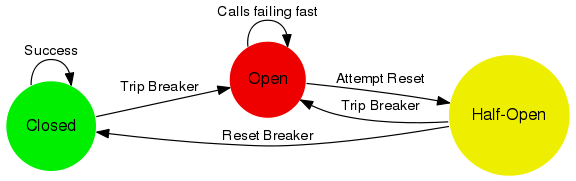
A flexible circuit breaker state machine.
The intent of this module is to provide a means of tracking a circuit breaker without forming opinions about how something is called. Use this API to blend circuit breaking into anything.
The reasoning behind this module is that too many libraries mix in the concept of timeouts, fallbacks, and promises vs callbacks into the circuit breaker pattern. These are implementation details that ultimately will vary from use case to use case, whereas the state machine itself will not.
A circuit breaker is used to provide stability and prevent cascading failures in distributed systems. These should be used in conjunction with judicious timeouts at the interfaces between remote systems to prevent the failure of a single component from bringing down all components. -- Akka Documentation on Circuit Breaker
CircuitBreakerState(options)- Constructor. Options:maxFailures- Maximum number of failures before circuit breaker flips open. Default3.resetTime- Time in ms before an open circuit breaker returns to a half-open state. Default10000. If 0 or less, manual resets will be used.
CircuitBreakerState.create(options)- Creates a newCircuitBreakerStateinstance.
Instance functions:
succeed()- Record a success.fail()- Record a failure. This may trip open the circuit breaker.test()- Utility function to test for the state being open. If so, returns an error (may be returned to user).tryReset()- Flips to half-open and cancels reset timer (if any).open- Istrueif this circuit breaker is open. Read-only.closed- Istrueif this circuit breaker is closed. Read-only.halfOpen- Istrueif this circuit breaker is half-open. Read-only.stats- The stats tracker object.maxFailures- Read-only.resetTime- Read-only.
Stats object:
increment(name)- Increment the givennamecount.reset(name)- Reset the givennamecount.resetAll()- Reset all counts.snapshot()- Take a snapshot of the stats object.
Wrapping a callback based function.
const CircuitBreakerState = require('circuit-state');
class Circuit {
constructor(func) {
this._func = func;
this._cb = new CircuitBreakerState();
}
run(...args) {
const callback = args[args.length - 1];
const error = this._cb.test();
// Fail fast
if (error) {
setImmediate(() => {
callback(error);
});
return;
}
// Wrap original callback
args[args.length - 1] = (error, ...result) => {
if (error) {
// Record a failure
this._cb.fail();
callback(error);
return;
}
// Record a success
this._cb.succeed();
callback(null, ...result);
};
return this._func.call(null, ...args);
}
}Here's an example with wrapping promises.
class Circuit {
constructor(asyncFunc) {
this._asyncFunc = asyncFunc;
this._cb = new CircuitBreakerState();
}
async run(...args) {
const error = this._cb.test();
// Fail fast
if (error) {
throw error;
}
try {
const result = await this._asyncFunc(...args);
this._cb.succeed();
return result;
}
catch (error) {
this._cb.fail();
throw error;
}
}
}