This repo contains my implementations of various machine learning algorithms using sklearn and Python.
To run the scripts found in this repository, you'll need to install the following Python packages:
- sklearn
- matplotlib
- numpy
- pandas
Additionally, if you want a graphical reprentation of the decision tree, you'll need to get GraphViz from here. Make sure the dot.exe from GraphViz's bin directory is in your PATH, or else the script will throw a FileNotFound error.
- Linear Regression
- K-Nearest Neighbour
- Support Vector Machine
- K-Means Clustering
- Decision Trees
- Neural Networks
Image taken from wikimedia.
Definition:
Linear Regression is the process of finding a line that best fits the data points available on the plot, so that we can use it to predict output values for inputs that are not present in the data set we have, with the belief that those outputs would fall on the line. -- Anas Al-Masri
Problem solved using the algorithm: Estimating the grades of students in G3 based on their results in G1 and G2 as well as their absences during the academic year, their failures and the time studied per week.
Besides predicting the final grade of a student, the linear_regression.py can also plot the relationship between two sets of data.
Accuracy: R²-Score of ~0.75 - ~0.9
In the linear_regression directory you can also find the linear_regression_no_lib.py which is my implementation of linear regression without using sklearn.
Image taken from wikimedia and made by user Agor153.
Definition:
KNN works by finding the distances between a query and all the examples in the data, selecting the specified number examples (K) closest to the query, then votes for the most frequent label (in the case of classification) or averages the labels (in the case of regression). -- Onel Harrison
Problem solved using the algorithm: Classify the acceptability of a car based on buying and maintenance price, number of doors, capacity in terms of persons, size of luggage boot and the car's safety rating.
Accuracy: ~95% - ~98%
Image taken from wikimedia and made by user Alisneaky.
Definition:
A Support Vector Machine (SVM) is a discriminative classifier formally defined by a separating hyperplane. In other words, given labeled training data (supervised learning), the algorithm outputs an optimal hyperplane which categorizes new examples. -- Savan Patel
Problem solved using the algorithm: Classify tumors as benign or malign, based on about 30 criteria such as size, growth and many more.
Accuracy: ~92% - ~96%
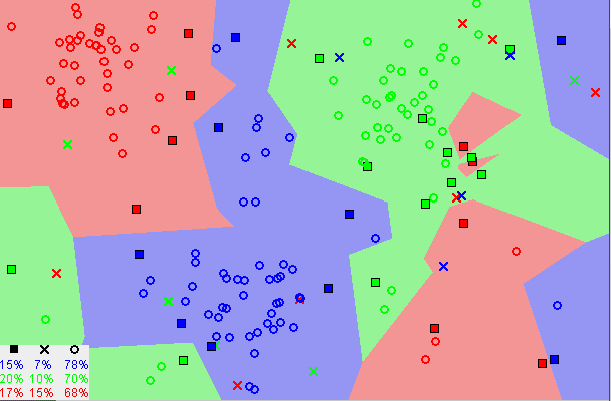
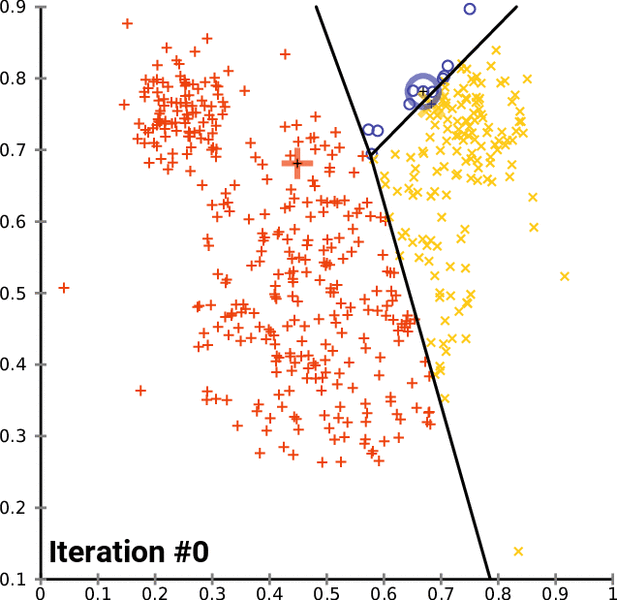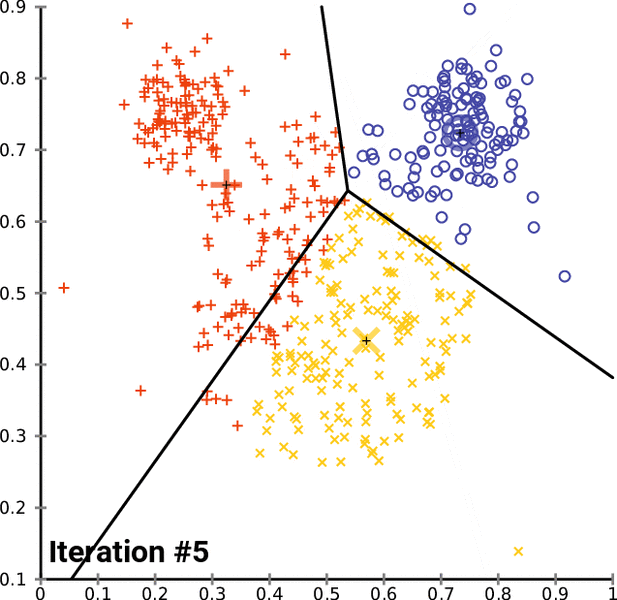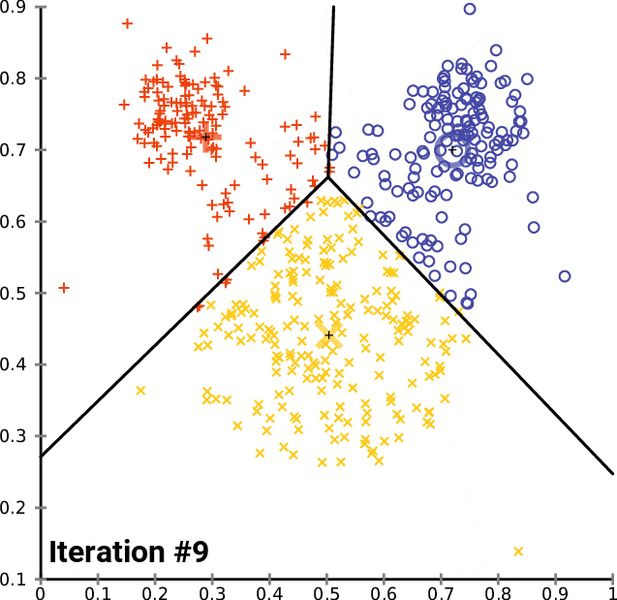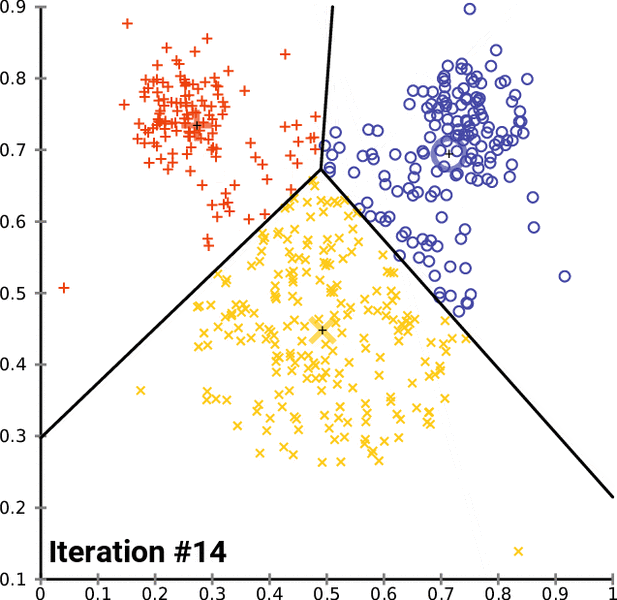
Image taken from wikimedia and made by user Chire.
Definition:
The k-means clustering algorithm attempts to split a given anonymous data set (a set containing no information as to class identity) into a fixed number (k) of clusters. Initially k number of so called centroids are chosen. A centroid is a data point (imaginary or real) at the center of a cluster. -- Ola Söder
Problem solved using the algorithm: Classifing handwritten digits.
Accuracy:
- inertia: 69510
- homogeneity: ~0.61
- completeness: ~0.66
- v-measure: ~0.63
- adjusted-rand: ~0.48
- adjusted-mutual-info: ~0.61
- silhouette: ~0.14
(can also be found as a comment in the k_means_cluster.py)
- inertia: within-cluster sum-of-squares
- homogeneity: each cluster contains only members of a single class (range 0 - 1)
- completeness: all members of a given class are assigned to the same cluster (range 0 - 1)
- v-measure: harmonic mean of homogeneity and completeness
- adjusted_rand: similarity of the actual values and their predictions, ignoring permutations and with chance normalization (range -1 to 1, -1 being bad, 1 being perfect and 0 being random)
- adjusted_mutual_info: agreement of the actual values and predictions, ignoring permutations (range 0 - 1, with 0 being random agreement and 1 being perfect agreement)
- silhouette: uses the mean distance between a sample and all other points in the same class, as well as the mean distance between a sample and all other points in the nearest cluster to calculate a score (range: -1 to 1, with the former being incorrect, and the latter standing for highly dense clustering. 0 indicates overlapping clusters.
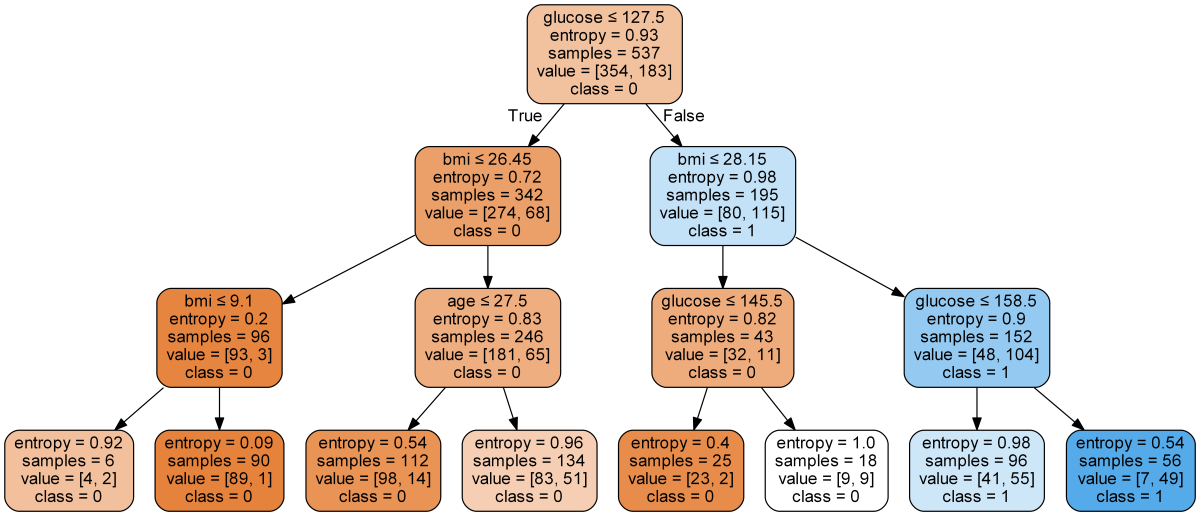
Image generated using decision_tree.py.
Definition:
In computer science, Decision tree learning uses a decision tree (as a predictive model) to go from observations about an item (represented in the branches) to conclusions about the item's target value (represented in the leaves). -- Wikipedia
Problem solved using the algorithm: Predicting the onset of diabetes based on diagnostic measures.
Accuracy:
- ~78% with a depth of 4 and information gain as attribute selection measure
- ~76% with a depth of 3 and information gain as attribute selection measure
- ~76% with a depth of 4 and gini impurity as attribute selection measure
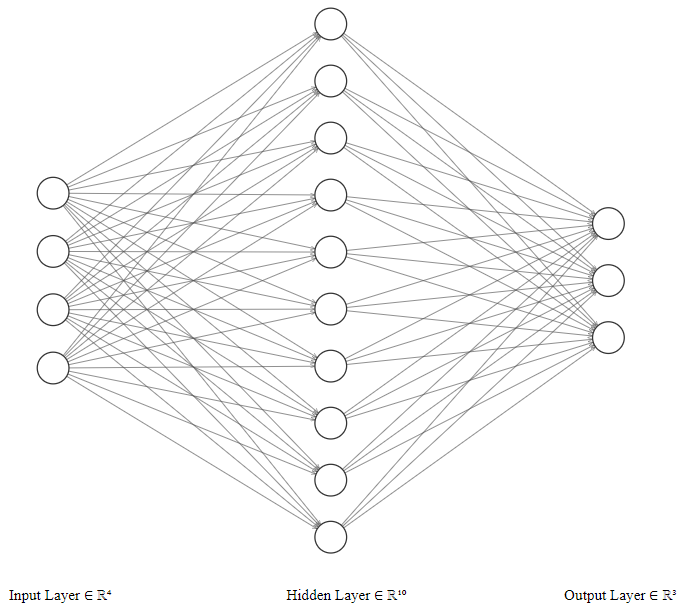
The first neural network declared in neural_network.py
The second network declared in neural_network.py
Definition:
Artificial neural networks (ANN) or connectionist systems are computing systems that are inspired by, but not identical to, biological neural networks that constitute animal brains. Such systems "learn" to perform tasks by considering examples, generally without being programmed with task-specific rules. -- Wikipedia
Problem solved using neural networks: Classifcation of iris flowers based on petal length and width as well as sepal length and width.
Accuracy: Both networks get a mean accuracy of around 0.9 to 1.0.