state.callabaToken,
'Content-Type':'application/json'
},
body: JSON.stringify({
restream_name: "Test restream",
restream_type: "RESTREAM_TYPE_SRT_TO_RTMP",
input: {
input_type: "INPUT_TYPE_SRT_SOFTWARE",
input_server_id: this.state.serverId,
input_stream_id: "publisher/test-srt-server/srt-stream-01",
module_name: "test youtube",
module_type: "MODULE_RESTREAM"
},
output: {
output_type: "OUTPUT_TYPE_OTHER_RTMP_URL",
output_stream_url : "rtmp://x.rtmp.youtube.com/live2" ,
output_stream_key: "f9da-dgj8-gq64-mjp2-7d0w"
},
active: true
})
})
.then(response => response.json())
.then(data => this.setState({restreamId: data._id}))
}
removeRestream(){
fetch('http://'+ this.state.ipAddress +'/api/restream/remove',
{
method: 'DELETE',
headers: {
'accept': 'application/json',
'x-access-token': this.state.callabaToken,
'Content-Type':'application/json'
},
body: JSON.stringify({id: this.state.restreamId})
})
.then(response => response.json())
.then(() => this.setState({restreamId: "no restream"}))
}
You can find a more detailed tutorial here.