Shipment List Demo Application - AWS in PROD and LocalStack on DEV environment
| Environment |   |
|---|---|
| Services | Amazon S3, Lambda, DynamoDB, SNS, SQS |
| Integrations | AWS SDK, Terraform, AWS CLI |
| Categories | Spring Boot, S3 Trigger |
| Level | Intermediate |
| Works on | LocalStack v2 |
UPDATE
The Terraform configuration file now randomly generates names for the bucket, in order to avoid conflicts at a global scale on AWS. This name shall be written out to a properties file, which the app will pick up and use for the S3 client. Furthermore, the name is also passed as an environment variable to the Lambda function by Terraform, so there's no need to worry about managing it.
Introduction
This application was created for demonstration purposes to highlight the ease of switching from using actual AWS dependencies to having them emulated on LocalStack for your developer environment . Of course this comes with other advantages, but the first focus point is making the transition.
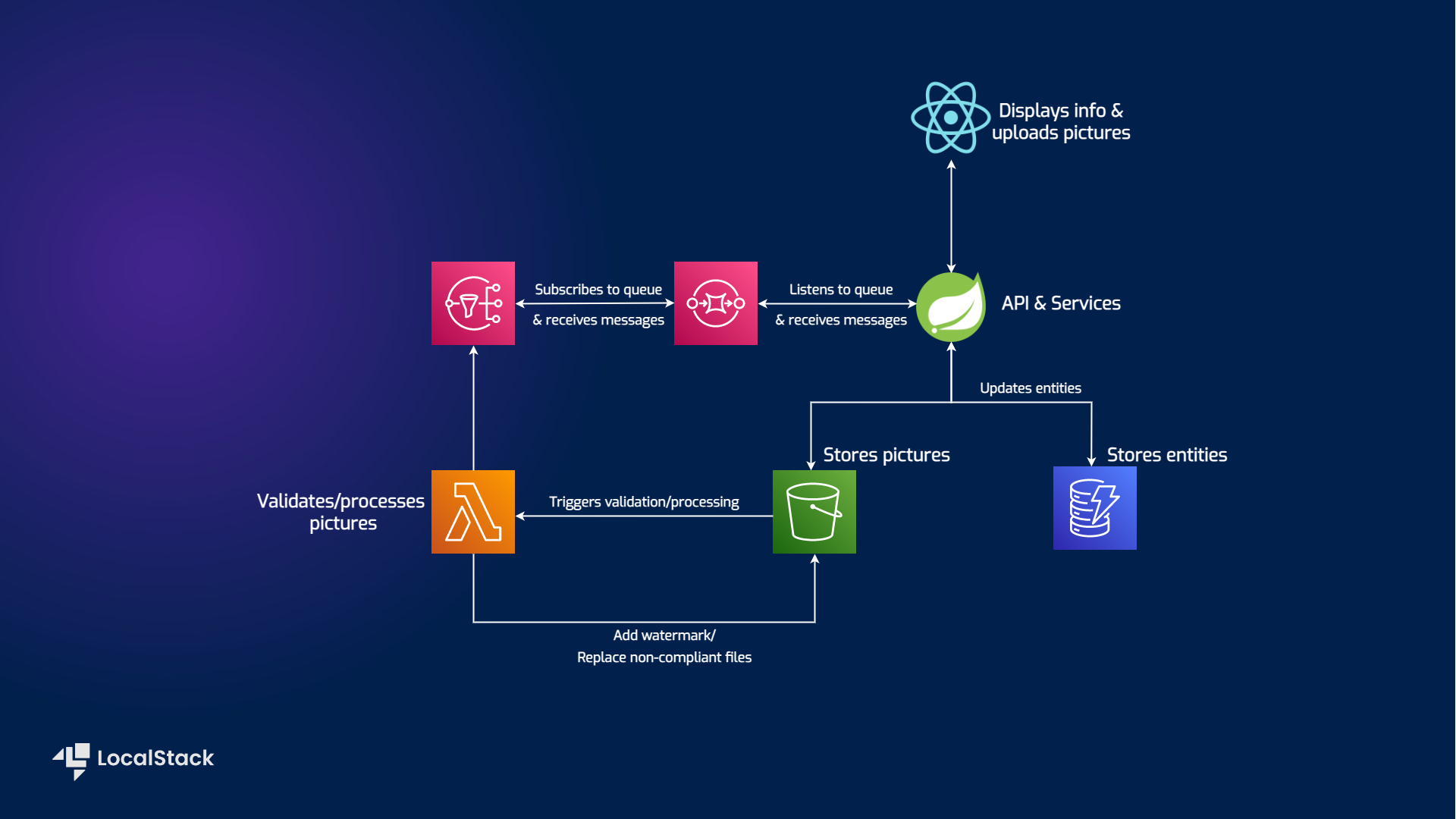
Architecture Overview
Prerequisites
- Maven 3.8.5 & Java 17
- AWS free tier account
- LocalStack
- Docker - for running LocalStack
- Terraform (+ Python pip for tflocal) for creating AWS & LocalStack resources
- npm - for running the frontend app
What it does
shipment-list-demo is a Spring Boot application dealing with CRUD operations a person can execute on a bunch of shipments that they're allowed to view - think of it like the Post app. The demo consists of a backend and a frontend implementation, using React to display the information. The AWS services involved are:
- S3 for storing pictures
- DynamoDB for the entities
- Lambda function that will validate the pictures, apply a watermark and replace non-compliant files.
- SNS that receives update notifications
- SQS that subscribes to a topic and delivers the messages to the Spring Boot app
How to use it
We’ll be walking through a few scenarios using the application, and we expect it to maintain the behavior in both production (AWS) and development (LocalStack) environments.
We’ll take advantage of one of the core features of the Spring framework that allows us to bind our
beans to different profiles, such as dev, test, and prod. Of course, these beans need to know how to
behave in each environment, so they’ll get that information from their designated configuration
files, application-prod.yml, and application-dev.yml.
Terraform
The Terraform configuration file will create the needed S3 bucket, the DynamoDB shipment table and populate it with some
sample data, the Lambda function that will help with the picture processing (make sure you create the jar),
the SQS and SNS which will bring back the notification when the processing is finished.
Instructions
Only run once
The following instructions only need to run once, weather you choose to run both cases, on AWS and LocalStack, or just jump straight to LocalStack.
Building the validator module
Step into the shipment-picture-lambda-validator module and run mvn clean package shade:shade.
This will create an uber-jar by packaging all its dependencies. We'll need this one in the next
steps. We can keep the same jar for both running on AWS and LocalStack.
Running the GUI
cd into src/main/shipment-list-frontend and run npm install and npm start.
This will spin up the React app that can be accessed on localhost:3000.
You'll only see the title, as the backend is not running yet to provide the list of shipments.
For running it on Windows, there are some extra requirements , but no worries, it should be straightforward.
How to use the GUI
After starting the backend, refreshing the React app will fetch a list of shipments. The weight of a shipment is already given, but not the size, that's why we need pictures to understand it better, using the "banana for scale" measuring unit. How else would we know??
Current available actions using the GUI:
- upload a new image
- delete shipment from the list
- create and update shipment are available only via Postman (or any other API platform)
Files that are not pictures will be deleted and the shipment picture will be replaced with a generic icon, because we don't want any trouble.
Running on AWS
Now, we don’t have a real production environment because that’s not the point here, but most likely
an application like this runs on a container orchestration platform, and all the necessary configs
are still provided. Since we’re only simulating a production instance, all the configurations are
kept in the application-prod.yml file.
User credentials
Before getting started, it's important to note that an IAM user, who's credentials will be used, needs to be created with the following policies:
- AmazonS3FullAccess
- AWSLambda_FullAccess
- AmazonDynamoDBFullAccess
- AmazonSNSFullAccess
- AmazonSQSFullAccess
- AWSLambdaExecute
- AmazonS3ObjectLambdaExecutionRolePolicy
For simplicity, we chose to use full access to all the services, so we don't have to add new permissions later on.
We will be using the user's credentials and export them as temporary environment variables with the
export (set on Windows) command:
$ export AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=[your_aws_access_key_id]
$ export AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=[your_aws_secret_access_key_id]
Creating resources - running Terraform
Make sure you have Terraform installed
Under terraform run:
$ terraform init
$ terraform plan
Once these 2 commands run successfully and no errors occur, it's time to run:
$ terraform apply
If everything finishes successfully, the AWS services should be up and running.
Starting the backend
Go back to the root folder and run the backend simply by using
$ mvn spring-boot:run -Dspring-boot.run.profiles=prod
Notice the prod profile is being set via command line arguments.
Using the application
At localhost:3000 you should now be able to see a list of shipments with standard icons,
that means that only the database is populated, the pictures still need to be added from the
sample-pictures folder.
You can now interact with the application using the React app. All services used in the backend are
running on the real AWS cloud.
Before moving on, make sure you clean up your AWS resources by running (also in the terraform folder):
$ terraform destroy
Running on LocalStack
To switch to using LocalStack instead of AWS services just run docker compose up in the root
folder to spin up a Localstack container.
Creating resources on LocalStack
To generate the exact same resources on LocalStack, we need tflocal, a thin wrapper script around
the terraform command line client. tflocal takes care of automatically configuring the local
service
endpoints, which allows you to easily deploy your unmodified Terraform scripts against LocalStack.
You can install the tflocal
command via pip (requires a local Python installation):
$ pip install terraform-local
Once installed, the tflocal command should be available, with the same interface as the terraform
command line. Try it out:
$ tflocal --help
Usage: terraform [global options] <subcommand> [args]
...
From here on, it's the same as using AWS. In the terraform folder, run the cleanup script
to get rid of any files that keep track of the resources' state. Then:
$ tflocal init
$ tflocal plan
$ tflocal apply
We run the exact same commands for the exact same file. We no longer need to pass any environment variables, since the bucket name is generated and passed by Terraform.
Starting the backend
After that, the Spring Boot application needs to start using the dev profile (make sure you're in the root folder):
$ mvn spring-boot:run -Dspring-boot.run.profiles=dev
Using the application
Go back to localhost:3000 and a new list will be available; notice that the functionalities of
the application have not changed.
There you have it, smooth transition from AWS to Localstack, with no code change. 👍🏻