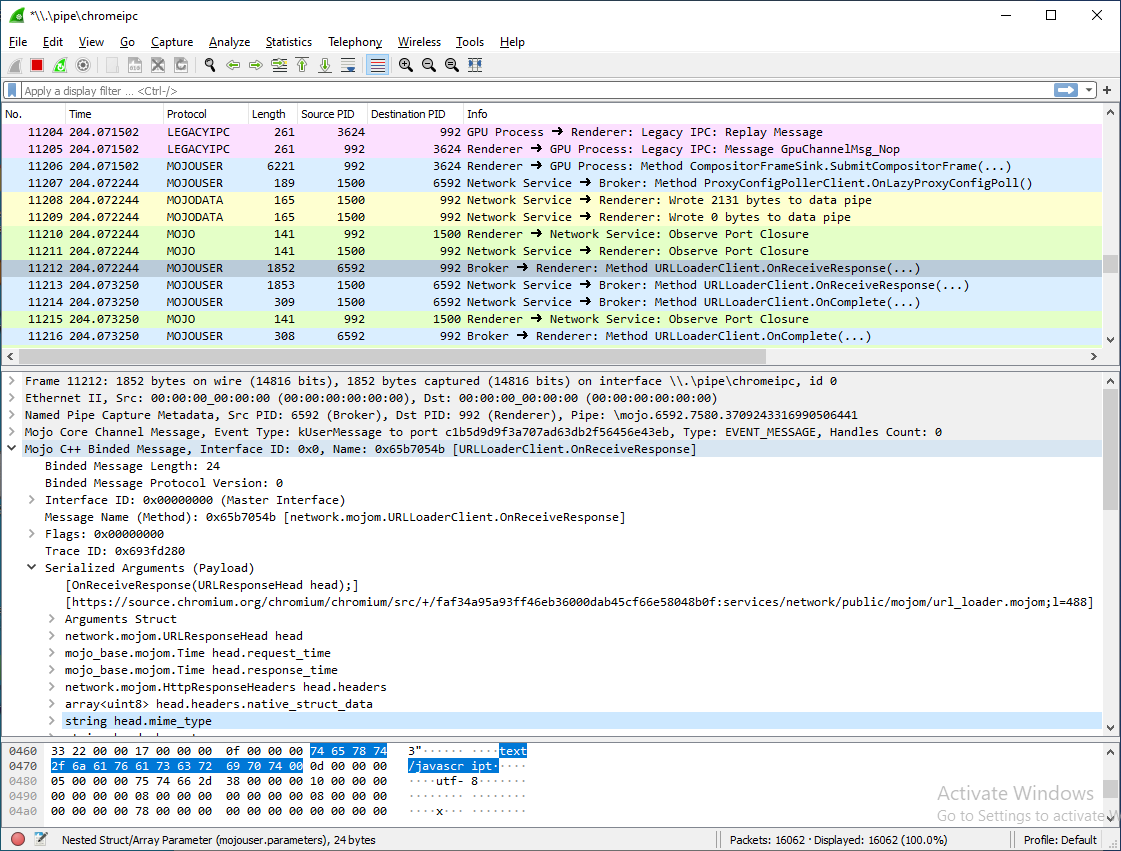
This utility helps you explore what Chrome processes are saying to each other under the hood in real-time, using Wireshark.
It captures data sent over the Named Pipe Inter-Process-Communication (IPC) primitive and sends it over to dissection.
- Mojo Core messages (Ports, Nodes, Invitations, Handles, etc.)
- IPCZ messages, aka Chromuim's new replacement for Mojo Core (Portals, Routers, Parcels, etc.)
- Mojo binded user messages (actual
.mojomIDL method calls) - Legacy IPC
- Mojo data pipe control messages (read/wrote X bytes)
- Audio sync messages (
\pipe\chrome.sync.xxxxx)
You are welcomed to look at some traffic examples as well.
However, this project won't see anything that doesn't go over pipes, which is mostly shared memory IPC:
- Mojo data pipe contents (raw networking buffers, audio, etc.)
- Sandbox IPC
- Possibly more things, such as some
ipczmethod calls
You can download pre-compiled binaries from the Releases page, and run:
C:\>chromeipc.exe
Chrome IPC Sniffer v0.5.0.0
Type -h to get usage help and extended options
[+] Starting up
[+] Determining your chromium version
[+] You are using chromium 83.0.4103.116
[+] Checking mojom interfaces information
[+] Checking legacy IPC interfaces information
[+] Extracting scrambled message IDs from chrome.dll...
[+] Copying LUA dissectors to Wirehsark plugins directory
[+] Enumerating existing chrome pipes
[+] Starting sniffing of chrome named pipe to \\.\pipe\chromeipc.
[+] Opening Wirehark
[+] Capturing 40 packets/second......
Wireshark should open automatically.
[P.S. The pipe \\.\pipe\chromeipc has nothing to do with Chrome itself, it's just where this tool will output its traffic to]
If you don't like pre-built binaries, you can clone and compile this repository at least using Visual Studio 2015. Note that it depends on the Newtonsoft.Json package.
Chrome IPC Sniffer v0.5.0.0
Syntax: chromeipc [options]
Available options:
Capturing:
--only-mojo
Records only packets sent over a "\\mojo.*" pipe (without "\\chrome.sync.*", etc.).
--only-new-mojo-pipes
Records only packets sent over mojo AND newly-created pipes since the start of the capture
This helps reducing noise and it might improve performance
(example: opening a new tab will create a new mojo pipe).
Interface resolving:
--update-interfaces-info
Forcefully re-scan the chromium sources (from the internet) and populate the *_interfaces.json files.
This might take a few good minutes. Use this if you see wrong interfaces info and wish to update
--extract-method-names
Forcefully re-scan chrome.dll file to find the message IDs and update the mojo_interfaces_map.lua file
This should happen automaticlly whenever chrome.dll changes.
It's worth noting that you can filter the results in Wireshark to show only packets of interest. Examples:
- To show only packets going to/from a particular process, use
npfs.pid == 1234 - To show only packets not going to/from the GPU Process, use
!(npfs.process_type contains "GPU Process") - To show only packets with a particular method name, use
mojouser.name contains "SomeMethod"
By default, the LUA dissectors will only show Nested Struct/Array trees and won't try to go through all the fields.
You can enable deep inspection, but it's slow for a large number of packets and not complete.
Go to Edit -> Prefrences -> Protocols -> MOJOUSER -> Enable structs deep dissection
- Supports Chrome 80+ on 64-bit Windows only
- Interfaces info are chromium version dependent, so running
--update-interfaces-infois needed from time to time - Names of methods as shown in Wireshark is based on the chromium sources, and some mojom interfaces use unscrambled ordinals, which won't be resolved
- Tested only on official, branded Chrome builds. Could theoretically work on other builds too, as well as other chromium-based browsers (Edge)
- Parsing is not 100% complete, e.g unions/enums/maps are not fully supported
Starting from Chrome v112, ipcz is used as the underlying transport instead of Mojo Core. Unfortunately in this mode a lot of the interesting messages are going through shared memory and not named pipes, which means this tool will not see.
You can force Chrome to use Mojo Core again by running it with these arguments:
chrome.exe --disable-features=MojoIpcz
tdevmonc.sys (or Tibbo Device Monitor) is a third-party kernel-mode driver that is used to capture the Named Pipe traffic.
The reason to include it is to avoid the need to enable test signing or to tamper with chrome processes.
The driver works by IoAttachDeviceToDeviceStacking on top of the \Device\NamedPipe device and acting as a filter driver. Then the data that is written to pipes is exposed to user mode using various IOCTLs.
You can find sources for this driver here, as well as binaries and PDB here.
Note that this driver is used by IO ninja, which is not entirely freeware. Also note this driver does not practically support unloading once it attaches to at least one device (you need to reboot).