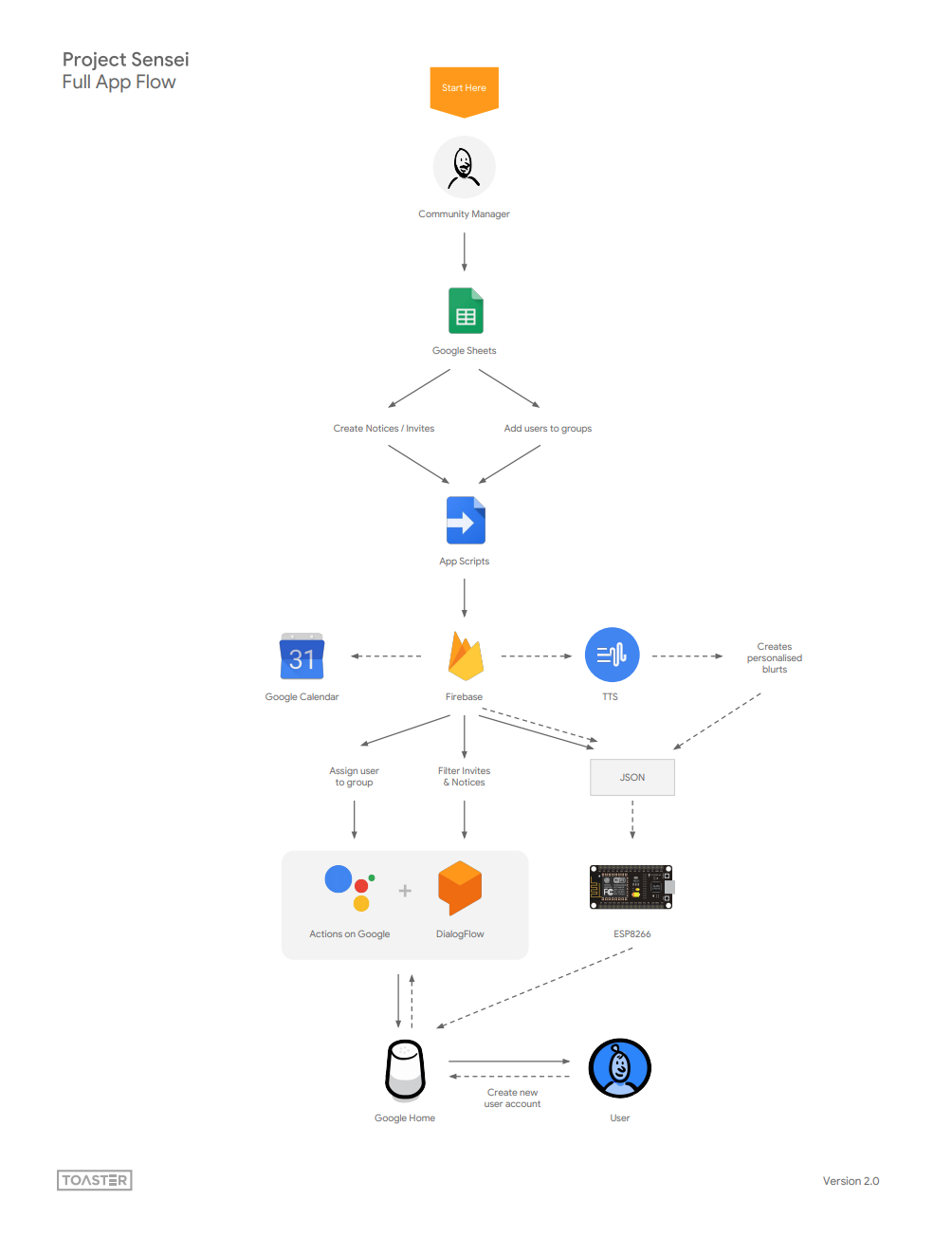
Community Keijiban is an experiment that explores how voice and the Assistant can make technology more accessible for new audiences. The Yamayuri Club of Wakabadai collaborated with us and friends at the Google Creative Lab to design a voice app that simplifies the lives of the people in the residential estate by bringing the community notice board to their living room. The app announces all new notices, tells the residents what activities are scheduled and reminds them when it's time to attend.
Anyone can customise the app for their local community by getting the code to build their own community management tool from scratch, controlled by Google Sheets.
This is an experiment, not an official Toaster or Google product. We will do our best to support and maintain this experiment but your results may vary.
Community Keijiban is built on Actions on Google, the platform that allows you to make things for the Google Assistant/Home. It uses Dialogflow to handle understanding what the user says, Firebase Cloud Functions and Firebase Realtime Database for backend code and storing data. It uses Google App Scripts to share the schedule from Google Sheets to Firebase, Cloud Text-to-Speech to create the custom user blurts for notifications and Arduino for programming the electronics.
This repo contains everything you need to create your own community noticeboard. We won't go into all the details but you can explore the source code of each part to learn how it all works together. The below instructions allow you to build your own community management tool from scratch.
- Clone this repo
- Make a copy of this sheet
- Go to Firebase and login.
- If you don't have an account it's free to sign up and use.
- In Firebase Console add a new project
- Give it a name e.g. Community Keijiban
- Select your locations and agree to the T&Cs
- Press
Create projectthenContinueonce its created
- Go to
Develop > Storageand pressGet Startedand follow the prompt. - In
Storagecreate a folder calledaudio - Then go to the
rulestab and replace the current rules to allow public reads, using the below code (PressPublishto save):service firebase.storage { match /b/{bucket}/o { match /{allPaths=**} { allow write: if request.auth != null; allow read; } } }
- Go to
Develop > Database, scroll down the page and findOr choose Realtime Databaseand clickCreate Databaseand then clickenable - Now go to your
⚙︎ > Project Settings > Generalin Firebase - Make a note of your
Project ID - Then go to your
⚙︎ > Project Settings > Service Accountsin Firebase and selectDatabase secrets - Then press
showand make a note of yourDatabase secret
- Open the sheet you copied.
- Go to
Tools > Script Editor - Inside Script Editor select the file
Code.gsand replace the following values:[PROJECT-ID]with yourProject IDFIREBASE_DATABASE_SECRETwith yourDatabase secret
- Save the changes
- Go to
File > Project Properties > Infoand make a note of theProject key - Close the Script Editor
- Refresh the Google Sheet
- Download and install Firebase CLI. Once you have completed step 4 under "Install the Firebase CLI" continue with the below steps.
- You need to initialize a new Firebase project, run the following command from within your project's directory
firebase initand follow the on screen intructions. For most options you can use the defaults except for the below:- Select
FunctionsandHosting - Select the project name you created via the Firebase Console e.g.
Community Keijiban- If your project name is not listed select
create a new projectand afterfirebase inithas completed you can usefirebase use --addto add your project name
- If your project name is not listed select
- Select
JavaScriptfor theFunctionslanguage - Say yes to enforce ESLint style
- When asked to overwrite
package.json,.eslintrc.josnandindex.jssay No
- Select
- Now you need to customise the functions for your use. Open
functions/config/constants.jsin your preferred IDE. Inconstants.jsyou will need update the values of the below properties. The other props in the file can also be updated but those are optional.- For
AUDIO_FILE_BUCKET_URL_PREFIXandGOOGLEAPI_REDIRECTreplace[PROJECT_ID]with your Firebase project ID - For
API_ORIGIN_WHITELISTreplace[APPSCRIPT_PROJECT_KEY]with your AppScriptsProject key
- For
- Now open
functions/language/blurts.json. The strings in this file are used by Cloud Text-to-Speech to create the blurts. You can modify these to match your project's needs. - Rename the folder
functions/keys-sampletofunctions/keys - Now open the project root in
TerminalorCommand Lineand typefirebase deploy - Once deployment has finished note down the
Hosting URL(e.g.https://[PROJECT-ID].firebaseapp.com) and the domain of theFunctions URL(e.g.us-central1-[PROJECT-ID].cloudfunctions.net)
- Go to Google Cloud Console, make sure to login using the same account you used to setup Firebase
- Select the project name you created in Firebase
- Go to
APIs & Services > Library - Search for
Cloud Text-to-Speech API - Select it and then press the Enable button.
- If you have not enabled billing you will be prompted to enable it. Follow the on-screen instructions to enable billing
- Go back to
APIs & Services > Libraryand search forGoogle Calendar API - Select it and press the Enable button
- Go to
APIs & Services > Credentials > OAuth consent screen
- Under
Support emailselect an email address
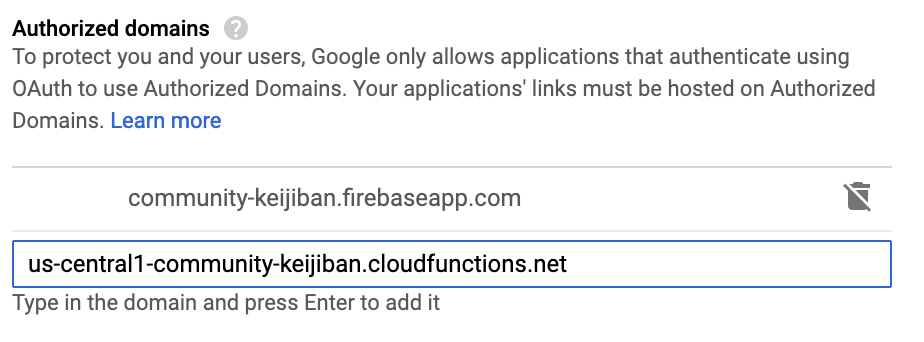
- Scroll down add the
Functions URLdomain underAuthorized domains. For example:us-central1-[PROJECT-ID].cloudfunctions.net
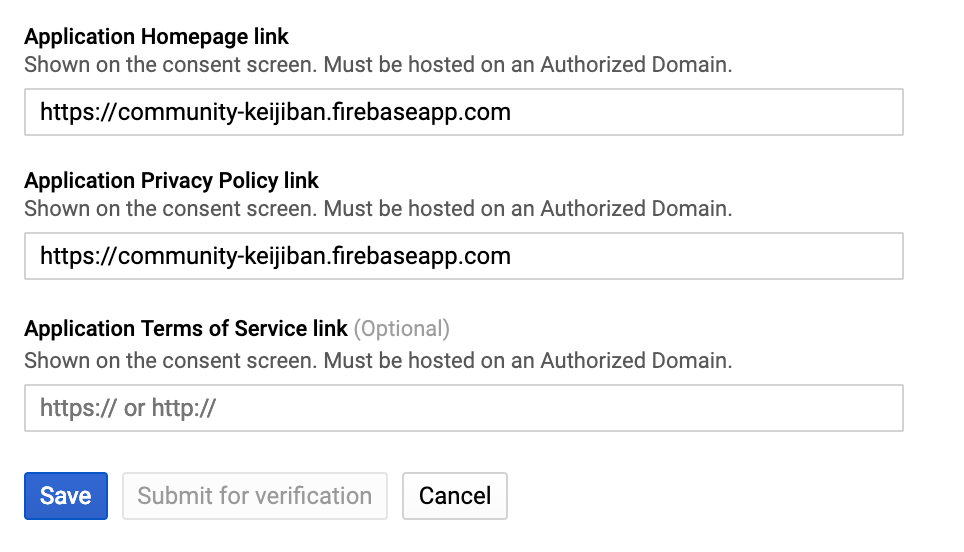
- Then add the
Hosting URLtoApplication Homepage linkandApplication Privacy Policy link. . For example:https://[PROJECT-ID].firebaseapp.com. Then press save.
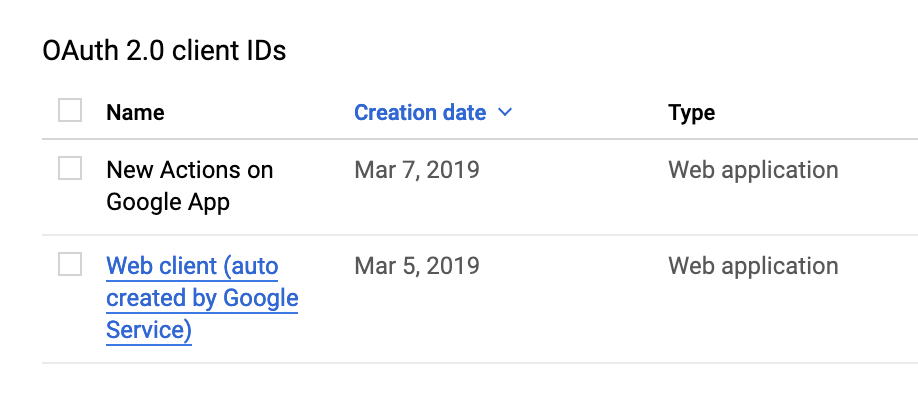
- This should redirect you back to
APIs & Services > Credentials. UnderOAuth 2.0 client IDsclick onWeb client (auto created by Google Service)
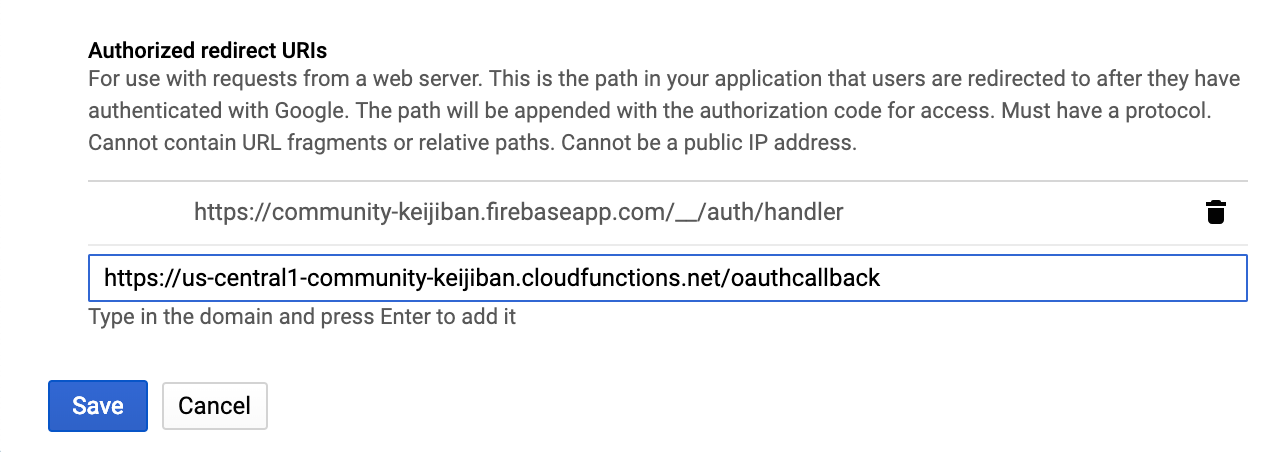
- Under
Authorized redirect URIsaddhttps://us-central1-[project-id].cloudfunctions.net/oauthcallbackreplacing[project-id]with your Firebase project ID. Then press save.
- This should redirect you back to
APIs & Services > Credentials. Now under underOAuth 2.0 client IDsdownload the JSON file forWeb client (auto created by Google Service) - Rename the file to
calendar.jsonand place into your project folder underfunctions>keys. You may need to create thekeysfolder if you do not have it or you may need to replacecalendar.jsonif one already exists. - Go back to
Google Cloud Consoleand openAPIs & Services > Credentialsand selectCreate credentials > Service account key - Create
New Service accountand name itTTS. Make sure the key type is set toJSONand role is set toProject > Owner. Then pressCreate - The JSON will autodownload. Rename it to
tts.jsonand place into your project folder underfunctions > keys. - Now open the project root in
TerminalorCommand Lineand typeFirebase deploy
- Go to Dialogflow and login using the same account you used to access Firebase.
- If you don't have an account it's free to sign up and use.
- Create a new agent
- Give it a name e.g.
CommunityKeijiban - Set the agent's default language and timezone
- For Google Project select the Firebase project you just created e.g.
community-keijiban - Press "Create"
- Give it a name e.g.
- Once created select the newly created agent and go to the settings page
- Click on
Export and Import - Click
IMPORT FROM ZIP, select the fileassets/dialogflow.zipfrom your project folder and type the word IMPORT to enable the import button.- After importing if
jadoes not display under your agent name you can add it by going toLanguagesin the Agent settings and selectingJapanese - jafrom the drop down.
- After importing if
- Now click on
Fullfilmentand enable theWebhookoption. - Then copy
https://us-central1-[PROJECT-ID].cloudfunctions.net/dialogflowWebhook, replace[PROJECT-ID]with your Firebase project ID, into the URL field - Under
DOMAINSselectEnable webhook for all domainsthen pressSave. - In Dialogflow click on
Integrationson the main menu and then click onIntegration Settingsunder Google Assistant. A modal window will popup - Toggle on
Auto-preview changes - Click on
Testto goto the Actions on Google Console - Go to
Setup > Invocation - Enter the name you want to use to invoke your action under
Display Namee.g. Community Keijiban- Tip: For best results use two words for your display name.
- Go to
Advanced Options >Account Linking - Select
Yes, allow users to sign up for new accounts via voiceand pressNext - Select
Google Sign Inand pressNext - Take note of the
Client IDand then infunctions/keysin your project folder openconstants.js. Replace[CLIENT-ID]with the client ID from Actions on Google console:
module.exports = {
ACTIONS_ON_GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID: '[CLIENT-ID]'
};- Now open the project root in
TerminalorCommand Lineand typeFirebase deploy - Once deployed succesfully open a browser window and go to this website, replacing
[project-id]with your Firebase project ID:https://us-central1-[project-id].cloudfunctions.net/authgoogleapi - The Sign-in with Google page will display. Select the account that used to create your Firebase project. Click
Allowfor prompts. If succesfull you will see:App successfully configured with new Credentials. You can now close this page. - Open
index.jsinsidefunctionsfolder in your project folder with your prefferred IDE - Then comment out lines 131 to 157 (this code is used for authorising the Cal. API and is only needed once).
- Now open the project root in
TerminalorCommand Lineand typeFirebase deploy
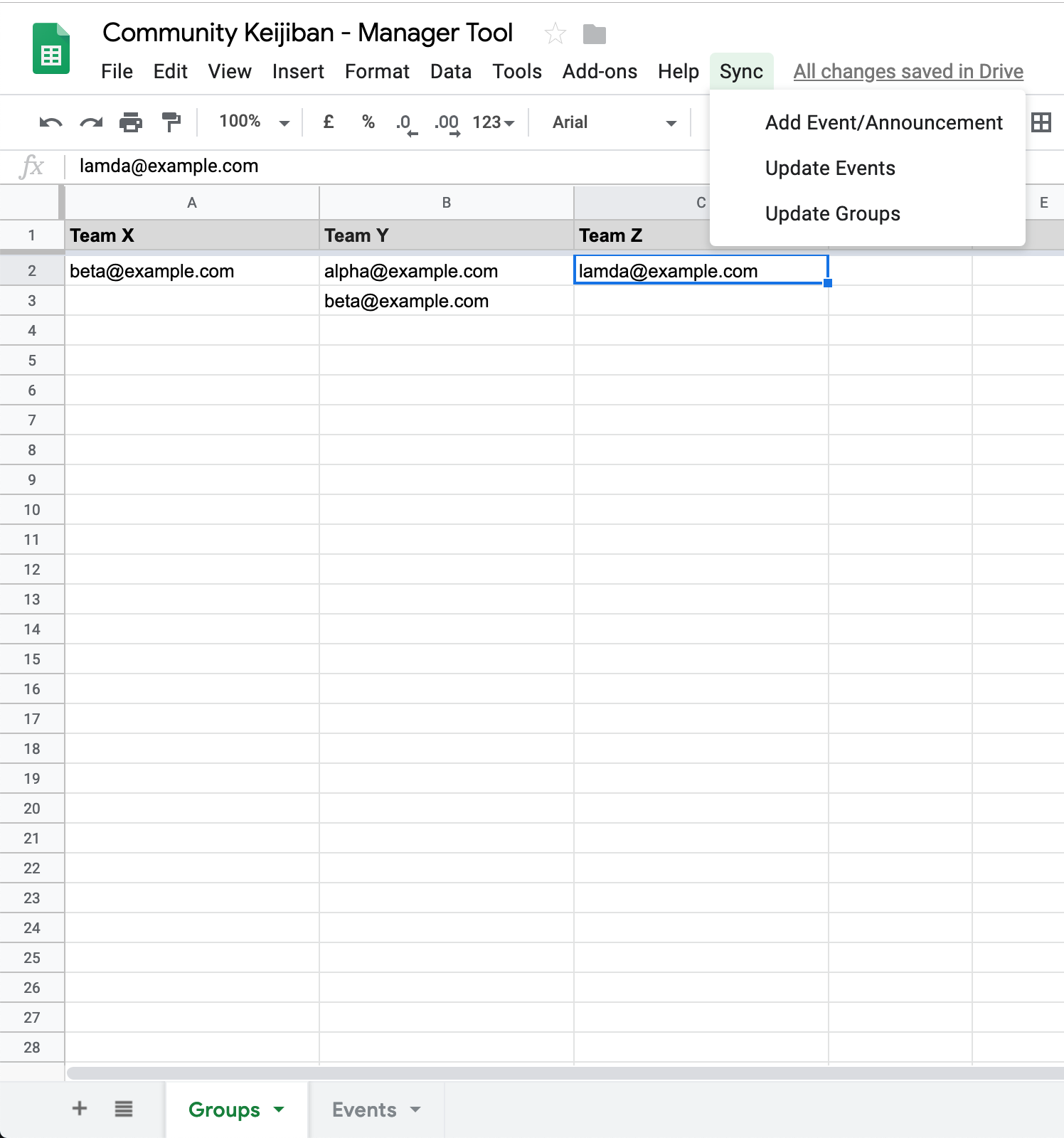
- Open the Google Sheet you copied
- Select the
Groupssheet - Add new group name in row 1 (header)
- Add user’s email to respective group
- Once done, go to
Sync > Update Groupsin toolbar, if this is your first time doing it follow the on screen instructions to authorize access.
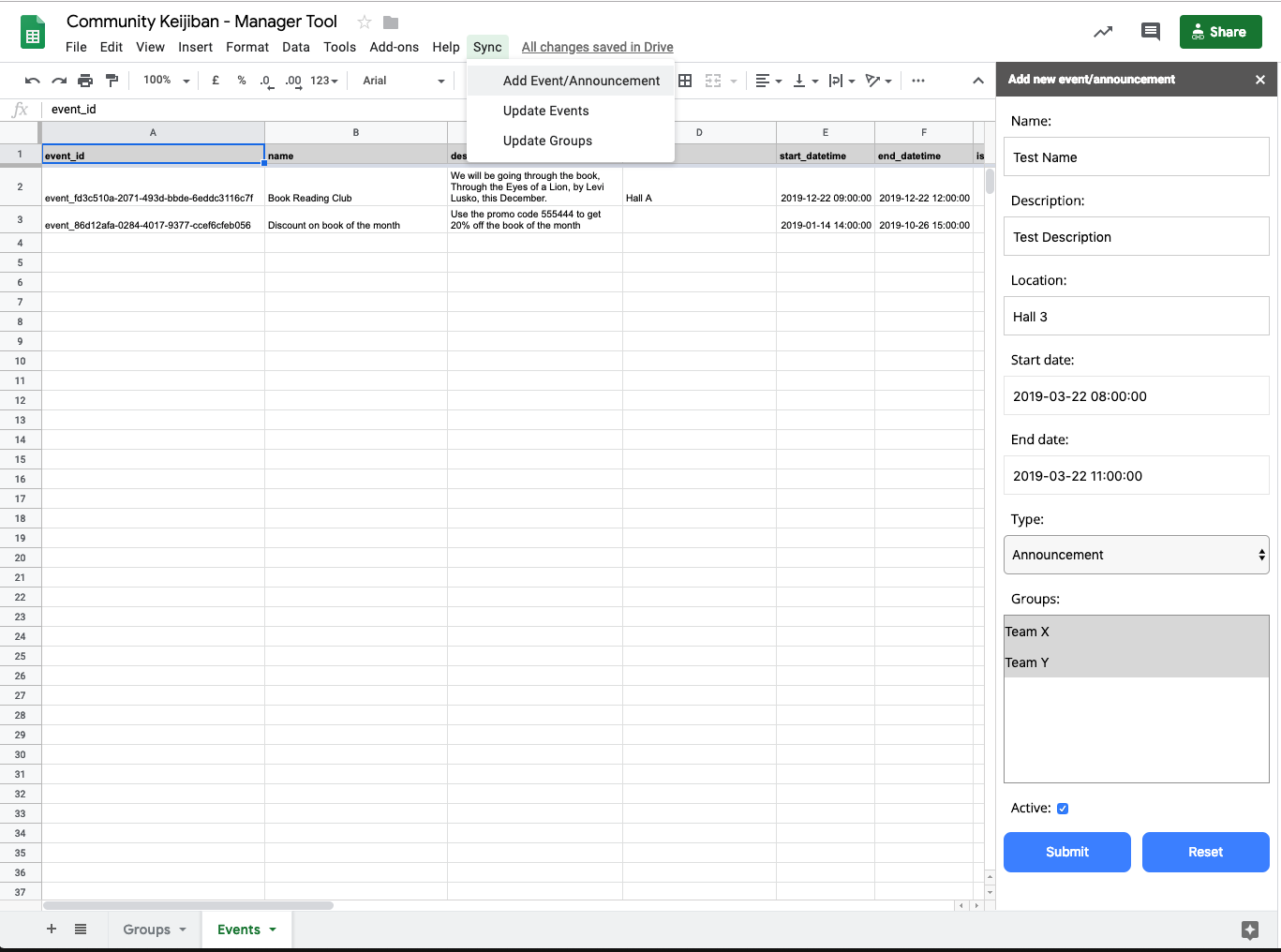
- Open the Google Sheet you copied
- Select the
Eventssheet - Go to
Sync > Add Event/Announcementin the toolbar - A form will appear on the left side
- Enter event’s details, select the
Eventtype - Select one or more (hold shift + click, to select more) groups of which the event belongs to
- Check “Active” to mark the event as an active event
- Click “Submit”
- Once done, go to
Sync > Update Eventsin toolbar, if this is your first time doing it follow the on screen instructions to authorize access.
- Go to the Actions on Google Console and select your project
- Click on
Test > Simulatorand try it out. You can also do this directly on your Google Assistant/Home that is logged in with you account.- Tip: If the Home says you do not have access or there is no action try sharing the Voice App with yourself from Actions on Google Console
You can find the parts we used below, or use similar parts you might already have lying around.
- LOLIN(Wemos) D1 Mini Pro ESP8266 WiFi
- Micro USB cable (data-syncing)
- Google Home, Google Mini or Phone with the Google Assistant (Android or iOS devices)
- USB Driver. The driver might be different if using a different board.
- CP2104 USB Driver (for LOLIN(Wemos) D1 Mini Pro)
- Arduino IDE
- Arduino IDE
version 1.8.9has an issue compilingESP8266WebServer. If1.8.9is the latest version try downloading a previous version such as1.8.8.
- Arduino IDE
- Open the
Arduino IDE - Go to
Arduino > Preferences - Copy and paste into the Additional Board Manager URLs field: http://arduino.esp8266.com/stable/package_esp8266com_index.json
- Press OK
- Restart the Arduino IDE
- Open the
Arduino IDE - Go to
Tools > Board > Boards Manager - Filter by ESP8266 and click install on
esp8266 by ESP8266 Communityversion 2.4.2 - Close the Boards Manager Window
- Open the Arduino IDE
- Go to
Sketch > Include Library > Manage Librarythen filter for and install the following libraries:- EasyNTPClient (v1.1.0)
- ArduinoJson (v5.13.4)
- Esp8266-google-home-notifier (v1.0.6)
- Esp8266-google-tts (v1.0.7)
- Close the Library Manager window once all libraries are installed
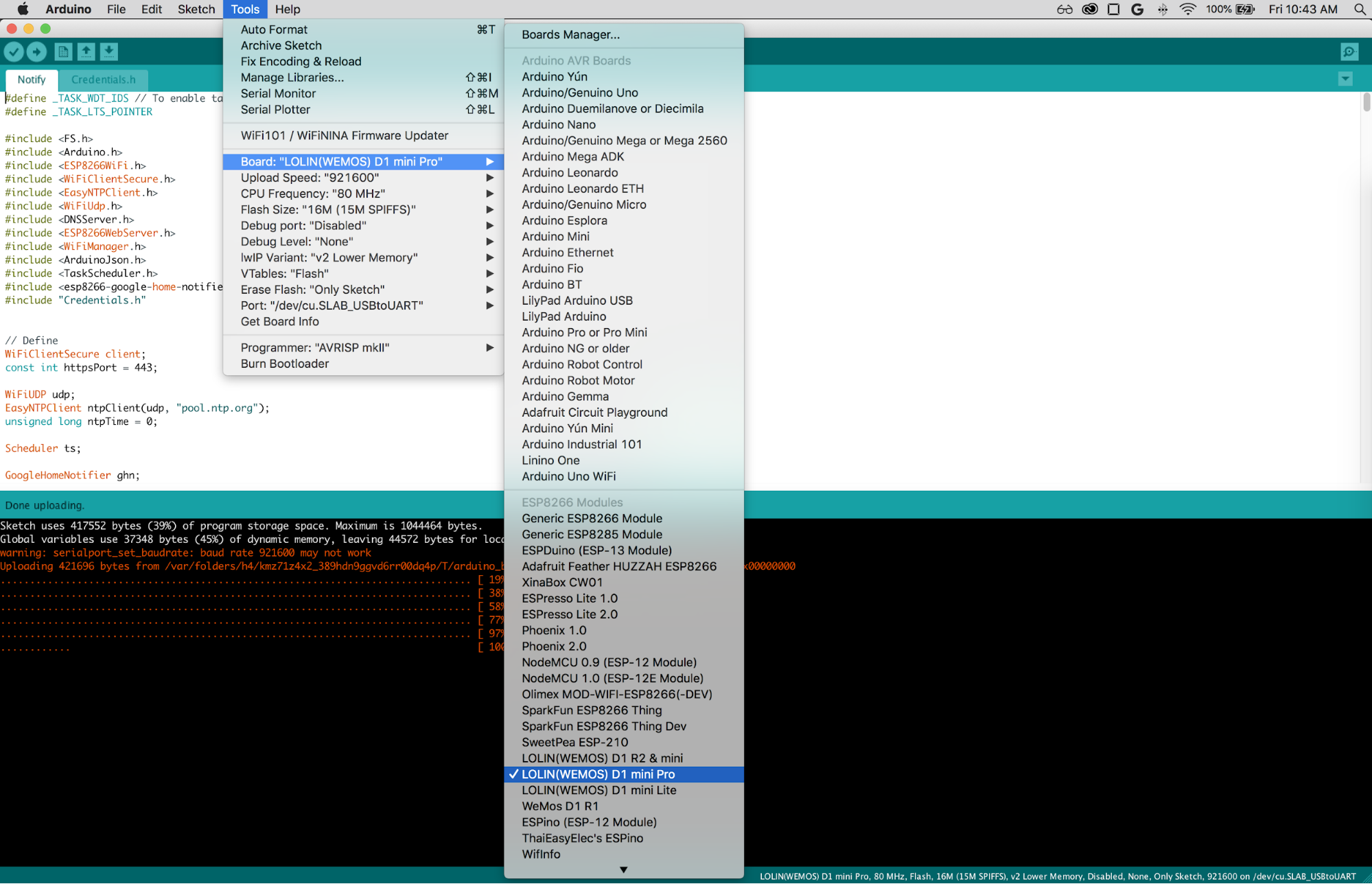
- Go to
Tools > Board - Select LOLIN(Wemos) D1 Mini Pro as your board or if you are holding non-pro version, choose LOLIN(Wemos) D1 R2 & Mini or any other board you are using
- Go to
Tools > Upload Speed - Select
921600 baud - Go to
Tools > Port - Select the matching COM port for your USB cable. It should be something like
USB.SLABtoUARTor/dev/cu.wchusbserial14530or/dev/cu.wchusbserial1420(if you don't see it plug in your microcontroller and try again) - Go to
Tools > CPU Frequency - Select
160 Mhz
- Open your Voice app on the Google Home
- In English say "Talk to Community Keijiban"
- Tip: If the Home says you do not have access or there is no action try sharing the Voice App with yourself from Actions on Google Console
- When your app runs for the first time it will ask you to sign in. You will need to do this to use the app.
- Tip: If you get stuck in a sign in loop… something like the below please check you have allowed the Assistant to use personal information.
- “Alright no problem- just so you know you will not be able to use your account with Community Keijiban. but you can come back and sign in again”
- Tip: If you get stuck in a sign in loop… something like the below please check you have allowed the Assistant to use personal information.
- Once signed in you can ask your app for your "Signal ID" by saying "What is my Signal ID" or simply "Signal ID". The signal id is used by the microcontroller to identify your account.
- Tip: It's easier to do this on the phone as it will return a written response which you can then copy for the next steps.
- Plug a USB B Mini into the microcontroller to power it and connect the other end of the cable into your computer.
- Open the Notify file you downloaded from step 1 in the Prerequisites for flashing microcontroller section. Make sure you open the INO file (Notify.ino). This should open the Arduino IDE.
- Also open
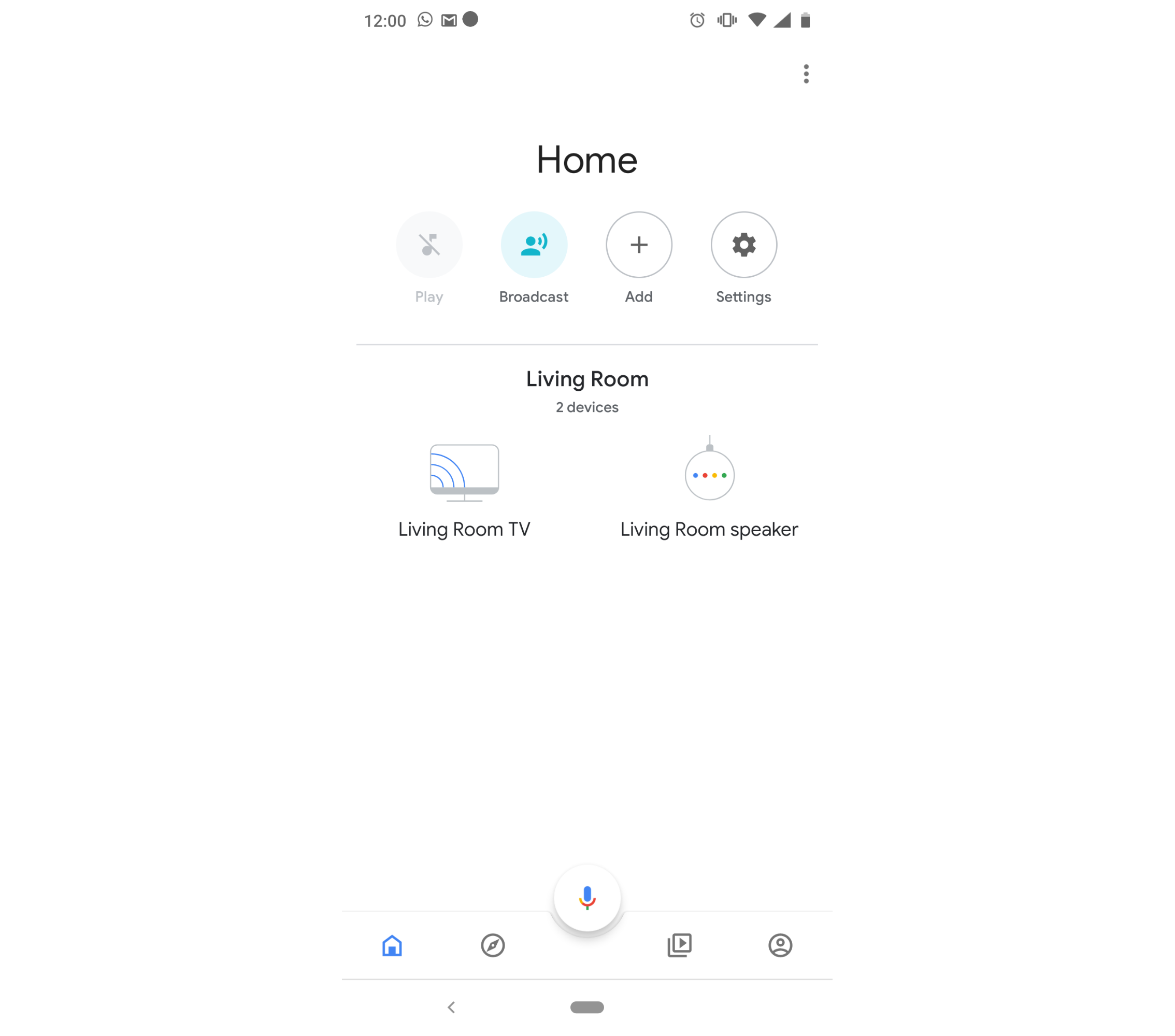
Config.hin the Arduino IDE and replace:[PROJECT_ID]inFIREBASE_URLwith your Firebase project Id.YOUR_WIFI_NETWORKandYOUR_WIFI_PASSWORDwith your WiFi details.your-signal-idwith your Signal ID.YOUR_HOME_SPEAKER_NAMEwith the name of the device you want to Cast to. You can get this from the Home App (see below screenshot):
- Save it.
- Click ➡️ (right arrow) icon to upload the code to your microcontroller.
- If the program fails to compile with references to
ESP8266WiFiandWiFiClientSecure. Try downloading and installing an older version of Arduino IDE (v1.8.8).
- If the program fails to compile with references to
- The microcontroller's LED will turn on when connected to your network and the Google Home will make a noise to confirm its connection.
Ideas on how to extend this project
- Currently the project only supports Japanese and English. This can be extended to support other languages with a few modifcations to the code.
- Close the loop by adding an attending status on the Google Sheet
- Change what the app says or add a bit of your own personality. You can do this directly in Dialogflow in the
Intentssection - Support your blurts by adding a LED or Servo to your micocontroller
- Create a case for your micocontroller out of paper, cardboard or even 3D print one
- Change the voice of your app, you can do this in Actions on Google Console
- Add recurring announcements/blurts
Made by Toaster and friends at the Google Creative Lab.
Copyright 2019 Toaster Ltd. Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.