- Bhupesh Dewangan - bhupesh98
- Debjyoti Ray - DebjyotiRay
- Harshal Gainer - Harshal5167
- Prakhar Shukla - tonyStark-Jr
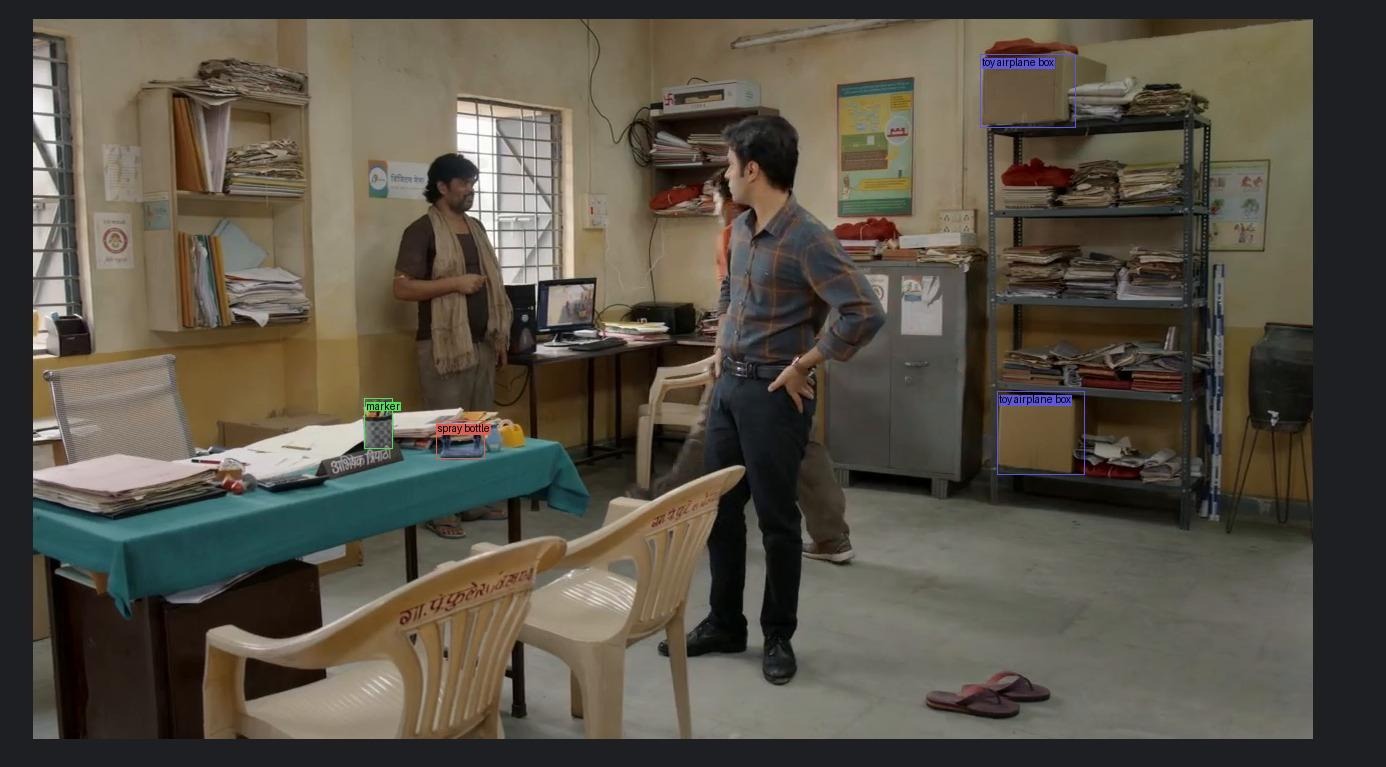
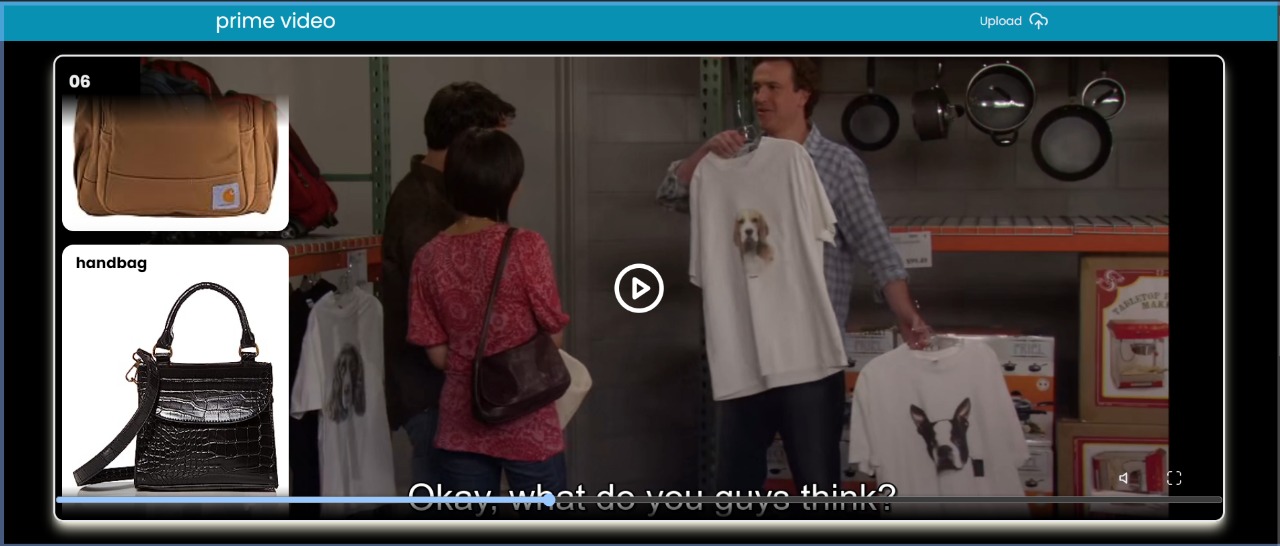
Detecting products from Amazon displayed in movies or series on Prime Video presents a unique challenge for traditional object detection models. With the vast number of products available on Amazon, it's impractical to gather sufficient training samples for each class. Traditional models require extensive labeled datasets to perform accurately, making them unsuitable for this task due to the sheer volume and diversity of products.
To address this challenge, we leverage few-shot object detection techniques, specifically using the DEtection Vision Transformer (DeVIT). Few-shot object detection models are designed to perform well with only a few annotated examples per class, making them ideal for scenarios where extensive labeled data is not available.
DeVIT, a state-of-the-art few-shot object detection model, excels in adapting to new classes with minimal data. You can learn more about DeVIT from its research paper and access the model repository here.
Our approach involves creating a diverse and robust dataset by integrating real-world scenes from the web series Panchayat with objects from the Amazon Berkeley dataset. This strategy ensures our model learns to detect objects accurately across various contexts, enabling efficient identification of Amazon products in Prime Video content.
-
Advanced Item Recognition Accuracy: Leverages the YOLO model to accurately identify items from multimedia content, using Amazon's vast product image database for enhanced model training and validation. Continuous learning methodologies ensure the system adapts quickly to new data, maintaining high accuracy without extensive retraining.
-
Enhanced User Engagement and Conversion: Monitors user interaction rates to gauge engagement with the item recognition and purchasing feature. Tracks conversion rates to measure the percentage of identified items leading to actual purchases on Amazon, providing insights into user behavior and system effectiveness.
-
Optimized System Performance: Measures system latency to ensure quick response times from item recognition to displaying purchase options. Monitors scalability performance to maintain optimal user experience under varying loads, leveraging AWS services like EC2 for computing power, S3 for storage, and SageMaker for dynamic model training.
-
Seamless Integration with Amazon Ecosystem: Extends capabilities to integrate with other Amazon services, such as Alexa, Kindle, and Fire TV, allowing users to interact with the system across different devices and platforms. This integration enhances the ability to identify and purchase items from a broader range of multimedia content within the Amazon ecosystem.
-
Utilization of Meta Learning: Employs meta learning approaches to handle the extensive and dynamic range of products on Amazon. This method is crucial given the constant influx of new products and the unequal training sets available for each product type. Meta learning enables efficient adaptation to new products and user interactions, ensuring scalability and relevance.
- Backend Development (Flask): Utilizes Flask to build lightweight and scalable backend services, handling API requests, processing multimedia content, and interfacing with the YOLO model.
- Frontend Development (Next.js): Employs Next.js to create a responsive, server-side rendered interface for smooth user interactions and enhanced performance.
- Object Detection (YOLO with Meta Learning): Leverages YOLO for real-time object detection, enhanced by meta learning to continuously improve accuracy and adapt to new items.
- Cloud Infrastructure (AWS): Deploys AWS services for scalable computing, storage, and machine learning, ensuring efficient data management and high availability.
- Make sure your device has an active internet connection.
- Open the terminal or shell supported by your OS on your PC.
- Navigate to the directory where you want to clone your project.
- Clone the repository to your local setup using the command:
git clone https://github.com/bhupesh98/Amazon-HackOn.git
- Once cloned, navigate to the frontend directory of the project:
cd frontend - Install all dependencies by running the following command:
npm install - Ensure you have the required environment variables saved in the
.env.localfile in the root of the project. A file.env.exampleis provided for reference. - After the dependencies are installed, start the development server with the command:
npm run dev - The application will be live on
http://localhost:3000.
- Once cloned, navigate to the backend directory of the project:
cd backend - Install Pipenv if you haven't already by running the following command:
pip install pipenv - Set up the virtual environment and install all dependencies using Pipenv:
pipenv install - Activate the virtual environment:
pipenv shell - After the setup is complete, start the Flask server with the command:
flask run - The backend will be live on
http://localhost:5000.
vit=l task=ovd dataset=coco bash scripts/train.sh # train open-vocabulary COCO with ViT-L
# task=ovd / fsod / osod
# dataset=coco / lvis
# vit=s / b / l
# few-shot env var `shot = 5 / 10 / 30`
vit=l task=fsod shot=10 bash scripts/train.sh
# one-shot env var `split = 1 / 2 / 3 / 4`
vit=l task=osod split=1 bash script/train.sh
# detectron2 options can be provided through args, e.g.,
task=ovd dataset=lvis bash scripts/train.sh MODEL.MASK_ON True # train lvis with mask head
# another env var is `num_gpus = 1 / 2 ...`, used to control
# how many gpus are usedAll evaluations can be run without training, as long as the checkpoints are downloaded.
The script-level environment variables are the same to training.
vit=l task=ovd dataset=coco bash scripts/eval.sh # evaluate COCO OVD with ViT-L/14
vit=l task=ovd dataset=lvis bash scripts/eval.sh DE.TOPK 3 MODEL.MASK_ON True # evaluate LVIS OVD with ViT-L/14bash scripts/train_rpn.sh ARG
# change ARG to ovd / os1 / os2 / os3 / os4 / fs14
# corresponds to open-vocabulary / one-shot splits 1-4 / few-shotCheck Tools.md for intructions to build prototype and prepare weights.
vit=l task=ovd dataset=coco bash scripts/train.sh # train open-vocabulary COCO with ViT-L
# task=ovd / fsod / osod
# dataset=coco / lvis
# vit=s / b / l
# few-shot env var `shot = 5 / 10 / 30`
vit=l task=fsod shot=10 bash scripts/train.sh
# one-shot env var `split = 1 / 2 / 3 / 4`
vit=l task=osod split=1 bash script/train.sh
# detectron2 options can be provided through args, e.g.,
task=ovd dataset=lvis bash scripts/train.sh MODEL.MASK_ON True # train lvis with mask head
# another env var is `num_gpus = 1 / 2 ...`, used to control
# how many gpus are usedAll evaluations can be run without training, as long as the checkpoints are downloaded.
The script-level environment variables are the same to training.
vit=l task=ovd dataset=coco bash scripts/eval.sh # evaluate COCO OVD with ViT-L/14
vit=l task=ovd dataset=lvis bash scripts/eval.sh DE.TOPK 3 MODEL.MASK_ON True # evaluate LVIS OVD with ViT-L/14bash scripts/train_rpn.sh ARG
# change ARG to ovd / os1 / os2 / os3 / os4 / fs14
# corresponds to open-vocabulary / one-shot splits 1-4 / few-shotCheck Tools.md for intructions to build prototype and prepare weights.
.png?raw=true)
.png?raw=true)
.png?raw=true)