Noirrit Kiran Chandra 8/19/2021
RcppGSL is required to use the codes. There might be some issues with
MS Windows users in setting up this package. Please refer to this
stackoverflow
link
for solutions.
library("Rcpp")
library("pracma")
library("tidyverse")## ── Attaching packages ─────────────────────────────────────── tidyverse 1.3.1 ──
## ✓ ggplot2 3.3.5 ✓ purrr 0.3.4
## ✓ tibble 3.1.3 ✓ dplyr 1.0.7
## ✓ tidyr 1.1.3 ✓ stringr 1.4.0
## ✓ readr 2.0.1 ✓ forcats 0.5.1
## ── Conflicts ────────────────────────────────────────── tidyverse_conflicts() ──
## x purrr::cross() masks pracma::cross()
## x dplyr::filter() masks stats::filter()
## x dplyr::lag() masks stats::lag()
library("ggpubr")
library("uwot")## Loading required package: Matrix
##
## Attaching package: 'Matrix'
## The following objects are masked from 'package:tidyr':
##
## expand, pack, unpack
## The following objects are masked from 'package:pracma':
##
## expm, lu, tril, triu
library("irlba")
library("mclust")## Package 'mclust' version 5.4.7
## Type 'citation("mclust")' for citing this R package in publications.
##
## Attaching package: 'mclust'
## The following object is masked from 'package:purrr':
##
## map
library("mcclust")## Loading required package: lpSolve
sourceCpp("DL_linear_split_merge_package.cpp") ##This is the souce C++ file## Registered S3 methods overwritten by 'RcppGSL':
## method from
## predict.fastLm RcppArmadillo
## print.fastLm RcppArmadillo
## summary.fastLm RcppArmadillo
## print.summary.fastLm RcppArmadillo
source("simulate_data_fxns.R") ##load a supplementary R file with supplementary functions##
## Attaching package: 'mvtnorm'
## The following object is masked from 'package:mclust':
##
## dmvnorm
Set the
-
dimension (
p) -
sample size (
n) -
dimension of the unobserved latent variables
eta(d) -
number of clusters (
k) which is unobserved.
set.seed(1)
p= 2500 # Observed dimension
n=2000 # Sample size
d=20 # Latent dimension
k= 15 # Number of true clustersSet the cluster memberships probabilities such that 2/3 of the clusters have same probabilities, the remaining 1/3 together have the same prob of a single big bluster.
pis <- c(rep(1/(round(k *2/3)+1), (round(k *2/3))),
rep((1/(round(k *2/3)+1))/(k - (round(k *2/3))), k - (round(k*2/3))))
pis <- pis/sum(pis) ##cluster weightsGenerate the observed p-dimensional data y
lambda = simulate_lambda(d,p,1) # Generate the loading matrix lambda
sc=quantile(diag(tcrossprod(lambda) ) ,.75); lambda=lambda/sqrt(sc) # Scaling lambda
s = sample.int(n=k,size=n, prob=pis, replace = TRUE) ##Cluster membership indicators
eta = matrix(rnorm(n*d), nrow=n, ncol=d) # Latent factors
shifts=2*seq(-k,k,length.out = k)
for(i in 1:k){
inds = which(s==i)
vars = sqrt(rchisq(d,1))
m = pracma::randortho(d) %*% diag(vars)
eta[inds,]= eta[inds,] %*% t(m)+shifts[i] # The i-th cluster is centered around rep(shifts[i],d) in the latent eta space
}
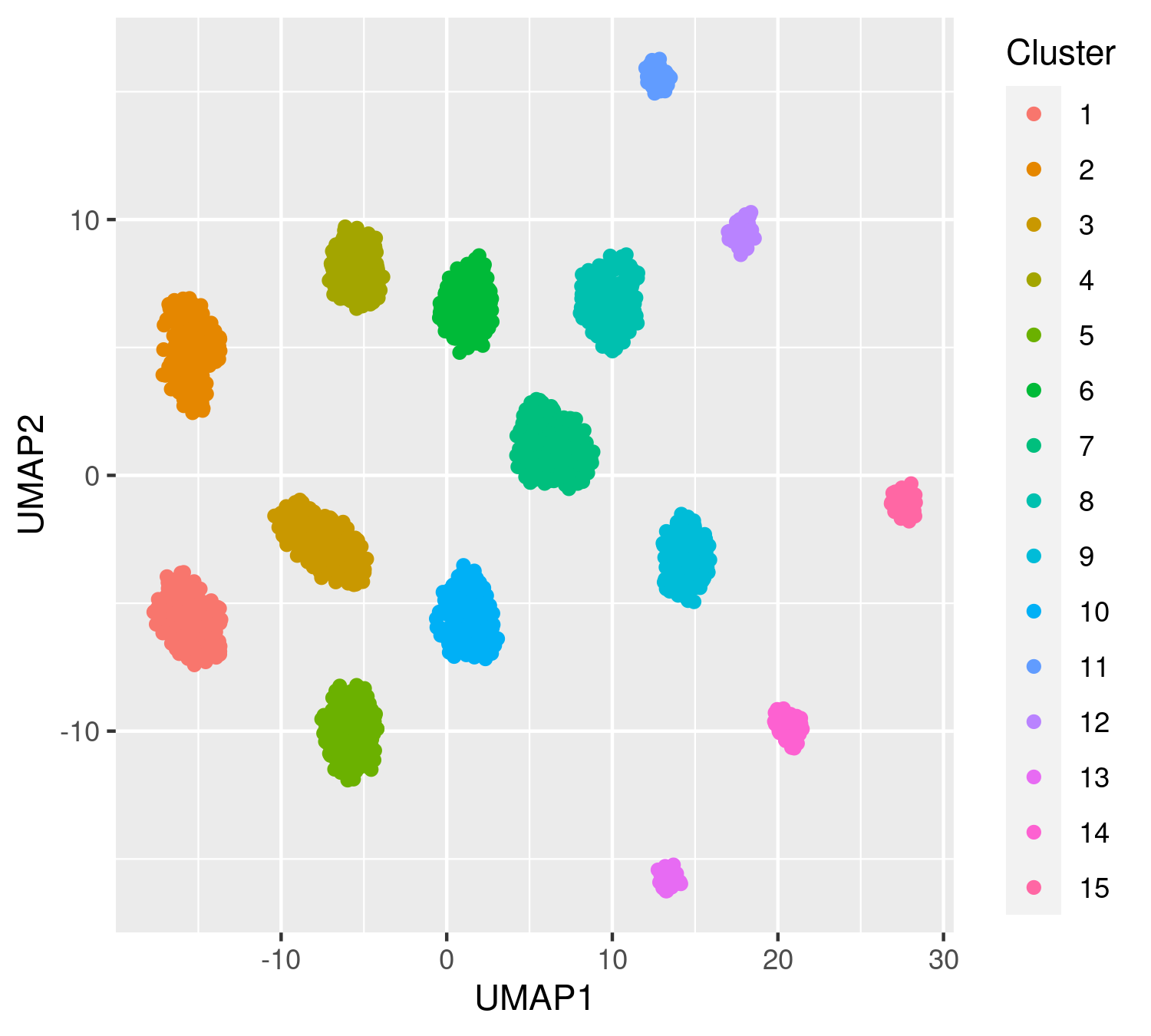
y <- tcrossprod(eta,lambda) + matrix(rnorm(p*n, sd=sqrt(.5)), nrow=n, ncol=p) # Observed dataumap_data=uwot::umap(y, min_dist=.8, n_threads = parallel::detectCores()/2) #2-dimensional UMAP scores of the original data
dat.true=data.frame(umap_data, Cluster=as.factor(s)); colnames(dat.true)= c("UMAP1","UMAP2", "Cluster")
p.true<-ggplot(data = dat.true, mapping = aes(x = UMAP1, y = UMAP2 ,colour=Cluster)) + geom_point()
p.trueFor any other dataset replace the simulated
ywith that and follow the proceeding steps.
We center the data with respect to the median and scale ALL variables with the median standard deviations of the observed variables.
y_original=y
y=y_original
centering.var=median(colMeans(y))
scaling.var=median(apply(y,2,sd))
y=(y_original-centering.var)/scaling.varPerform a sparse PCA on the pre-processed data.
pca.results=irlba::irlba(y, nv=40)d is set to be the minimum number of eigenbalues explaining at least
95% of the variability in the data.
cum_eigs= cumsum(pca.results$d)/sum(pca.results$d)
d=min(which(cum_eigs>.95))
d=ifelse(d<=15,15,d) # Set d= at least 15Left and right singular values of y are used to initialize eta and
lambda respectively for the MCMC.
eta= pca.results$u %*% diag(pca.results$d)
eta=eta[,1:d] #Left singular values of y are used as to initialize eta
lambda=pca.results$v[,1:d] #Right singular values of y are used to initialize lambdacluster.start = kmeans(y, 80)$cluster - 1as = 1; bs = 0.3
a=0.5
diag_psi_iw=20
niw_kap=1e-3
nu=d+50
a_dir=.1
b_dir=.1result.lamb <- DL_mixture(a_dir, b_dir, diag_psi_iw=diag_psi_iw, niw_kap=niw_kap, niw_nu=nu,
as=as, bs=bs, a=a,
nrun=5e3, burn=1e3, thin=5,
nstep = 5,prob=0.5, #With probability `prob` either the Split-Merge sampler with `nstep` Gibbs scans or Gibbs sampler in performed
lambda, eta, y,
del = cluster.start,
dofactor=1 #If dofactor set to 0, clustering will be done on the initial input eta values only; eta will not be updated in MCMC
)We compute summaries of the MCMC samples of cluster allocation variables following Wade and Ghahramani (2018, Bayesian Analysis).
burn=2e2 #burn/thin
post.samples=result.lamb[-(1:burn),]+1
sim.mat.lamb <- mcclust::comp.psm(post.samples) # Compute posterior similarity matrix
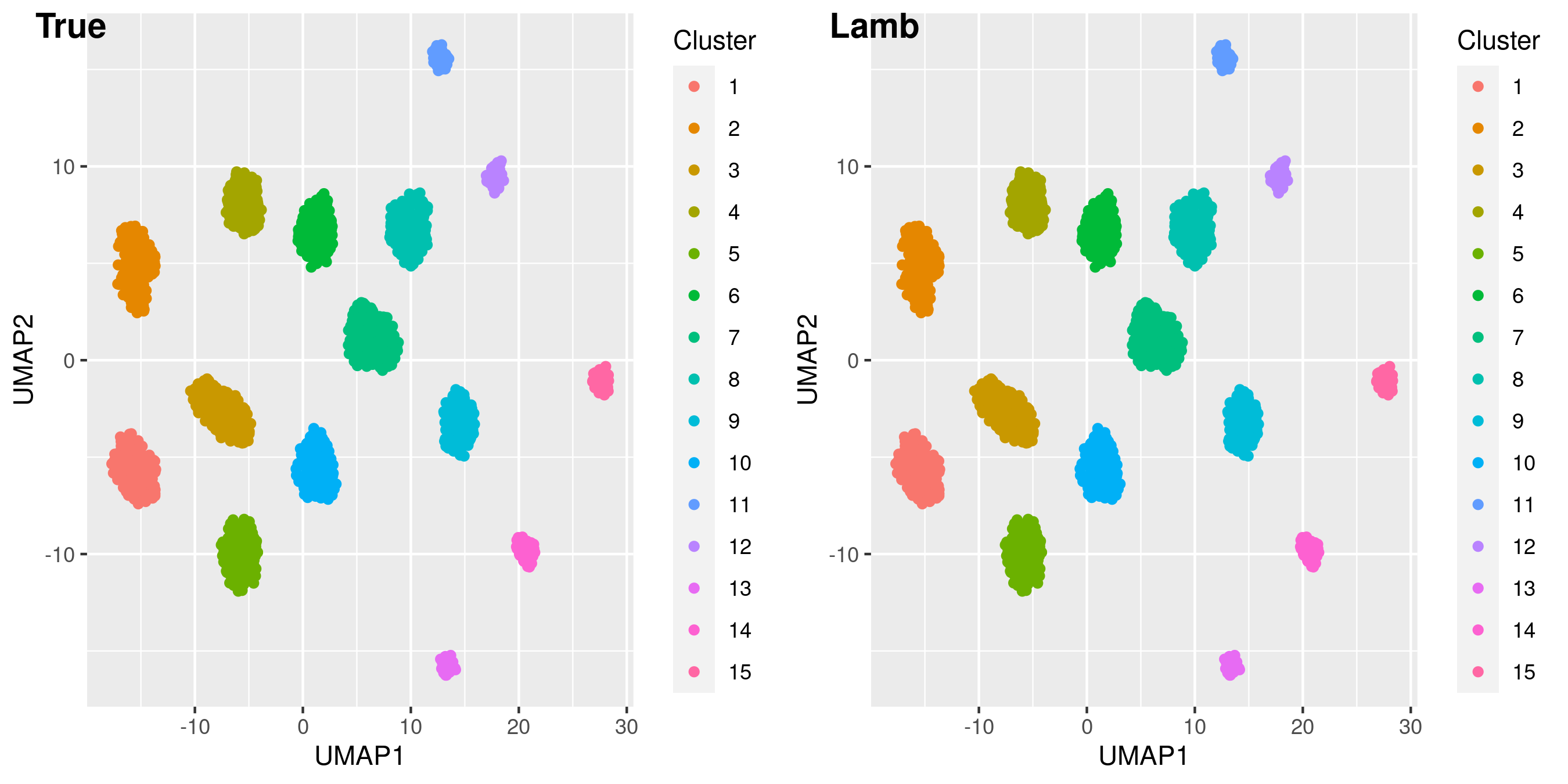
clust.lamb <- minbinder(sim.mat.lamb)$cl # Minimizing Binder loss across MCMC estimatesadjustedRandIndex( clust.lamb, s)## [1] 0.9990262
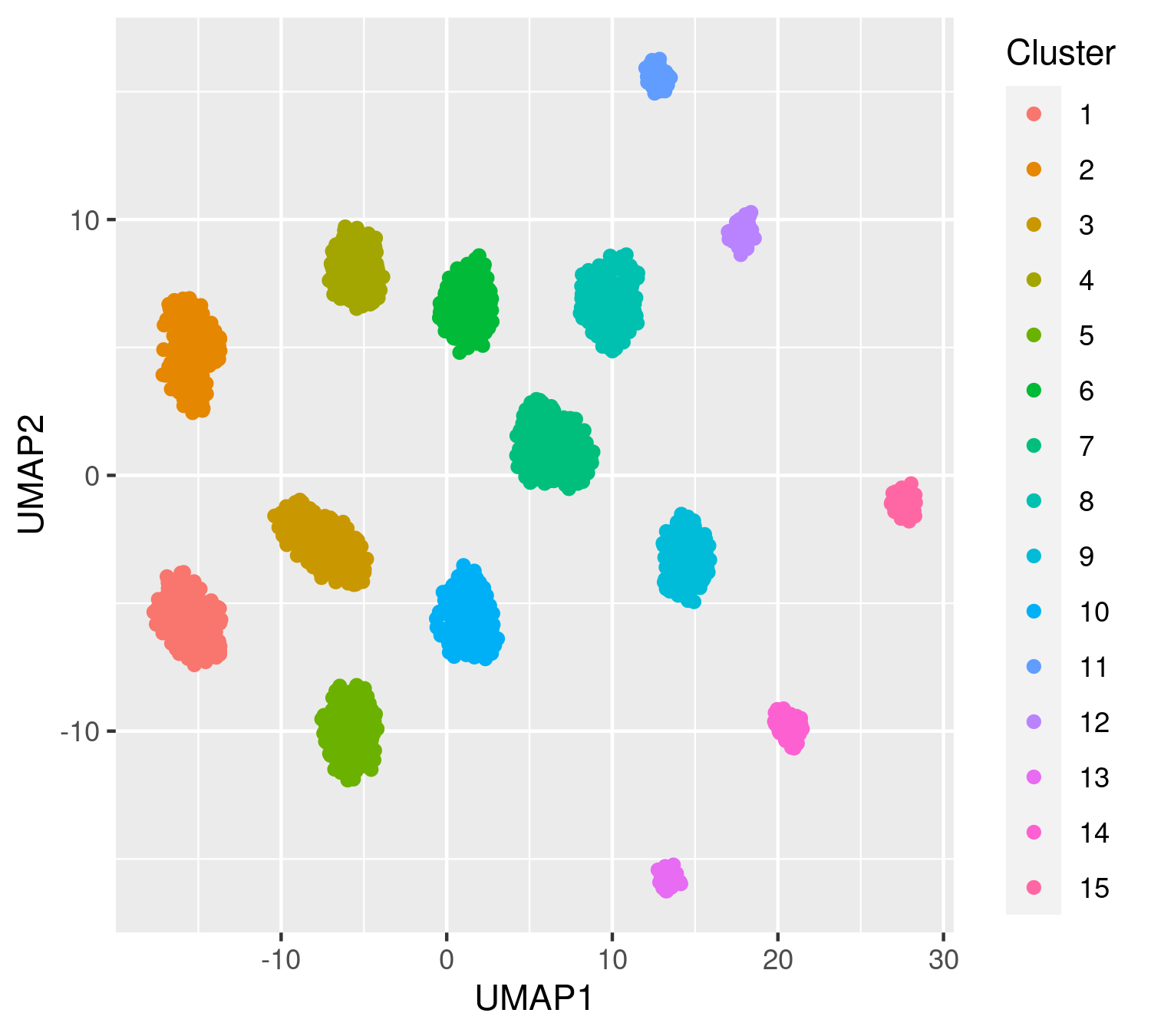
dat.lamb=data.frame(umap_data, Cluster=as.factor(clust.lamb)); colnames(dat.true)= c("UMAP1","UMAP2", "Cluster")
p.lamb<-ggplot(data = dat.true, mapping = aes(x = UMAP1, y = UMAP2 ,colour=Cluster)) + geom_point()
p.lambggpubr:: ggarrange(p.true,p.lamb,nrow=1,ncol=2, labels = c("True", "Lamb"))If you use the Lamb method, kindly cite Chandra, et al. (2021+). Escaping the curse of dimensionality in Bayesian model based clustering, https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.02700