The OmiseGO Android SDK allows developers to easily interact with a node of the OmiseGO eWallet.
- Requirements
- Installation
- Usage
- Run Kotlin Lint
- Test
- Contributing
- License
- Sample Project
- Minimum Android SDK version 19
To use the OmiseGO SDK in your android project, simply add the following line in the module's build.gradle
dependencies {
implementation 'co.omisego:omisego-sdk:<latest-sdk-version>'
}Before using the SDK to retrieve a resource, you need to initialize the client (EWalletClient) with a ClientConfiguration object.
You should do this as soon as you obtain a valid authentication token corresponding to the current user from the Wallet API.
Then you need to pass it to the EWalletClient.Builder and call build() to get the EWalletClient instance.
Lastly, you will need to pass the instance that you got from the previous step to the OMGAPIClient's constructor.
For example,
val config = ClientConfiguration(
baseURL = "YOUR_BASE_URL",
apiKey = "YOUR_API_KEY",
authenticationToken = "YOUR_AUTH_TOKEN"
)
val eWalletClient = EWalletClient.Builder {
clientConfiguration = config
debug = false
}.build()
val omgAPIClient = OMGAPIClient(eWalletClient)Where:
apiKeyis the api key generated from your OmiseGO admin panel.authenticationTokenis the token corresponding to an OmiseGO Wallet user retrievable using one of our server-side SDKs.
You can find more info on how to retrieve this token in the OmiseGO server SDK documentations.
baseURLis the URL of the OmiseGO Wallet API. Note: This need to be ended with '/'.debug(Optional) is a boolean indicating if the SDK should print logs in the console. default:false.
Once you have a client object in the initialization section, you can retrieve different resources.
Every call takes an OMGCallback interface that returns a OMGResponse object:
interface OMGCallback<in T> {
fun success(response: OMGResponse<T>)
fun fail(response: OMGResponse<APIError>)
}data class OMGResponse<out T>(val version: String, val success: Boolean, val data: T)
data class APIError(val code: ErrorCode, val description: String)Where:
success is the function invoked when the success boolean in the response is true. This function will provide the corresponding data model to an API endpoint.
fail is the function invoked when the success boolean in the response is false. This function will provide the APIError object which contains information about the failure.
omgAPIClient.getCurrentUser().enqueue(object: OMGCallback<User>{
override fun fail(response: OMGResponse<APIError>) {
}
override fun success(response: OMGResponse<User>) {
}
})omgAPIClient.getWallets().enqueue(object: OMGCallback<WalletList>{
override fun fail(response: OMGResponse<APIError>) {
}
override fun success(response: OMGResponse<WalletList>) {
}
})Note: For now a user will have only one wallet.
omgAPIClient.getSettings().enqueue(object: OMGCallback<Setting>{
override fun fail(response: OMGResponse<APIError>) {
}
override fun success(response: OMGResponse<Setting>) {
}
})This returns a paginated filtered list of transactions.
In order to get this list you will need to create a ListTransactionParams object:
val request = ListTransactionParams.create(
page = 1,
perPage = 10,
sortBy = Paginable.Transaction.SortableFields.CREATE_AT,
sortDir = SortDirection.ASCENDING,
searchTerm = "confirmed", // or searchTerms = mapOf(STATUS to "completed")
address = null
)Where
-
pageis the page you wist to receive -
perPageis the number of results per page -
sortByis the sorting field. The available values are:ID,STATUS,FROM,TO,CREATED_ATimport co.omisego.omisego.model.pagination.Paginable.Transaction.SortableFields.* -
sortDiris the sorting direction. The available values are:ASCENDING,DESCENDINGimport co.omisego.omisego.model.pagination.SortDirection.* -
searchTerm(optional) is a term to search for all of the searchable fields. Conflict withsearchTerms, only use one of them. The available values are:ID,STATUS,FROM,TO,import co.omisego.omisego.model.pagination.Paginable.Transaction.SearchableFields.* -
searchTerms(optional) is a key-value map of fields to search with the available fields (same assearchTerm) For example:mapOf(FROM to "some_address", ID to "some_id")
-
address(optional) is an optional address that belongs to the current user (primary wallet address by default)
Then you can call:
omgAPIClient.getTransactions(request).enqueue(object: OMGCallback<PaginationList<Transaction>>{
override fun fail(response: OMGResponse<APIError>) {
//TODO: Handle the error
}
override fun success(response: OMGResponse<PaginationList<Transaction>>) {
//TODO: Do something with the paginated list of transactions
}
})There is PaginationList<Transaction> inside the response.data which contains data: List<Transaction> and pagination: Pagination
Where:
-
datais an array of transactions -
paginationis aPaginationobjectWhere:
perPageis the number of results per page.currentPageis the retrieved page.isFirstPageis a bool indicating if the page received is the first pageisLastPageis a bool indicating if the page received is the last page
The SDK offers 2 ways for transferring tokens between addresses:
- A simple one way transfer from one of the current user's wallets to an address.
- A highly configurable send/receive mechanism in 2 steps using transaction requests.
The most basic way to transfer tokens is to use the omgAPIClient.createTransaction() method, which allows the current user to send tokens from one of its wallet to a specific address.
val request = TransactionCreateParams(
fromAddress = "1e3982f5-4a27-498d-a91b-7bb2e2a8d3d1",
toAddress = "2e3982f5-4a27-498d-a91b-7bb2e2a8d3d1",
amount = 1000.bd,
tokenId = "BTC:xe3982f5-4a27-498d-a91b-7bb2e2a8d3d1",
idempotencyToken = "some token"
)
omgAPIClient.createTransaction(request).enqueue(object : OMGCallback<Transaction>{
override fun success(response: OMGResponse<Transaction>) {
// Do something
}
override fun fail(response: OMGResponse<APIError>) {
// Handle error
}
})There are different ways to initialize a TransactionCreateParams by specifying either toAddress, toAccountId or toProviderUserId.
A more configurable way to transfer tokens between 2 addresses is to use the transaction request flow.
To make a transaction happen, a TransactionRequest needs to be created and consumed by a TransactionConsumption.
To generate a new transaction request you can call:
/* Short version */
val request = TransactionRequestCreateParams(
type = TransactionRequestType.RECEIVE,
tokenId = "a_token_id"
)
/* Full version */
val request = TransactionRequestCreateParams(
type = TransactionRequestType.RECEIVE,
tokenId = "a_token_id",
amount = 10_240, /* If the token has subUnitToUnit = 1,000, it means this request want to receive 10.24 OMG */
address = "receiver_address",
correlationId = "correlation_id",
requireConfirmation = false,
maxConsumption = 10,
consumptionLifetime = 60000,
expirationDate = null,
allowAmountOverride = true,
maxConsumptionsPerUser = null,
metadata = mapof<String, Any>(),
encryptedMetadata = mapOf<String, Any>()
)
val omgAPIClient = YOUR_OMG_API_CLIENT
omgAPIClient.createTransactionRequest(request).enqueue(object : OMGCallback<TransactionRequest> {
override fun success(response: OMGResponse<TransactionRequest>) {
//TODO: Do something with the transaction request (get the QR code representation for example)
}
override fun fail(response: OMGResponse<APIError>) {
//TODO: Handle the error
}
})Where:
requestis aTransactionRequestParamsdata class constructed using:type: The QR code type, only supportsTransactionRequestType.RECEIVEfor now.tokenId: The id of the desired token.amount: (optional) The amount of token to receive. This amount can be either inputted when generating or consuming a transaction request.address: (optional) The address specifying where the transaction should be sent to. If not specified, the current user's primary wallet address will be used.correlationId: (optional) An id that can uniquely identify a transaction. Typically an order id from a provider.requireConfirmation: A boolean indicating if the request needs a confirmation from the requester before being proceeded.maxConsumptions: (optional) The maximum number of time that this request can be consumed. Defaultnull(unlimited).consumptionLifetime: (optional) The amount of time in millisecond during which a consumption is valid. Defaultnull(forever).expirationDate: (optional) The date when the request will expire and not be consumable anymore. Defaultnull(never expired).allowAmountOverride: (optional) Allow or not the consumer to override the amount specified in the request. This needs to be true if the amount is not specified
Note that if amount is nil and allowAmountOverride is false the init will fail and return null.
maxConsumptionsPerUser: (optional) The maximum number of consumptions allowed per unique user. Defaultnull(unlimited).metadata: Additional metadata embedded with the requestencryptedMetadata: Additional encrypted metadata embedded with the request
A TransactionRequest object is passed to the success callback, you can generate its QR code representation using transactionRequest.generateQRCode(size).
The previously created transactionRequest can then be consumed:
/* Short version */
val request = TransactionConsumptionParams.create(
transactionRequest
)
/* Full version */
val request = TransactionConsumptionParams.create(
transactionRequest,
amount = 25_000.bd, // BigDecimal
address = "an address",
tokenId = "A token id",
idempotencyToken = "An idempotency token",
correlationId = "a correlation id",
metadata = mapOf(),
encryptedMetadata = mapOf()
)
omgAPIClient.consumeTransactionRequest(request).enqueue(object : OMGCallback<TransactionConsumption> {
override fun success(response: OMGResponse<TransactionConsumption>) {
// Handle success
}
override fun fail(response: OMGResponse<APIError>) {
// Handle error
}
})Where
requestis aTransactionConsumptionParamsdata class constructed using:-
transactionRequest: The transactionRequest obtained from the QR scanner. -
address: (optional) The address from which to take the funds. If not specified, the current user's primary wallet address will be used. -
tokenId: (optional) The token id to use for the consumption. -
amount: (optional) The amount of token to send. This amount can be either inputted when generating or consuming a transaction request.Note that if the amount was not specified in the transaction request it needs to be specified here, otherwise the init will fail and throw
IllegalArgumentException. -
idempotencyToken: The idempotency token used to ensure that the transaction will be executed one time only on the server. If the network call fails, you should reuse the same idempotencyToken when retrying the request. -
correlationId: (optional) An id that can uniquely identify a transaction. Typically an order id from a provider. -
metadata: A dictionary of additional data to be stored for this transaction consumption. -
encryptedMetadata: A dictionary of additional encrypted data to be stored for this transaction consumption.
-
The TransactionConsumption object can be used to approve or reject the transaction consumption.
Once you receive the transactionConsumption object, you can call approve or reject function.
The function will then return the OMGCall<TransactionConsumption> object to be used for making the actual request to the API.
val approveRequest = transactionConsumption.approve(omgAPIClient)
val rejectRequest = transactionConsumption.reject(omgAPIClient)
// Approve a transaction consumption
approveRequest.enqueue(object: OMGCallback<TransactionConsumption>{
override fun success(response: OMGResponse<TransactionConsumption>) {
// Handle success
}
override fun fail(response: OMGResponse<APIError>) {
// Handle error
}
})
// Reject a transaction consumption
rejectRequest.enqueue(object: OMGCallback<TransactionConsumption>{
override fun success(response: OMGResponse<TransactionConsumption>) {
// Handle success
}
override fun fail(response: OMGResponse<APIError>) {
// Handle error
}
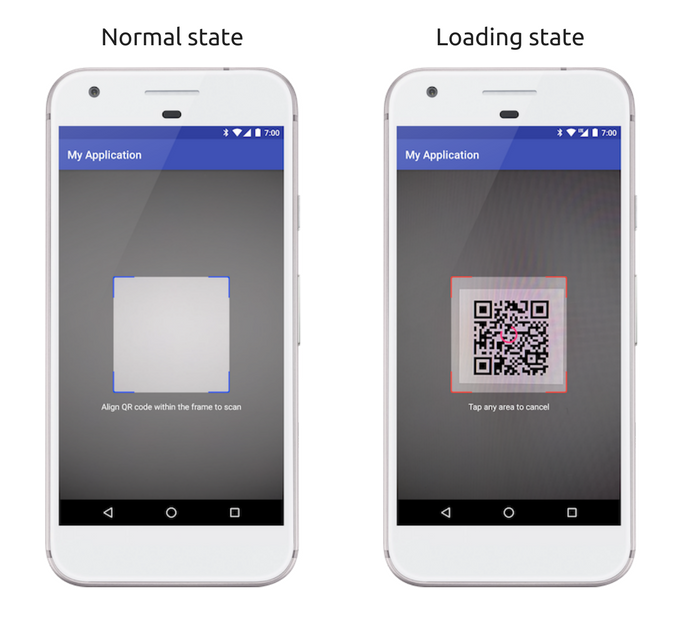
})This SDK offers the possibility to generate and consume transaction requests. Typically these actions should be done through the generation and scan of QR codes.
Once a TransactionRequest is created, you can get its QR code representation using generateQRCode(size).
This method takes an optional size param that can be used to define the expected size of the generated QR bitmap.
val bitmap = txRequest.generateQRCode(512) // Create a 512x512 QR code You can then use the OMGQRScannerView to scan the generated QR code.
First, you need to add OMGQRScannerView to your xml.
Note: You can customize the border color of the QR code frame of the scanner like the following
activity_qr_scanner.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<co.omisego.omisego.qrcode.scanner.OMGQRScannerView
android:id="@+id/scannerView"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
app:borderColor="@color/qrBorderColor"
app:borderColorLoading="@color/qrBorderColorLoading" />
</FrameLayout>Then, you can call scannerView.startCamera passing your OMGAPIClient and OMGQRScannerContract.Callback respectively to start the camera.
Note: You need to handle the camera permission first
class QRScannerActivity : AppCompatActivity(), OMGQRScannerContract.Callback {
private lateinit var omgAPIClient: OMGAPIClient
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_qrscanner)
omgAPIClient = your_omg_api_client
scannerView.startCamera(omgAPIClient, this)
}
override fun scannerDidCancel(view: OMGQRScannerContract.View) {
}
override fun scannerDidDecode(view: OMGQRScannerContract.View, payload: OMGResponse<TransactionRequest>) {
}
override fun scannerDidFailToDecode(view: OMGQRScannerContract.View, exception: OMGResponse<APIError>) {
}
override fun onPause() {
super.onPause()
scannerView.stopCamera()
}
override fun onResume() {
super.onResume()
scannerView.startCamera(omgAPIClient, this)
}
}As you can see, the OMGQRScannerContract.Callback offers the following interface:
/**
* Called when the user tap on the screen. The request to the backend will be cancelled.
*
* @param view The QR scanner view
*/
fun scannerDidCancel(view: OMGQRScannerContract.View)
/**
* Called when a QR code was successfully decoded to a TransactionRequest object
*
* @param view The QR scanner view
* @param transactionRequest The transaction request decoded by the scanner
*/
fun scannerDidDecode(view: OMGQRScannerContract.View, transactionRequest: OMGResponse<TransactionRequest>)
/**
* Called when a QR code has been scanned but the scanner was not able to decode it as a TransactionRequest
*
* @param view The QR scanner view
* @param exception The error returned by the scanner
*/
fun scannerDidFailToDecode(view: OMGQRScannerContract.View, exception: OMGResponse<APIError>)When the scanner successfully decodes a TransactionRequest it will call its delegate method scannerDidDecode(view: OMGQRScannerContract.View, transactionRequest: TransactionRequest).
Finally, add the following lines to your AndroidManifest.xml
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.your.package">
<!-- Add this 3 lines -->
<uses-feature android:name="android.hardware.camera" />
<uses-feature android:name="android.hardware.camera.autofocus" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.CAMERA" />
<application>
<!-- Your activities -->
</application>
</manifest>The transaction request flow is as follow:
- Create a
TransactionRequestsuccessfully. - Consume that
TransactionRequestwhich will generate a TransactionConsumption. - Approve or reject the
TransactionConsumptiongenerated in step 2.
This section describes the use of the OMGSocketClient in order to listen for events which happens after step 2 or step 3.
Similarly to the OMGAPIClient, the OMGSocketClient needs to be first initialized with a ClientConfiguration before using it.
val config = ClientConfiguration(
baseURL = "YOUR_BASE_URL",
apiKey = "YOUR_API_KEY",
authenticationToken = "YOUR_AUTH_TOKEN"
)
val socketClient = OMGSocketClient.Builder {
clientConfiguration = config
debug = false
}.build()Where:
apiKeyis the API key (typically generated on the admin panel).authenticationTokenis the token corresponding to an OmiseGO Wallet user retrievable using one of our server-side SDKs.
You can find more info on how to retrieve this token in the OmiseGO server SDK documentations.
baseURLis the URL of the OmiseGO Wallet API, this needs to be an ws(s) url. Note: This need to be ended with '/'.debug(Optional) is a boolean indicating if the SDK should print logs in the console. default:false.
The system event is giving general information related to the status of the web socket connection. All listenable system events are the Connection status and the Channel status.
SocketConnectionListener (optional) is the listener that listens for a web socket's server connection status. The possible events are:
onConnected(): Invoked when the web socket client has connected to the eWallet web socket API successfully.onDisconnected(throwable: Throwable): Invoked when the web socket client has disconnected from the eWallet web socket API. Throws an exception if the web socket was not disconnected successfully.
Usage
socketClient.setConnectionListener(object : SocketConnectionListener {
override fun onConnected() {
// Do something
}
override fun onDisconnected(throwable: Throwable?) {
// Do something
}
})SocketChannelListener (optional) is the listener that listens for a channel connection status. The possible events are:
onJoinedChannel(topic: String): Invoked when the client have been joined the channel successfully.onLeftChannel(topic: String): Invoked when the client have been left the channel successfully.onError(apiError: APIError): Invoked when something goes wrong while connecting to a channel.
Usage
socketClient.setChannelListener(object : SocketChannelListener {
override fun onJoinedChannel(topic: String) {
// Do something
}
override fun onLeftChannel(topic: String) {
// Do something
}
override fun onError(apiError: APIError) {
// Handle an error
}
})Custom event are special events that are currently limited to the TransactionRequest and the TransactionConsumption event.
All custom events will be a sub-class of the SocketCustomEventListener. SocketCustomEventListener is a required generic listener that you will need to pass its sub-class when joining to the channel for listening to the events.
All possible listeners are the following:
When creating a TransactionRequest that requires a confirmation it is possible to listen for all incoming events using the TransactionRequestListener.
The possible events are:
onTransactionConsumptionRequest(TransactionConsumption): Invoked when aTransactionConsumptionis trying to consume theTransactionRequest. This allows the requester to confirm or not the consumption if legitimate.onTransactionConsumptionFinalizedSuccess(TransactionConsumption): Invoked if aTransactionConsumptionhas been finalized successfully, and the transfer was made between the 2 addresses.onTransactionConsumptionFinalizedFail(TransactionConsumption, APIError): Invoked if aTransactionConsumptionfails to consume the request.
Similarly to the TransactionRequestListener, a TransactionConsumption can be listened for incoming confirmations using the TransactionConsumptionListener.
The possible events are:
onTransactionConsumptionFinalizedSuccess(TransactionConsumption): Invoked if aTransactionConsumptionhas been finalized successfully, and the transfer was made between the 2 addresses.onTransactionConsumptionFinalizedFail(TransactionConsumption, APIError): Invoked if aTransactionConsumptionfails to consume the request.
Usage
// The transaction requestor listen for the event
transactionRequest.startListeningEvents(socketClient, listener = object: SocketCustomEventListener.TransactionRequestListener() {
override fun onTransactionConsumptionRequest(transactionConsumption: TransactionConsumption) {
// Do something
}
override fun onTransactionConsumptionFinalizedSuccess(transactionConsumption: TransactionConsumption) {
// Do something
}
override fun onTransactionConsumptionFinalizedFail(transactionConsumption: TransactionConsumption, apiError: APIError) {
// Do something
}
})
// The transaction consumer listen for the event
transactionConsumption.startListeningEvents(socketClient, listener = object: SocketCustomEventListener.TransactionConsumptionListener() {
override fun onTransactionConsumptionFinalizedSuccess(transactionConsumption: TransactionConsumption) {
// Do something
}
override fun onTransactionConsumptionFinalizedFail(transactionConsumption: TransactionConsumption, apiError: APIError) {
// Do something
}
})You might want to listen for the event later after you got the TransactionRequest or TransactionConsumption object, but you might not want to pass the object around.
In this case, it is possible to keep only the SocketTopic directly.
Then you can alternatively listening for custom events by using joinChannel method of the OMGSocketClient instance.
This implementation will provide the exactly same result as the implementation above ☝️. For example,
// The transaction requestor listen for the event
// Typically, it doesn't need to create a [SocketTopic] instance. it can be retrieved from the `TransactionRequest` or `TransactionConsumption` object.
val topic = SocketTopic<SocketCustomEventListener.TransactionRequestListener>("transaction_request:1234")
socketClient.joinChannel(topic, listener = object: SocketCustomEventListener.TransactionRequestListener(){
override fun onTransactionConsumptionRequest(transactionConsumption: TransactionConsumption) {
// Do something
}
override fun onTransactionConsumptionFinalizedSuccess(transactionConsumption: TransactionConsumption) {
// Do something
}
override fun onTransactionConsumptionFinalizedFail(transactionConsumption: TransactionConsumption, apiError: APIError) {
// Do something
}
})
// The transaction consumer listen for the event
// Typically, it doesn't need to create a [SocketTopic] instance. it can be retrieved from the `TransactionRequest` or `TransactionConsumption` object.
val topic = SocketTopic<SocketCustomEventListener.TransactionConsumptionListener>("transaction_request:1234")
socketClient.joinChannel(topic, listener = object: SocketCustomEventListener.TransactionConsumptionListener() {
override fun onTransactionConsumptionFinalizedSuccess(transactionConsumption: TransactionConsumption) {
// Do something
}
override fun onTransactionConsumptionFinalizedFail(transactionConsumption: TransactionConsumption, apiError: APIError) {
// Do something
}
})A user can also be listened and will receive all events that are related to him:
user.startListeningEvents(socketClient, listener = object: SocketCustomEventListener.AnyEventListener() {
override fun onEventReceived(data: SocketReceive) {
data.event.either(this::handleSocketSystemEvent, this::handleSocketCustomEvent)
}
})
fun handleSocketSystemEvent(systemEvent: SocketSystemEvent){
when(systemEvent){
SocketSystemEvent.CLOSE -> {
// Do something
}
SocketSystemEvent.ERROR -> {
// Do something
}
}
}
fun handleSocketCustomEvent(customEvent: SocketCustomEvent){
when(customEvent){
SocketCustomEvent.TRANSACTION_CONSUMPTION_FINALIZED -> {
// Do something
}
SocketCustomEvent.TRANSACTION_CONSUMPTION_REQUEST -> {
// Do something
}
}
}Where:
onEventReceived: An event callback. This method will be called when any event regarding to the user is received.SocketReceive: A raw object which is a response from the eWallet socket API.
For more information can be found here.
When you don't need to receive events anymore, you should call stopListening(client: SocketClient) for the corresponding Listenable object.
This will leave the corresponding socket channel and close the connection if no other channel is active.
For example,
transactionRequest.stopListening(socketClient)
// Or
transactionConsumption.stopListening(socketClient)The web socket client will be disconnected automatically if no other channel is active, so you won't receive any system event after that.
By the way, if you want to stop listening before that happen, you can pass null to both omgSocketClient.setConnectionListener and omgSocketClient.setChannelListener.
Simply run ./gradlew ktlintCheck under project root directory.
./gradlew clean testIn order to run the live tests (bound to a working server), you need to create a file secret.json under src/liveTest/resources/ directory (You can take a template from secret.example.json there).
The secret.json file will be using the following format which is the same as the secret.example.json file.
{
"base_url": "YOUR_BASE_URL",
"socket_base_url": "YOUR_SOCKET_BASE_URL",
"api_key": "YOUR_API_KEY",
"auth_token": "YOUR_AUTH_TOKEN"
}You will need to fill the corresponding variables, then runs the following command to execute the live test.
./gradlew clean test -Plive=trueSee how you can help.
The OmiseGO Android SDK is released under the Apache License.
You can check out the latest sample app from the following repo : OMGShop