This project calculates approximate SDFs for triangle meshes. It works for non-watertight meshes (meshes with holes), self-intersecting meshes, meshes with non-manifold geometry and meshes with inconsistently oriented faces.
pip3 install mesh-to-sdf
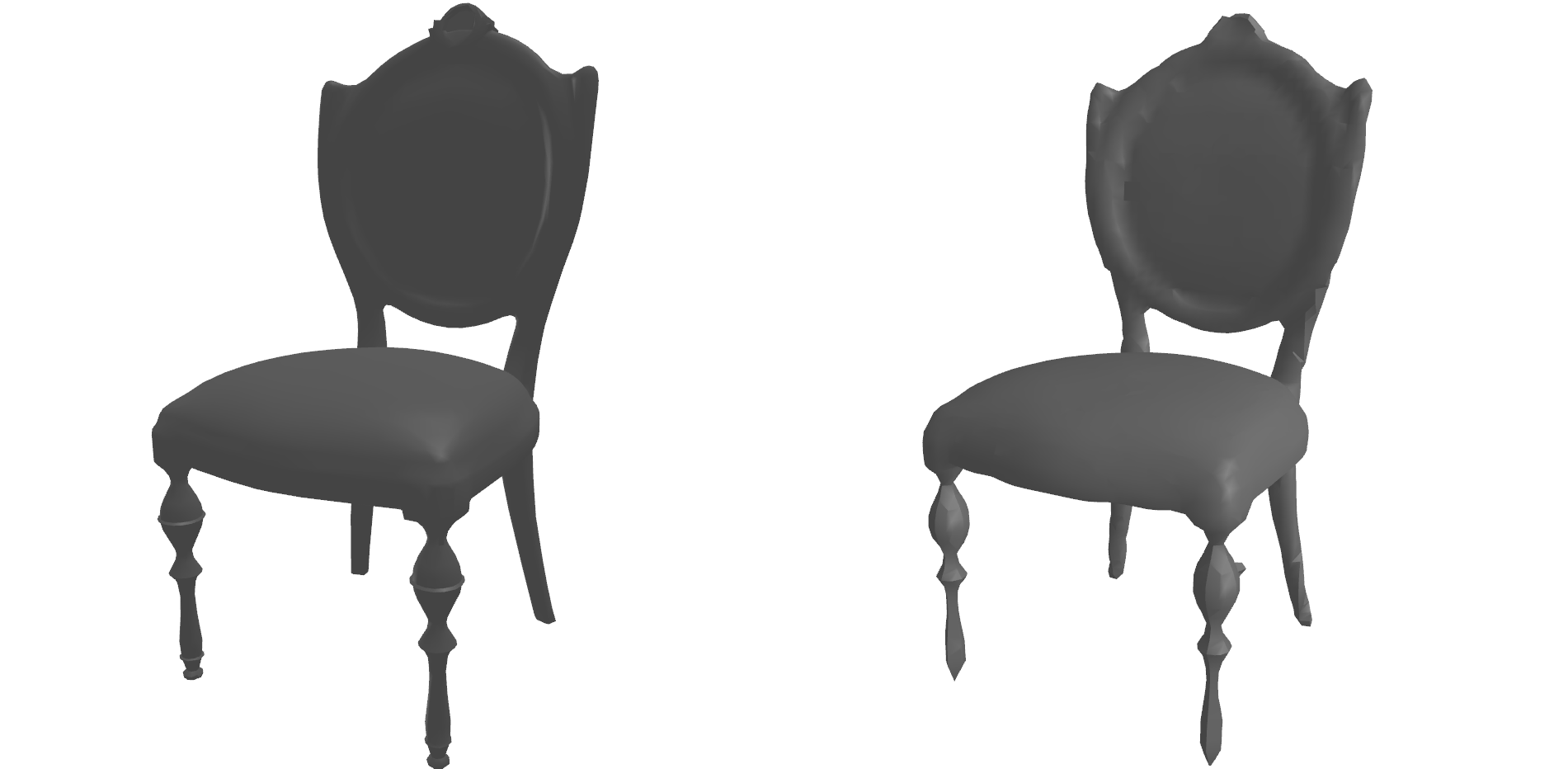
The mesh_to_voxels function creates an N ✕ N ✕ N array of SDF values.
In this example, a mesh reconstructed using Marching Cubes and then rendered.
from mesh_to_sdf import mesh_to_voxels
import trimesh
import skimage
mesh = trimesh.load('chair.obj')
voxels = mesh_to_voxels(mesh, 64, pad=True)
vertices, faces, normals, _ = skimage.measure.marching_cubes_lewiner(voxels, level=0)
mesh = trimesh.Trimesh(vertices=vertices, faces=faces, vertex_normals=normals)
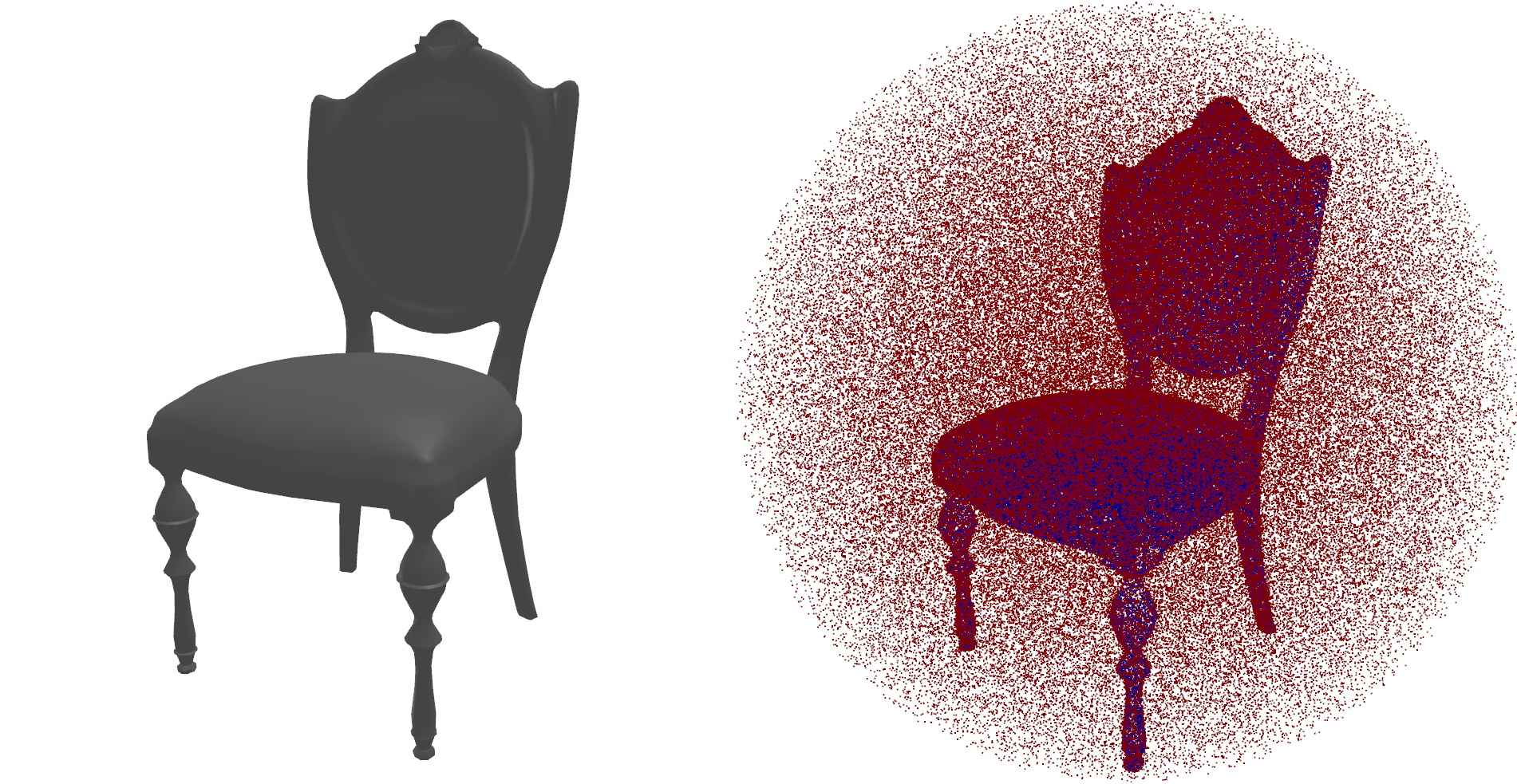
mesh.show()This example creates 250,000 points, where most of the points are close to the surface and some are sampled uniformly. This is the method that is proposed and used in the DeepSDF paper. In this example, the resulting points are rendered in red where the SDF is positive and in blue where it is negative.
from mesh_to_sdf import sample_sdf_near_surface
import trimesh
import pyrender
import numpy as np
mesh = trimesh.load('chair.obj')
points, sdf = sample_sdf_near_surface(mesh, number_of_points=250000)
colors = np.zeros(points.shape)
colors[sdf < 0, 2] = 1
colors[sdf > 0, 0] = 1
cloud = pyrender.Mesh.from_points(points, colors=colors)
scene = pyrender.Scene()
scene.add(cloud)
viewer = pyrender.Viewer(scene, use_raymond_lighting=True, point_size=2)The general pipeline for calculating SDF in this project is as follows:
- Create 100 virtual laser scans of the shape from multiple angles. These each consist of a normal buffer and a depth buffer.
- Use the inverse MVP matrix and depth buffer of each scan to calculate a world-space surface point cloud
- Determine the value of the SDF for each query point by finding the closest surface point using a kd-tree
- Determine the sign of the SDF using either the normal of the closest surface point or by checking it against the depth buffers of the scans. When using normals, the sign is determined with a dot product. When using the depth buffer method, the point is projected in the frame of each render. By comparing the depth element of the depth buffer and depth of the query point, we determine if the query point is seen by the camera. The sign of the point is positive if it is seen by any of the cameras.
This repository contains an implementation of the procedure proposed in the DeepSDF paper, as well as some alternatives.
Calculate signed distance values for an array of given query points
mesh_to_sdf.mesh_to_sdf(mesh, query_points, surface_point_method='scan', sign_method='normal', bounding_radius=None, scan_count=100, scan_resolution=400, sample_point_count=10000000, normal_sample_count=11)Parameters
mesh: a trimesh meshquery_points: an N ✕ 3 numpy array, containing the points for which the signed distance function should be calculated.- See common parameters for the remaining parameters
Returns
- a numpy array with N elemenents, containing the SDF for each query point
Calculate an N ✕ N ✕ N voxel volume of signed distance values for a given mesh. The mesh is first transformed to fit inside a cube ranging from -1 to 1.
mesh_to_sdf.mesh_to_voxels(mesh, voxel_resolution=64, surface_point_method='scan', sign_method='normal', scan_count=100, scan_resolution=400, sample_point_count=10000000, normal_sample_count=11, pad=False, check_result=False)Parameters
mesh: a trimesh meshvoxel_resolution: the resolution N of the resulting voxel volumepad: ifTrue, the resulting array is padded with ones, ensuring a mesh without holes when reconstructing with Marching Cubescheck_result: ifTrue, the result is checked for continuity. If the voxel volume is not a plausible signed distance field, an exception is thrown.- See common parameters for the remaining parameters
Returns
- a numpy array of shape N ✕ N ✕ N (or N + 2 ✕ N + 2 ✕ N + 2 when using padding)
Sample some points uniformly and some points near the shape surface and calculate SDFs for these points. This follows the procedure proposed in the DeepSDF paper. The mesh is first transformed to fit inside the unit sphere.
mesh_to_sdf.sample_sdf_near_surface(mesh, number_of_points = 500000, surface_point_method='scan', sign_method='normal', scan_count=100, scan_resolution=400, sample_point_count=10000000, normal_sample_count=11, min_size=0)Parameters
mesh: a trimesh meshnumber_of_points: the number N of points to be sampled, including surface points and uniform pointsmin_size: The fraction of uniformly sampled that should be inside the shape. If this is 0.015 and less than 1.5% of uniformly sampled points have negative SDFs, an exception is thrown. This can be used to detect bad meshes.- See common parameters for the remaining parameters
Returns
points: an N ✕ 3 numpy array containing the sample pointssdf: a numpy array of size N with the corresponding SDF values
Returns an intermediate data structure containing a surface point cloud, scans and a kd-tree of the point cloud. This can be used if SDFs will be calculated multiple times for the same mesh or for debugging.
mesh_to_sdf.get_surface_point_cloud(mesh, surface_point_method='scan', bounding_radius=1, scan_count=100, scan_resolution=400, sample_point_count=10000000, calculate_normals=True)Parameters
mesh: a trimesh mesh- See common parameters for the remaining parameters
Returns
- an instance of
SurfacePointCloud
-
surface_point_method: The method to generate a surface point cloud. Either'scan'or'sample'. The scanning method creates virtual scans while the sampling method uses the triangles to sample surface points. The sampling method only works with watertight meshes with correct face normals, but avoids some of the artifacts that the scanning method creates. -
sign_method: The method to determine the signs of the SDF values. Either'normal'or'depth'. The normal method uses normals of the point cloud. It works better for meshes with holes, but sometimes results in "bubble" artifacts. The depth method avoids the bubble artifacts but is less accurate. -
bounding_radius: The radius of a sphere that contains all mesh vertices. IfNone, this value is calculated using the mesh. -
scan_count: Number of scans when using the scanning method -
scan_resolution: Resolution for the scans in pixels. -
sample_point_count: Number of points to sample when usingsurface_point_method='sample' -
normal_sample_count: Number of nearby surface points to check when usingsign_method='normal'. The sign of the resulting SDF is determined by majority vote.