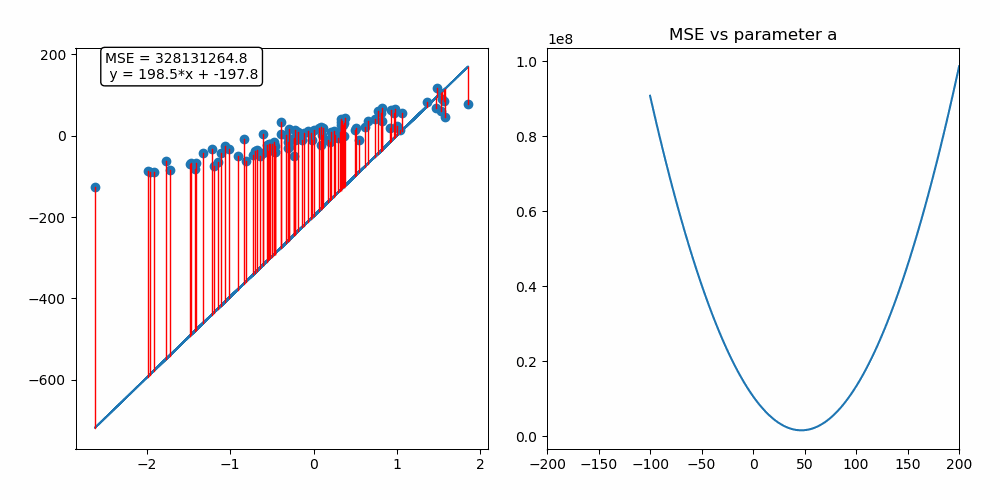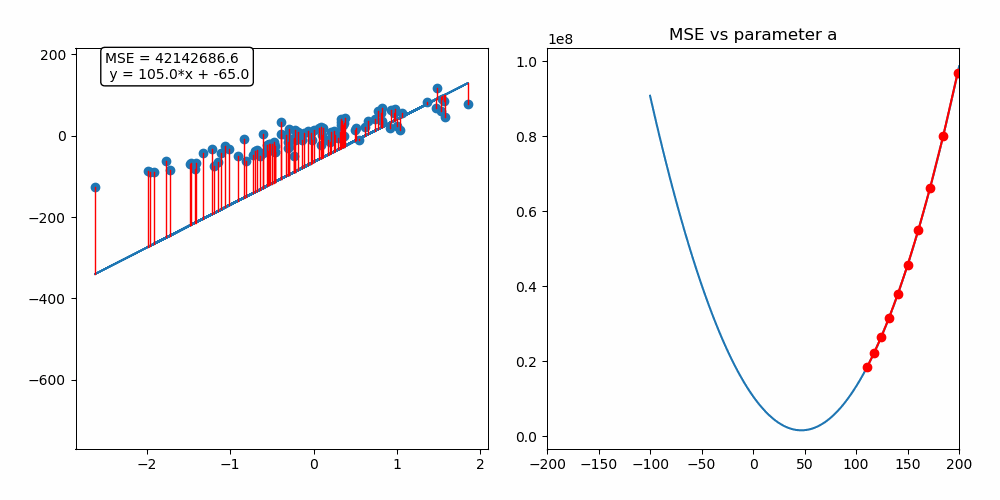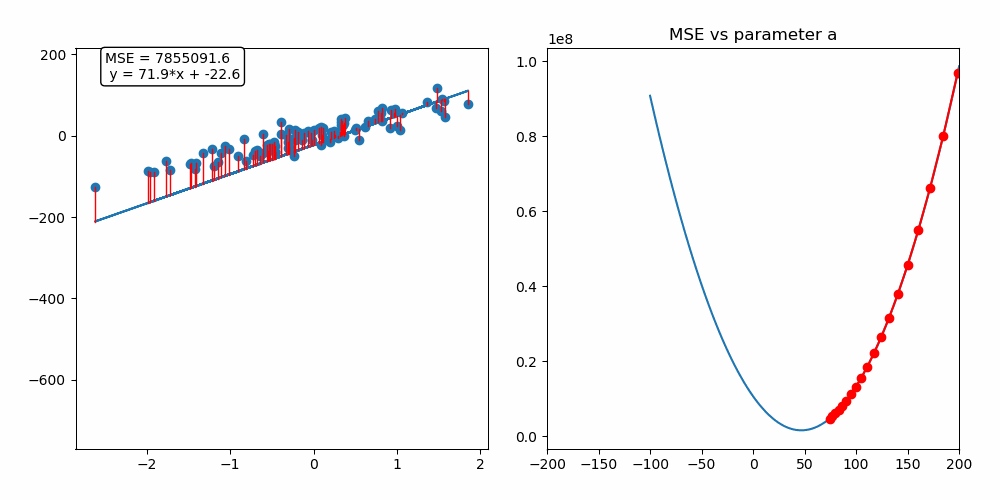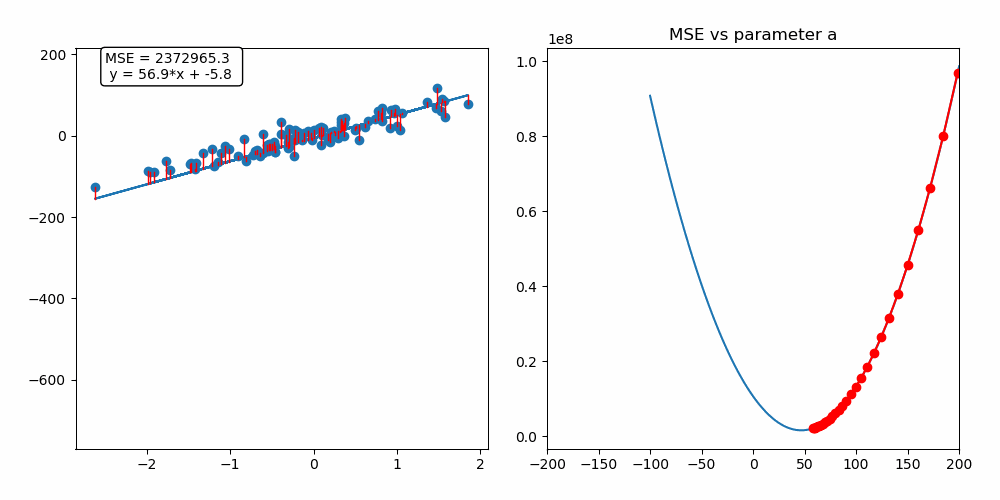
This repository contains a custom implementation of the gradient descent algorithm applied to a linear regression problem. The interactive notebook (.ipynb) provides a detailed example of how gradient descent works, along with a step-by-step breakdown of the implementation.
- Understand the inner workings of the gradient descent algorithm.
- Implement gradient descent from scratch.
- Apply the algorithm to solve a simple linear regression problem.
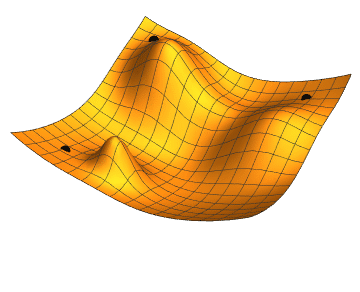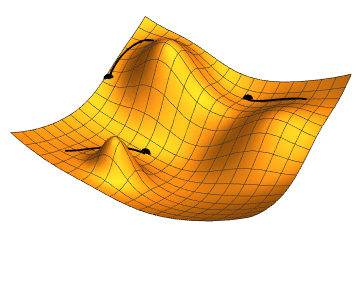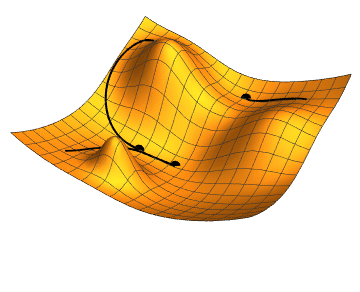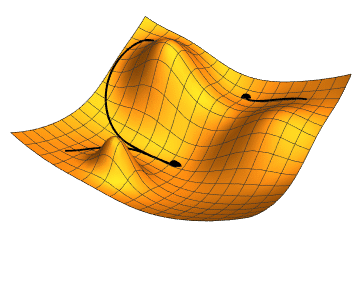
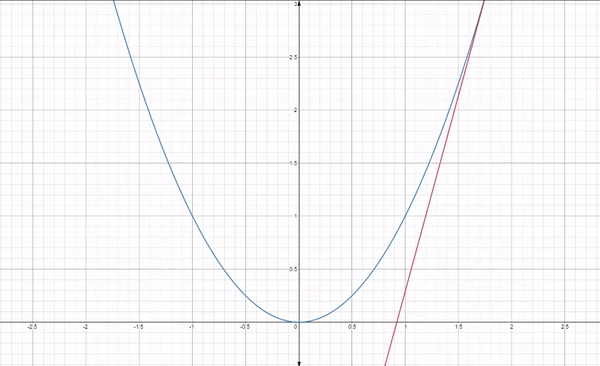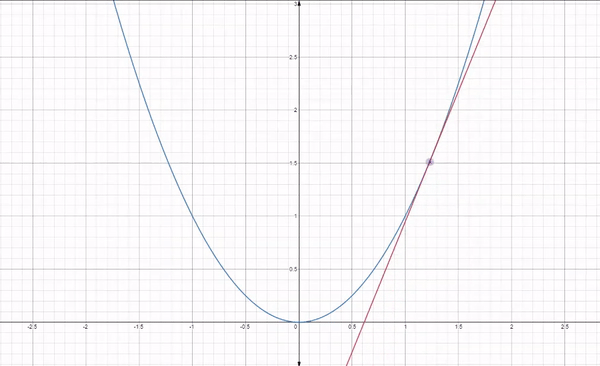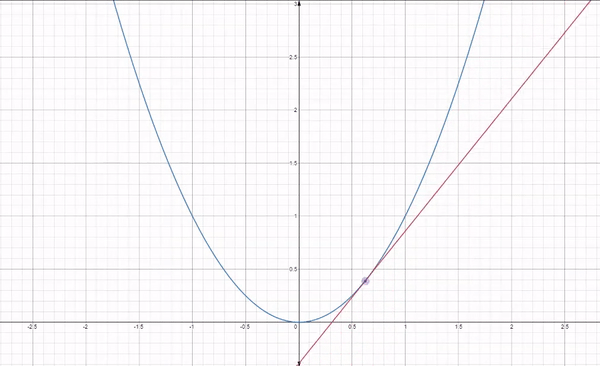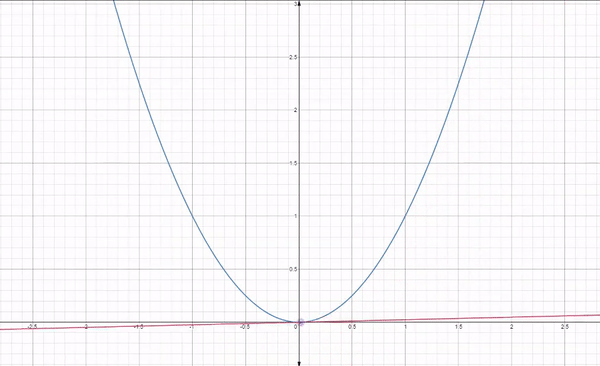
Gradient descent is an iterative optimization algorithm used for finding the minimum of a function. In the context of machine learning, it is used to minimize a loss function to improve the performance of a model.
The basic idea behind gradient descent is as follows:
- Initialize Parameters: Start with initial values for the parameters of the model.
- Calculate Gradient: Compute the gradient (partial derivatives) of the loss function with respect to each parameter.
- Update Parameters: Adjust the parameters in the opposite direction of the gradient to minimize the loss.
- Repeat: Iterate steps 2 and 3 until convergence or a stopping criterion is met.
By following this process, gradient descent gradually moves towards the optimal set of parameters that minimizes the loss function. It works because the gradient vector (partial derivatives) gives the function's growth direction, so moving in the opposite direction will minimize it.
Feel free to use this code as a learning resource or as a starting point for your own projects. If you find it helpful, consider giving it a star! 🤩