Provision a Fedora CoreOS-based vanilla Kubernetes on a local Proxmox hypervisor.
This repo consists of two parts. The basic cluster setup is provisioned with the terraform modules in infra, the configuration of kubernetes resources is performed via ArgoCD and its configurations in gitops.
- terraform creates certificates for communication with matchbox
- terraform sets up a matchbox server (as lxc container)
- matchbox will provide ignition configs for VMs with specific MAC addresses
- certificates are configured
- terraform provisions VMs with Fedora CoreOS and according to the spec
- VMs boot from a custom iPXE image and await configuration
- VMs will load (extra steps required) ignition configs from the matchbox server
- VMs will be configured after a few minutes and form a Kubernetes cluster
- terraform will generate a kubeconfig to connect
- configure the cluster: install ArgoCD and initialize it with the provided configuration
You should now have an ArgoCD managed Kubernetes server. 🚀
- Proxmox
- at least 8GB RAM
- at least 500GB available storage
- default configuration, i.e. no special network configs, storage, firewalls etc.
- a user belonging to the admin group, could be the default
root
- A Debian LXC image
- A bootable iPXE ISO image. Cluster VMs need this to be able to load the boot resources over HTTPS.
- Clone https://github.com/ipxe/ipxe.git
- Enable HTTPS support (
DOWNLOAD_PROTO_HTTPS) inipxe/src/config/general.h - Build the ISO:
make bin/ipxe.iso - Copy the ISO to the Proxmox' local storage, name it
https-ipxe.iso
- DHCP on the host network for matchbox, control and worker nodes
- at least one free static IP for the load balancer deployed
kubectl&helm
You probably want to create a configuration file for the modules, e.g. infra/credentials.auto.tfvar:
proxmox_target_node = "box" # hostname of the proxmox node
proxmox_api_token_id = "tf@pam!tf-api" # user create for terraform
proxmox_api_token_secret = "<uuid>"
container_root_password = "hunter2"
container_template_name = "local:vztmpl/debian-12-standard_12.7-1_amd64.tar.zst" # you should download some debian image and put the appropriate name here.
ssh_private_key_path = "~/.ssh/id_ed25519"
ssh_public_keys = [
"ssh-ed25519 ...",
]
controller_number = 1
controller_cpus = 2
controller_memory = 3096
worker_number = 1
worker_cpus = 6
worker_memory = 4096
cluster_name = "lab"
cluster_api_address = "lab.example.com"
node_domain = "local"
node_fcos_version = "40.20240920.3.0"
Note: The kubeconfig being generated points at cluster_api_address, port 6443. You should either pick a name that is instantly resolvable to a control plane node or configure routing accordingly.
(there is currently an issue with the terraform module dependencies, so you need to run them manually in sequence)
terraform apply --target=module.basics
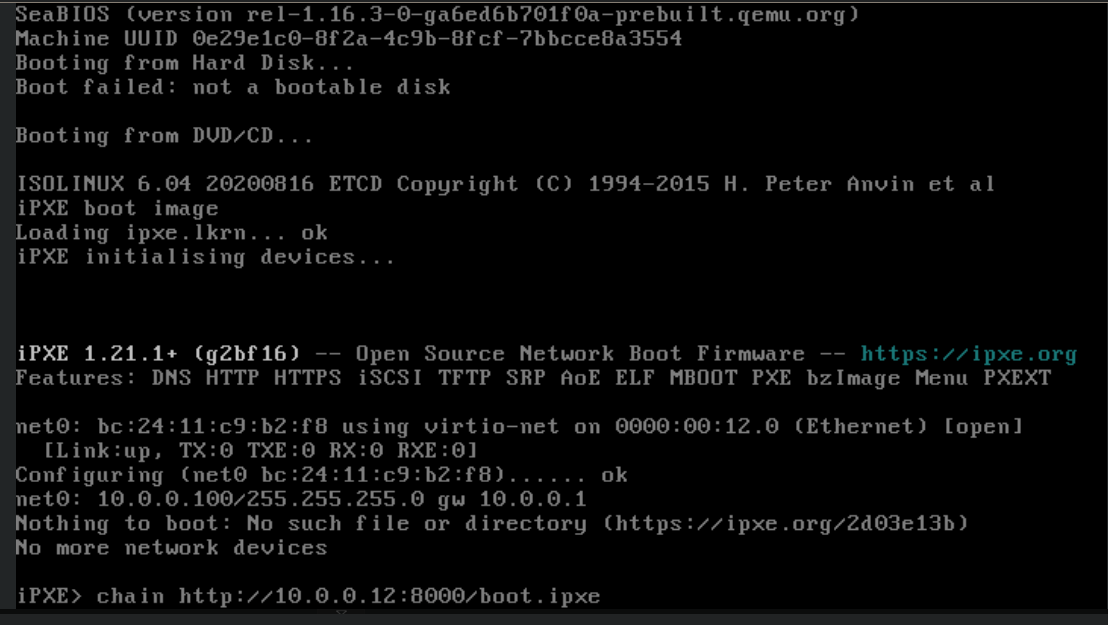
terraform apply --target=module.clusterAs soon as VMs are started, go to the Proxmox Web UI, open the serial console to each VM and open an iPXE command line using CTRL+B (you may need to wait for the right moment when iPXE reports having an IP address) . Until you do, the VMs will boot-loop. On the command line, enter:
chain http://<your-matchbox-ip>:8000/boot.ipxe
See the following image for reference:
You should now see the VM download Fedora CoreOS and its ignition files from matchbox.
If the VM can't access the matchbox server, I found the following to be helpful.
- Logs: connect to the matchbox server and
journalctl -fu matchbox.service - Connectivity: test that you can access the service:
curl $MATCHBOX_IP:8080
# should return "matchbox"- TLS: check the generated TLS certificates:
terraform output -raw matchbox_ca_crt_pem > ca.crt
terraform output -raw matchbox_client_crt_pem > client.crt
terraform output -raw matchbox_client_key_pem > client.key
openssl s_client -connect $MATCHBOX_IP:8081 -CAfile ca.crt -cert client.crt -key client.key | head
# output should contain "CONNECTED"Get the kubeconfig generated by terraform "cluster-kubeconfig" - either copy it to ~.kube/config or EXPORT KUBECONFIG=..../cluster-kubeconfig. You should now be able to kubectl get nodes.
There is small script in the gitops folder that bootstraps ArgoCD: gitops/kickstart.sh. It helm-installs ArgoCD and installs two resources that will generate the rest of the contents of the gitops directory.
NOTE: The gitops directory is hard-wired to this specific repository. You will probably need to change all repository URLs etc.
NOTE: The gitops directory contains configuration for metal-lb which will assign the IP 10.0.0.15 to the load balancer. You probably want to change that and configure routing from the internet to that IP on ports 80 & 443 (and any other ingress ports you need).