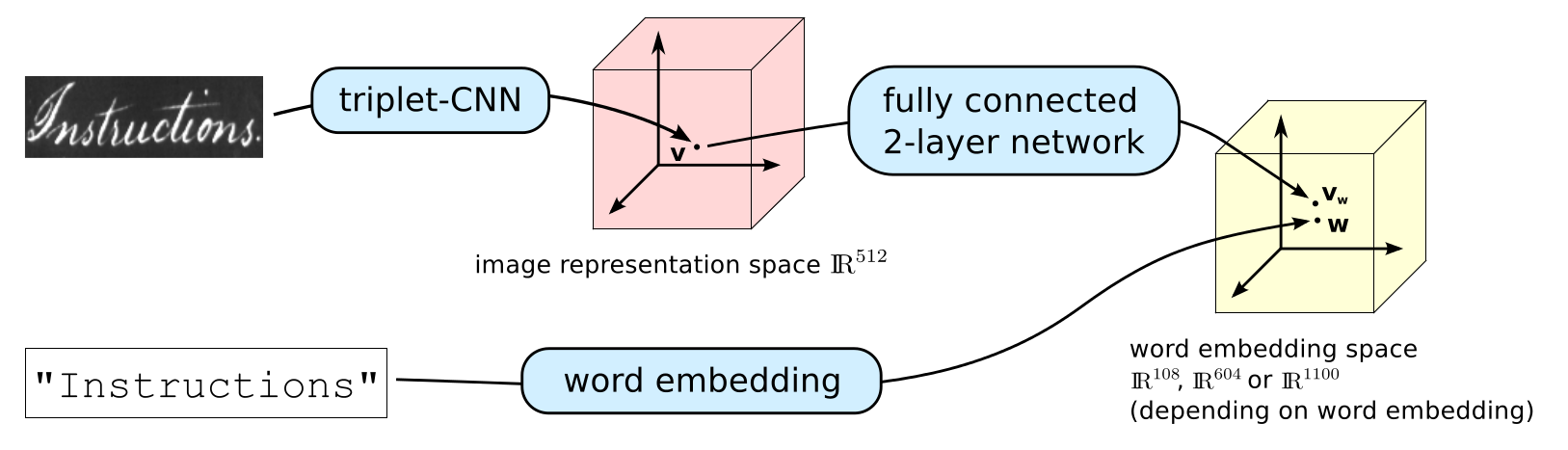
This is a minimal implementation of the model from the paper Semantic and Verbatim Word Spotting using Deep Neural Networks. The model allows you to embed word images into any general vector space in which you can perform query-by-example and query-by-string word spotting (image retrieval) and probably perform decent enough transcription of word images. The model is a pre-activation ResNet followed by a small MLP that embeds an image into a word embedding space.
This space can be verbatim (distance corresponds to string similarity) and semantic (distance corresponds to string and semantic similarity). Two of the embeddings investigated in the paper are learned word embeddings extracted from the LSTM-char-large model from the paper Character-Aware Neural Language Model. Get authors' Torch implementation from here.
Parts of this code is based on the PN-Net architecture for learning local image descriptors, available at https://github.com/vbalnt/pnnet.
If you make use of this code in a scientific context, please cite
@inproceedings{Wilkinson2016_WS,
booktitle = {International Conference on Frontiers in Handwriting Recognition},
author = {Wilkinson, Tomas and Brun, Anders.},
title = {{Semantic and Verbatim Word Spotting using Deep Neural Networks}},
year = {2016}
}
When preparing my code for this release, I have discovered mistake in the paper. I accidentally write that I use the original ResNet model but I actually used the pre-activation ResNet.
As of now, the code requires an NVIDIA GPU with CUDA installed. The triplet network requires less than 6 GBs of memory while the embedding network requires less than 2 GBs. You can further reduce the memory footprint by using the OptNet package. This could be useful if you have trouble fitting your models on your GPUs.
The code is written in Python and Lua, and requires Torch, which can be installed from here.
It also requires the following Torch packages:
- npy4th
- hdf5
which can be installed with
luarocks install npy4th
luarocks install hdf5
It also has the following python dependencies:
- numpy
- scipy
- h5py
- scikit-image
which can be installed using the command
pip install numpy scipy skimage h5py
You can download the Washington dataset from this link or using
cd data/washington
wget http://ciir.cs.umass.edu/downloads/gw/gw_20p_wannot.tgz
tar -xzf gw_20p_wannot.tgz
cd ../../
You also need to download the embeddings and put them in the embeddings folder
mkdir embeddings
cd embeddings
wget http://user.it.uu.se/~tomwi522/washington_embeddings.zip
unzip washington_embeddings.zip
cd ../
Finally, you need to download the model used to initialize the networks, trained on the CVL dataset.You can find it here. Save the model to the folder `pretrained´.
You can download some pre-trained models for a fold 1 using the 4 embeddings. Trained using this code base. Note that these models are saved as CudaTensors and thus require cutorch and cudnn.
Code to setup the Washington dataset is suplied in misc/preprocess.py. Running
python misc/preprocess.py
will load the Washington dataset, setup the necessary image and embedding hdf5 databases.
Make sure to download the Washington dataset before running this
Then run
./train_net.sh
To train the triplet network and the 4 different embeddings. You can comment away some of the commands if you're only interested in one specific embedding.
To evaluate the models first run
th misc/eval.lua
to extract descriptors for each word image, then run
python eval_test.py
to get QbE and QbS MaP scores for the different. It should look something like this:
triplet Washington QbE 94.0120767804 , QbS: -100.0
semantic Washington QbE 96.7435996072 , QbS: 71.2676505913
ngram Washington QbE 96.9961577901 , QbS: 82.7666758942
phoc Washington QbE 97.7626788718 , QbS: 92.6989763255
dct3 Washington QbE 97.3370356691 , QbS: 94.1436752847
To train on a new dataset you need to create corresponding function in misc/db_utils.py that loads the dataset in question. The function should return a list of data where each entry is a dictionary with the following keys/values:
- file: The absolute path to the word image
- split: one of 'train'/'val'/'test'
- text: the ground truth transcription.
all values should be strings. Then you need to modify misc/preprocess.py to load your dataset instead and create your hdf5 databases. The rest of the process should just require minor changes to the existing scripts to train on a new dataset.