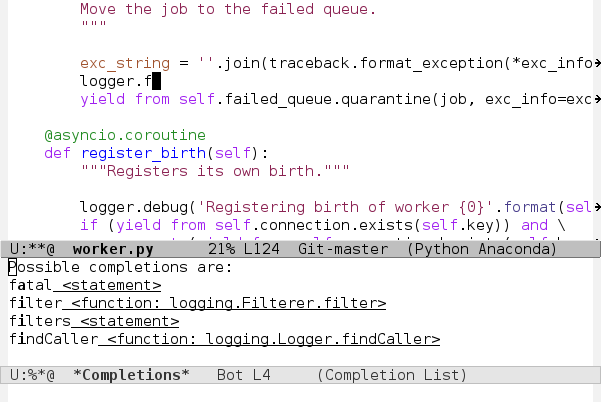
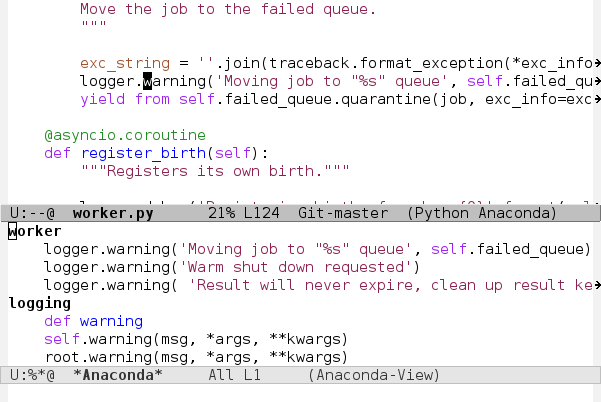
Code navigation, documentation lookup and completion for Python.
Anaconda mode provides the following features
- context-sensitive code completion
- jump to definitions
- find references
- view documentation
- virtual environment
- eldoc mode
- all this stuff inside vagrant, docker and remote hosts
2.7, 3.4, 3.5, 3.6, 3.7
To use this package you need to install setuptools.
All you need to do is install the package from Melpa
M-x package-install RET anaconda-mode RET
Clone this repository somewhere and add this directory to your
load-path.
anaconda-mode is included in the Emacs
Prelude distribution. You can
use it as well. Look at the prelude-python module to see more
details.
anaconda-mode is included in the
Spacemacs distribution. You
can use it as well. Look at the python language layer to see more
details.
You can automatically enable anaconda-mode in all python buffers
with following code in your configuration:
(add-hook 'python-mode-hook 'anaconda-mode)anaconda-eldoc-mode provide document function to eldoc-mode so
when your point is between the parenthesis of a function call, its
parameters are shown in the echo area. All You need is to enable
anaconda-eldoc-mode in addition to the previous setup.
(add-hook 'python-mode-hook 'anaconda-eldoc-mode)To start a completion press C-M-i. This is the standard emacs
binding for complete-at-point function. You can use
company-mode with
company-anaconda
backend to get more intelligent UI.
Here is a list of interactive commands available with anaconda-mode
| Keybinding | Description |
|---|---|
| C-M-i | anaconda-mode-complete |
| M-. | anaconda-mode-find-definitions |
| C-x 4 . | anaconda-mode-find-definitions-other-window |
| C-x 5 . | anaconda-mode-find-definitions-other-frame |
| M-= | anaconda-mode-find-assignments |
| C-x 4 = | anaconda-mode-find-assignments-other-window |
| C-x 5 = | anaconda-mode-find-assignments-other-frame |
| M-r | anaconda-mode-find-references |
| C-x 4 r | anaconda-mode-find-references-other-window |
| C-x 5 r | anaconda-mode-find-references-other-frame |
| M-, | xref-pop-marker-stack |
| M-? | anaconda-mode-show-doc |
If multiple candidates are found for definitions, assignments or usages, you'll see an advanced anaconda navigator buffer.
You can add your project to the Emacs PYTHONPATH. If you store
project dependencies somewhere on your machine, you can add them as
well.
(add-to-list 'python-shell-extra-pythonpaths "/path/to/the/project")
(add-to-list 'python-shell-extra-pythonpaths "/path/to/the/dependency")Use a virtual environment to isolate your project dependencies from others on the system. You can additionally install your project in an editable mode in the virtual environment. This will improve search functionality. Then activate this virtual environment inside Emacs.
M-x pythonic-activate RET /path/to/virtualenv RET
Also you can use pyenv-mode or similar package to hold virtual environment in actual state.
Each action above applies to anaconda-mode immediately. The next
anaconda-mode command you call will use this environment for search
completion candidates.
It's possible to use anaconda-mode on a remote server when you connect to it using tramp. Anaconda-mode can search for completion candidates and all other stuff on remote server while you're running Emacs locally. Just open an interesting remote file.
C-x C-f /ssh:remote_host:project/__init__.py RET
After tramp successfully connects and you see actual buffer content, completion and definitions search should work as usual. You can even use virtual environment from remote host.
M-x pythonic-activate RET /ssh:remote_host:/home/user/venv RET
Or specify another remote interpreter
(setq python-shell-interpreter "/usr/bin/python")It is important to remember that remote_host must be a real host
name or an IP address. SSH aliases not allowed to be used with
anaconda-mode. All kinds of searching from inside the virtual
environment are available from any buffer. However searching inside
your project is available only if you open it on the same machine as
the interpreter.
You can get all the intelligent features of anaconda-mode with virtual environments deployed on your vagrant box. Fire up the vagrant machine as usual. The easiest way to handle authentication is to copy your public ssh key to the vagrant box.
ssh-copy-id vagrant@localhost -p 2222
Now open your project inside the vagrant box.
C-x C-f /ssh:vagrant@localhost#2222:/vagrant/polls/views.py
Optionally you can activate your project environment, if installed inside vagrant.
M-x pythonic-activate RET /ssh:vagrant@localhost#2222:/vagrant/polls/venv RET
You can use definition, reference and auto-completion search for
dependencies installed in the Docker container. Let suppose your
project layout is the same as in Compose and
Django tutorial. To use
anaconda-mode together with Docker you need to install two
additional external dependencies. First of all, you need to install
docker-tramp Emacs
package. The second step is to install Unix socat utility. You
should have your containers up and running
docker-compose up web
After that, you can set Python interpreter to one installed inside container
(setq python-shell-interpreter "/usr/local/bin/python")Now you can open some file inside the project running inside a container
C-x C-f /docker:root@django_web_1:/code/manage.py
If you try to find the definition of the Django module imported in
this buffer, anaconda-mode will jump to the package installed inside
this Docker container.
If you see constant response reading error, try to change localhost
address from default 127.0.0.1 to localhost. This is likely to
fix problems on Mac OS.
(setq anaconda-mode-localhost-address "localhost")Please attach *anaconda-mode*, *anaconda-response* and
*anaconda-socat* buffer content to every created issue.
- Dmitry Gutov @dgutov
- Bo Lin @sadboy
- Vasilij Schneidermann @wasamasa
- Fredrik Bergroth @fbergroth
- Fabio Corneti @fabiocorneti
- Tom Davis @tdavis
- Sviridov Alexander @sviridov
- Mario Rodas @marsam