Table of contents
- The idea
- TypeScript compatibility
- Error reporters
- Custom error messages
- Community
- TypeScript integration
- Implemented types / combinators
- Recursive types
- Tagged unions
- Branded types / Refinements
- Exact types
- Mixing required and optional props
- Custom types
- Generic Types
- Piping
- Tips and Tricks
Blog post: "Typescript and validations at runtime boundaries" by @lorefnon
A value of type Type<A, O, I> (called "codec") is the runtime representation of the static type A.
Also a codec can
- decode inputs of type
I(throughdecode) - encode outputs of type
O(throughencode) - be used as a custom type guard (through
is)
class Type<A, O, I> {
readonly _A: A
readonly _O: O
readonly _I: I
constructor(
/** a unique name for this codec */
readonly name: string,
/** a custom type guard */
readonly is: (u: unknown) => u is A,
/** succeeds if a value of type I can be decoded to a value of type A */
readonly validate: (input: I, context: Context) => Either<Errors, A>,
/** converts a value of type A to a value of type O */
readonly encode: (a: A) => O
) {}
/** a version of `validate` with a default context */
decode(i: I): Either<Errors, A>
}Note. The Either type is defined in fp-ts, a library containing implementations of
common algebraic types in TypeScript.
Example
A codec representing string can be defined as
import * as t from 'io-ts'
const isString = (u: unknown): u is string => typeof u === 'string'
const string = new t.Type<string, string, unknown>(
'string',
isString,
(u, c) => (isString(u) ? t.success(u) : t.failure(u, c)),
t.identity
)A codec can be used to validate an object in memory (for example an API payload)
import * as t from 'io-ts'
const User = t.type({
userId: t.number,
name: t.string
})
// validation succeeded
User.decode(JSON.parse('{"userId":1,"name":"Giulio"}')) // => Right({ userId: 1, name: "Giulio" })
// validation failed
User.decode(JSON.parse('{"name":"Giulio"}')) // => Left([...])The stable version is tested against TypeScript 3.2.4.
| io-ts version | required TypeScript version |
|---|---|
| 1.6.x+ | 3.2.2+ |
| 1.5.3 | 3.0.1+ |
| 1.5.2- | 2.7.2+ |
Note. This library is conceived, tested and is supposed to be consumed by TypeScript with the strict flag turned on.
Note. If you are running < typescript@3.0.1 you have to polyfill unknown.
You can use unknown-ts as a polyfill.
A reporter implements the following interface
interface Reporter<A> {
report: (validation: Validation<any>) => A
}This package exports a default PathReporter reporter
Example
import { PathReporter } from 'io-ts/lib/PathReporter'
const result = User.decode({ name: 'Giulio' })
console.log(PathReporter.report(result))
// => [ 'Invalid value undefined supplied to : { userId: number, name: string }/userId: number' ]You can define your own reporter. Errors has the following type
interface ContextEntry {
readonly key: string
readonly type: Decoder<any, any>
}
interface Context extends ReadonlyArray<ContextEntry> {}
interface ValidationError {
readonly value: unknown
readonly context: Context
}
interface Errors extends Array<ValidationError> {}Example
const getPaths = <A>(v: t.Validation<A>): Array<string> => {
return v.fold(errors => errors.map(error => error.context.map(({ key }) => key).join('.')), () => ['no errors'])
}
console.log(getPaths(User.decode({}))) // => [ '.userId', '.name' ]You can set your own error message by providing a message argument to failure
Example
const NumberFromString = new t.Type<number, string, unknown>(
'NumberFromString',
t.number.is,
(u, c) =>
t.string.validate(u, c).chain(s => {
const n = +s
return isNaN(n) ? t.failure(u, c, 'cannot parse to a number') : t.success(n)
}),
String
)
console.log(PathReporter.report(NumberFromString.decode('a')))
// => ['cannot parse to a number']- io-ts-types - A collection of codecs and combinators for use with io-ts
- io-ts-reporters - Error reporters for io-ts
- geojson-iots - codecs for GeoJSON as defined in rfc7946 made with io-ts
- graphql-to-io-ts - Generate typescript and cooresponding io-ts types from a graphql schema
- io-ts-promise - Convenience library for using io-ts with promise-based APIs
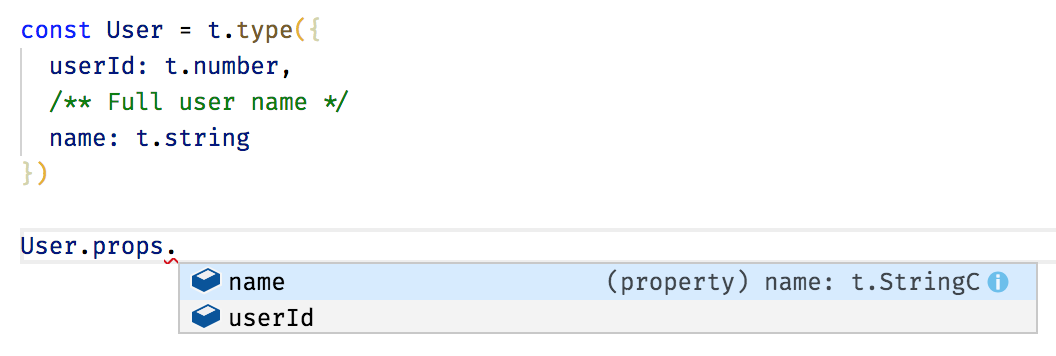
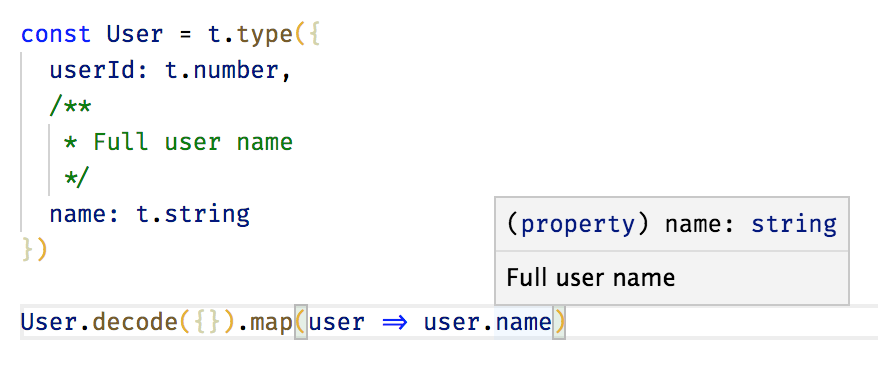
codecs can be inspected
This library uses TypeScript extensively. Its API is defined in a way which automatically infers types for produced values
Note that the type annotation isn't needed, TypeScript infers the type automatically based on a schema (and comments are preserved).
Static types can be extracted from codecs using the TypeOf operator
type User = t.TypeOf<typeof User>
// same as
type User = {
userId: number
name: string
}| Type | TypeScript | codec / combinator |
|---|---|---|
| null | null |
t.null or t.nullType |
| undefined | undefined |
t.undefined |
| void | void |
t.void or t.voidType |
| string | string |
t.string |
| number | number |
t.number |
| boolean | boolean |
t.boolean |
| unknown | unknown |
t.unknown |
| never | never |
t.never |
| object | object |
t.object |
| array of unknown | Array<unknown> |
t.UnknownArray |
| array of type | Array<A> |
t.array(A) |
| record of unknown | Record<string, unknown> |
t.UnknownRecord |
| record of type | Record<K, A> |
t.record(K, A) |
| function | Function |
t.Function |
| literal | 's' |
t.literal('s') |
| partial | Partial<{ name: string }> |
t.partial({ name: t.string }) |
| readonly | Readonly<A> |
t.readonly(A) |
| readonly array | ReadonlyArray<A> |
t.readonlyArray(A) |
| type alias | type T = { name: A } |
t.type({ name: A }) |
| tuple | [ A, B ] |
t.tuple([ A, B ]) |
| union | A | B |
t.union([ A, B ]) or t.taggedUnion(tag, [ A, B ]) |
| intersection | A & B |
t.intersection([ A, B ]) |
| keyof | keyof M |
t.keyof(M) |
| recursive types | ✘ | t.recursion(name, definition) |
| branded types / refinements | ✘ | t.brand(A, predicate, brand) |
| integer | ✘ | t.Int (built-in branded codec) |
| exact types | ✘ | t.exact(type) |
| strict | ✘ | t.strict({ name: A }) (an alias of t.exact(t.type({ name: A }))) |
Recursive types can't be inferred by TypeScript so you must provide the static type as a hint
interface Category {
name: string
categories: Array<Category>
}
const Category: t.Type<Category> = t.recursion('Category', () =>
t.type({
name: t.string,
categories: t.array(Category)
})
)interface Foo {
type: 'Foo'
b: Bar | undefined
}
interface Bar {
type: 'Bar'
a: Foo | undefined
}
const Foo: t.Type<Foo> = t.recursion('Foo', () =>
t.interface({
type: t.literal('Foo'),
b: t.union([Bar, t.undefined])
})
)
const Bar: t.Type<Bar> = t.recursion('Bar', () =>
t.interface({
type: t.literal('Bar'),
a: t.union([Foo, t.undefined])
})
)If you are encoding tagged unions, instead of the general purpose union combinator, you may want to use the
taggedUnion combinator in order to get better performances
const A = t.type({
tag: t.literal('A'),
foo: t.string
})
const B = t.type({
tag: t.literal('B'),
bar: t.number
})
// the actual presence of the tag is statically checked
const U = t.taggedUnion('tag', [A, B])You can brand / refine a codec (any codec) using the brand combinator
// a unique brand for positive numbers
interface PositiveBrand {
readonly Positive: unique symbol // use `unique symbol` here to ensure uniqueness across modules / packages
}
const Positive = t.brand(
t.number, // a codec representing the type to be refined
(n): n is t.Branded<number, PositiveBrand> => n >= 0, // a custom type guard using the build-in helper `Branded`
'Positive' // the name must match the readonly field in the brand
)
type Positive = t.TypeOf<typeof Positive>
/*
same as
type Positive = number & t.Brand<PositiveBrand>
*/Branded codecs can be merged with t.intersection
// t.Int is a built-in branded codec
const PositiveInt = t.intersection([t.Int, Positive])
type PositiveInt = t.TypeOf<typeof PositiveInt>
/*
same as
type PositiveInt = number & t.Brand<t.IntBrand> & t.Brand<PositiveBrand>
*/You can make a codec exact (which means that additional properties are stripped) using the exact combinator
const ExactUser = t.exact(User)
User.decode({ userId: 1, name: 'Giulio', age: 45 }) // ok, result is right({ userId: 1, name: 'Giulio', age: 45 })
ExactUser.decode({ userId: 1, name: 'Giulio', age: 43 }) // ok but result is right({ userId: 1, name: 'Giulio' })You can mix required and optional props using an intersection
const A = t.type({
foo: t.string
})
const B = t.partial({
bar: t.number
})
const C = t.intersection([A, B])
type C = t.TypeOf<typeof C>
// same as
type C = {
foo: string
} & {
bar?: number | undefined
}You can apply partial to an already defined codec via its props field
const PartialUser = t.partial(User.props)
type PartialUser = t.TypeOf<typeof PartialUser>
// same as
type PartialUser = {
name?: string
age?: number
}You can define your own types. Let's see an example
// represents a Date from an ISO string
const DateFromString = new t.Type<Date, string, unknown>(
'DateFromString',
(u): u is Date => u instanceof Date,
(u, c) =>
t.string.validate(u, c).chain(s => {
const d = new Date(s)
return isNaN(d.getTime()) ? t.failure(u, c) : t.success(d)
}),
a => a.toISOString()
)
const s = new Date(1973, 10, 30).toISOString()
DateFromString.decode(s)
// right(new Date('1973-11-29T23:00:00.000Z'))
DateFromString.decode('foo')
// left(errors...)Note that you can deserialize while validating.
Polymorphic codecs are represented using functions. For example, the following typescript:
interface ResponseBody<T> {
result: T
_links: Links
}
interface Links {
previous: string
next: string
}Would be:
// t.Mixed = t.Type<any, any, unknown>
const ResponseBody = <C extends t.Mixed>(codec: C) =>
t.interface({
result: type,
_links: Links
})
const Links = t.interface({
previous: t.string,
next: t.string
})And used like:
const UserModel = t.type({
name: t.string
})
functionThatRequiresRuntimeType(ResponseBody(t.array(UserModel)), ...params)You can pipe two codecs if their type parameters do align
const NumberCodec = new t.Type<number, string, string>(
'NumberCodec',
t.number.is,
(s, c) => {
const n = parseFloat(s)
return isNaN(n) ? t.failure(s, c) : t.success(n)
},
String
)
const NumberFromString = t.string.pipe(
NumberCodec,
'NumberFromString'
)No, however you can define your own logic for that (if you really trust the input)
import * as t from 'io-ts'
import { Either, right } from 'fp-ts/lib/Either'
const { NODE_ENV } = process.env
export function unsafeDecode<A, O, I>(value: I, codec: t.Type<A, O, I>): Either<t.Errors, A> {
if (NODE_ENV !== 'production' || codec.encode !== t.identity) {
return codec.decode(value)
} else {
// unsafe cast
return right(value as any)
}
}
// or...
import { failure } from 'io-ts/lib/PathReporter'
export function unsafeGet<A, O, I>(value: I, codec: t.Type<A, O, I>): A {
if (NODE_ENV !== 'production' || type.encode !== t.identity) {
return codec.decode(value).getOrElseL(errors => {
throw new Error(failure(errors).join('\n'))
})
} else {
// unsafe cast
return value as any
}
}Use keyof instead of union when defining a union of string literals
const Bad = t.union([
t.literal('foo'),
t.literal('bar'),
t.literal('baz')
// etc...
])
const Good = t.keyof({
foo: null,
bar: null,
baz: null
// etc...
})Benefits
- unique check for free
- better performance,
O(log(n))vsO(n)