Compatibility Matrix
Client version compatibility to MSB versions:
| 1.5.x-RELEASE | |
|---|---|
| 1.0.x | x |
If you want to contribute, please read the Contribution Guidelines.
If you want to test this client by using its sources and a sample app, read the App Sample.
If you want to know how to use this client in your own project, read below.
TODO: Link to general documentation about VFK MSB
You can use this client to connect a node app to VFK MSB.
- nodeJs and npm installed: https://nodejs.org/en/
- MSB client npm package installed
Install npm package
npm install --save @vfk_research/msb-client-websocket-nodejsImport to your applicaton
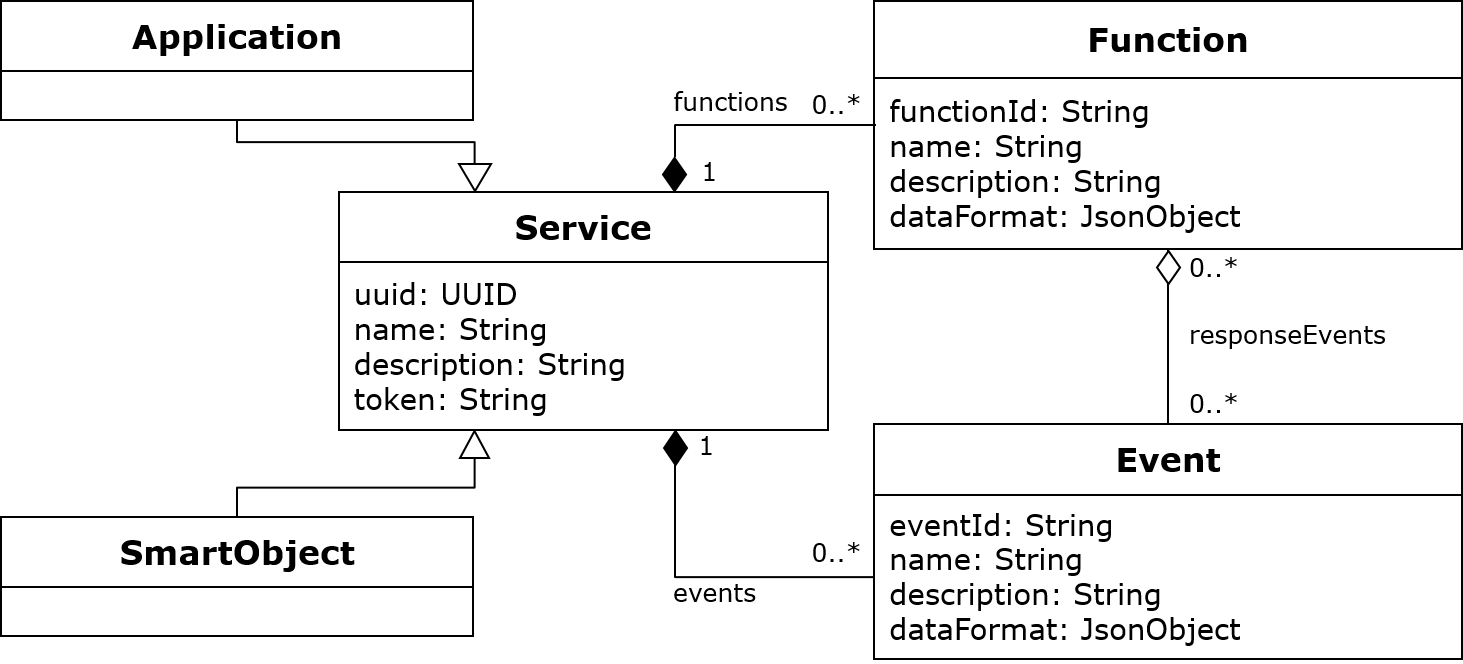
var MsbClient = require('@vfk_research/msb-client-websocket-nodejs');The figure below shows a minimal required self-description model of a smart object / application.
Every smart object / application requires (must have) a uuid and a token.
The uuid is competent for identification
and the token is used to verify the smart object / application for its owner on the MSB side.
TODO: Here you can find more information about
the self-description structure and supported data formats.
Add the main description by adding an application.poperties file to the root of your project:
Generate the uuid e.g. by a tool like https://www.uuidgenerator.net/
msb.uuid=76499d88-34cf-4836-8cc1-7e0d9c54dacx
msb.name=YourSmartObjectName
msb.description=YourSmartObjectDesc
msb.token=5e0d9c54dacx
msb.type=SmartObjectWhen initializing your msb client instance, the application.properties file will be loaded.
var myMsbClient = new MsbClient();If you do not provide an application.properties file, use the constructor to define the basic self description.
var type = 'SmartObject';
var uuid = uuidv4(); // you can type in an own uuid here instead of generating it
var name = 'SO ' + uuid;
var description = 'SO Desc' + uuid;
var token = uuid.substring(0, 7);
var myMsbClient = new MsbClient(
type,
uuid,
name,
description,
token
);Add events to your smart object / application which can be send to MSB.
var event_id = 'E1';
var event_name = 'EVENT ' + event_id;
var event_description = 'EVENT Description for ' + event_name;
var event_datatype = 'string'; // see available datatypes below
var event_priority = 1; // 0 (LOW), 1 (MEDIUM), 2 (HIGH)
var isArray = false; // just one value or array of it?
myMsbClient.addEvent(
event_id,
event_name,
event_description,
event_datatype,
event_priority,
isArray
);myMsbClient.addEvent({
eventId: 'E2',
name: 'Event E2',
description: 'Description for Event E2',
dataFormat: {
dataObject: {
'$ref': '#/definitions/MyDevice'
},
MyDevice: {
type: 'object',
properties: {
deviceName: {
type: 'string'
},
deviceWeight: {
type: 'number', format: 'float'
},
submodules: {
type: 'array',
items: {
'$ref': '#/definitions/MyModule'
},
},
}
},
MyModule: {
type: 'object',
properties: {
moduleName: {
type: 'string'
}
}
}
},
implementation: {
priority: 1,
}
});See app_sample.js for more event creation examples.
Add functions and their implementations your smart object / application is able to handle.
var function_id = 'F1';
var function_name = 'FUNC ' + function_id;
var function_description = 'FUNC Description for ' + function_name;
var function_dataformat = 'string'; // see available dataformats below
var isArray = false; // handle array of values or just one value?
var responseEvents = []; // you can link to response events here by event_id
myMsbClient.addFunction(
function_id,
function_name,
function_description,
function_dataformat,
printMsg,
isArray,
responseEvents
);
// the implementation of the function (handle event message here)
function printMsg(msg) {
console.info('PrintMsg: ' + JSON.stringify(msg));
}myMsbClient.addFunction({
functionId: 'F2',
name: 'Function F2',
description: 'Description for Function F2',
dataFormat: {
dataObject: {
type: 'object', $ref: '#/definitions/MyCar',
},
MyCar: {
type: 'object',
properties: {
carColor: {
type: 'string'
},
carNrOfSeats: {
type: 'integer', format: 'int32',
},
carWeight: {
type: 'number', format: 'float',
},
},
},
},
responseEvents: [],
implementation: function(msg) {
console.info('F1 has been called, message:' + msg.dataObject);
},
});See app_sample.js of the application template for more (and complex) examples.
var msb_url = 'ws://127.0.0.1:8085';
myMsbClient.connect(msb_url);
myMsbClient.register();You will get an IO_CONNECTED and IO_REGISTERED event from MSB, if successful.
For publishing an event to a websocket broker interface,
only the eventId and data are required of the already specified event (see above).
var event_id = 'E1';
var event_value = 'Hello World!';
myMsbClient.publish(
event_id,
event_value
);The MSB responds with an IO_PUBLISHED event, if successful.
By default events are published with a low priority.
It is also possible to set the priority of an event.
There are three possible priorities for events like it is shown at the following table.
Constant |
Value |
|---|---|
| LOW | 0 |
| MEDIUM | 1 |
| HIGH | 2 |
var event_id = 'E1';
var event_value = 'Hello World!';
var event_priority = 2;
myMsbClient.publish(
event_id,
event_value,
event_priority
);Another option is to publish an event as cached event by setting the cache parameter to true.
This means that the event is not deleted if the connection is broken.
var event_id = 'E1';
var event_value = 'Hello World!';
var event_priority = 2;
var event_isCached = true;
myMsbClient.publish(
event_id,
event_value,
event_priority,
event_isCached
);You can also pass a event object to the publish function in the format:
{
eventId: 'eventId',
value: 'value',
priority: 1,
cached: true,
postDate: new Date().toISOString(),
correlationId: correlationId
}As mentioned above, only eventId and value are required fields
var event_id = 'E1';
var event_value = 'Hello World!';
var event_priority = 2;
var event_isCached = true;
var event_correlationId = '72047f33-a9ae-4aa5-b7ae-c1c4a2797cac';
myMsbClient.publish({
eventId: event_id,
value: event_value,
priority: event_priority,
cahced: event_isCached,
postDate: new Date().toISOString(),
correlationId: event_correlationId
});For values based on complex data formats it will look like this:
var event_id = 'E2';
var event_priority = 2;
var event_isCached = true;
var event_correlationId = '72047f33-a9ae-4aa5-b7ae-c1c4a2797cac';
myMsbClient.publish({
eventId: event_id,
value: {
deviceName: 'Dev001',
deviceWeight: 62.22,
submodules: [
{moduleName: 'Module 1'},
{moduleName: 'Module 2'},
],
},
priority: event_priority,
cahced: event_isCached,
postDate: new Date().toISOString(),
correlationId: event_correlationId
});As shown above the addFunction method includes a function pointer
to point to the function implementation.
Configuration parameters are a simple list of key value pairs for the smart object / application. It is displayed and can be customized in the MSB UI to change your apps behaviour during runtime.
Add condifuration parameters:
var param_name_1 = 'testParam1';
var param_value_1 = true;
var param_datatype_1 = 'boolean';
myMsbClient.addConfigParameter(param_name_1, param_value_1, param_datatype_1);
var param_name_2 = 'testParam2';
var param_value_2 = 'StringValue';
var param_datatype_2 = 'string';
myMsbClient.addConfigParameter(param_name_2, param_value_2, param_datatype_2);
var param_name_3 = 'testParam3';
var param_value_3 = 1000;
var param_datatype_3 = 'int32';
myMsbClient.addConfigParameter(param_name_3, param_value_3, param_datatype_3);Get configuration parameter (after changed in MSB UI) to change your app behaviour:
// get by getConfigParameter using name as key
var parameterValueFound_1 = myMsbClient.getConfigParameter(param_name_1);
var parameterValueFound_2 = myMsbClient.getConfigParameter(param_name_2);
var parameterValueFound_3 = myMsbClient.getConfigParameter(param_name_3);To enable SSL/TLS, you need to specify wss:// or https:// in the URL instead of ws:// or http://.
Furthermore, it is necessary to specify a trust store in the client, which contains the public certificate of the MSB interface, so that it is considered trustworthy.
var msb_url = 'wss://<hostname>:<port>';
myMsbClient.connect(msb_url);
myMsbClient.register();If you use an IP instead of a public url during development, it will be necessary to disable the hostname verification to connect via web socket secure.
myMsbClient.disableHostnameVerification(true);If connection to the common websocket interface is broken the client performs a reconnect.
After a reconnect the registration at the MSB will be redone automatically by the client.
You can also change this intervally by setting an integer value in ms for the reconnect interval.
myMsbClient.setReconnectInterval(10000);Or you can disable the automatic reconnect.
myMsbClient.disableAutoReconnect(true);If the client loses the connection, the published events are cached in a queue.
After a successfull reconnection, the queued events are published to MSB (FIFO principle). The default size of the queue is 1000 entries. The size can be changed:
myMsbClient.setEventCacheSize(1000);If no event caching is needed, you can disable it.
myMsbClient.disableEventCache(true);To debug your clients communication with MSB, you can enable the debug mode
myMsbClient.enableDebug(true);It mgiht be also helpful to enable data format validation, to check if an event value is valid
myMsbClient.enableDataFormatValidation(true);If you get an "undefined" error for the config values from the application properties on Windows 7, change the line endings of the application.properties file from LF (Linux) to CRLF (Windows).
Windows 10 should be able to handle both.